Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In one of our previous blogposts, you learnt in detail about network footprinting. It is performed to discover assets of the organization that are exposed to the internet. In this blogpost, you will learn about a tool. amass that can discover majority of any organization’s exposed assets.
OWASP Amass used mainly to find assets mapped to a particular domain, perform sub-domain enumeration, autonomous system numbers (ASNs) etc. Although there are many other tools that can enumerate sub-domains etc. (for example gobuster), this tool as you can see is backed by OWASP. Let’s see how to use this tool to discover assets of an organization.
Amass is installed by default in almost all pen testing distros. For this blogpost, we will be using Kali Linux. It doesn’t have a man page yet, but we can see all the options it supports using the help option.
Amass has 5 subcommands as shown below.
Each subcommand has its own help section. For example, let’s see the “intel” subcommand first.
amass intel
The ‘intel’ subcommand is used to discover targets to perform enumeration later. We can specify an IP address, IP address range, domain etc as targets to this command.
Apart from these, even ASN can also be specified as target.
amass enum
This sub command is used to perform enumeration and network mapping of the discovered targets.
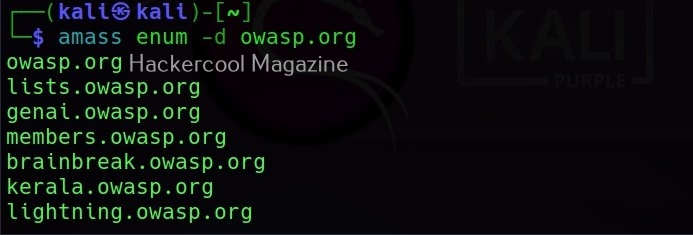
Using it, we can perform DNS enumeration too. All the findings of “amass enum” command are stored in a graph database, which is located in the amass’s default output folder. To enumerate subdomains of a domain using amass enum, this is the command.
amass enum -d owasp.org -whois
Adding, “-ip” option to the above command, we can also get IP addresses for the sub domains discovered.
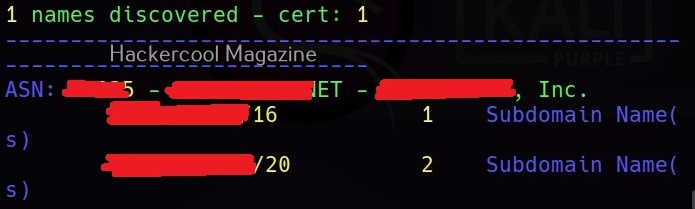
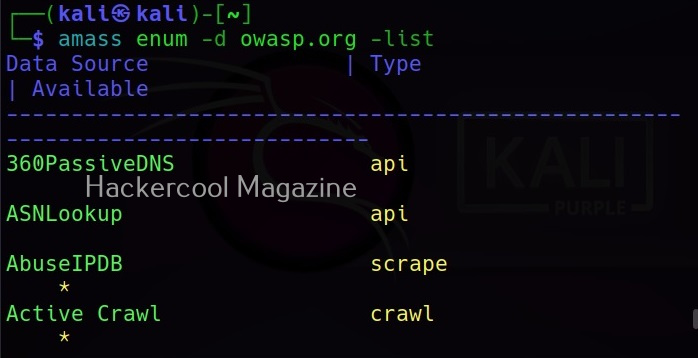
Amass queries more than 80 sources to collect information. All the sources it queries can be seen using the list flag.
Learn how to perform OSINT with theharvester tool.
Follow Us