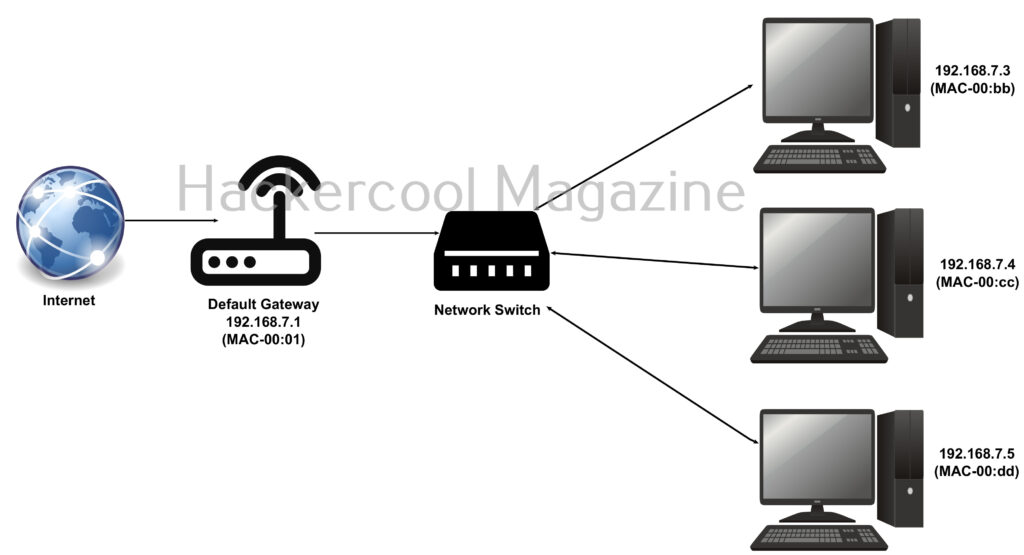
Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous article on Data Link layer attacks, you have learnt what is a LAN, what is a Network Hub and network Switch and their uses, what is a MAC address, what is a CAM table and various types of attacks that take place in LAN. In this article, you will learn about one of the attacks taking place on the LAN known as ARP poisoning.
What is ARP Poisoning?
ARP poisoning or ARP spoofing or ARP cache poisoning is an hacking attack in which malicious ARP reply packets are sent to the default gateway. This packets are sent to change the MAC address value corresponding to a specific IP address.
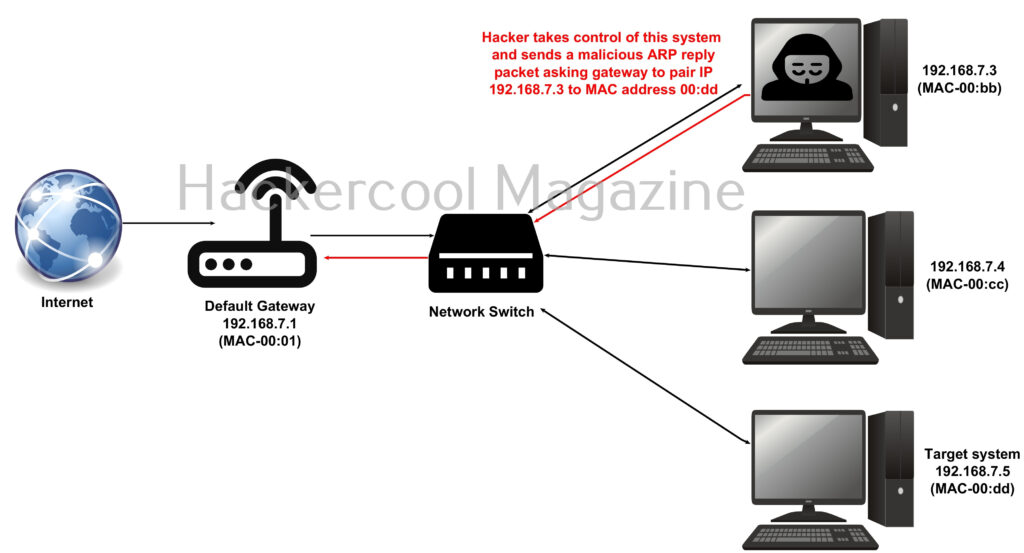
ARP protocol translates IP addresses to MAC addresses. ARP spoofing is usually performed by sending a malicious ARP reply to the network gateway, asking it to associate its MAC address with the IP address of the machine the hacker wants to target. Once the default gateway saves this message and broadcasts it to all the machines on the network, all the traffic of the target system passes through the attacker controlled machine.
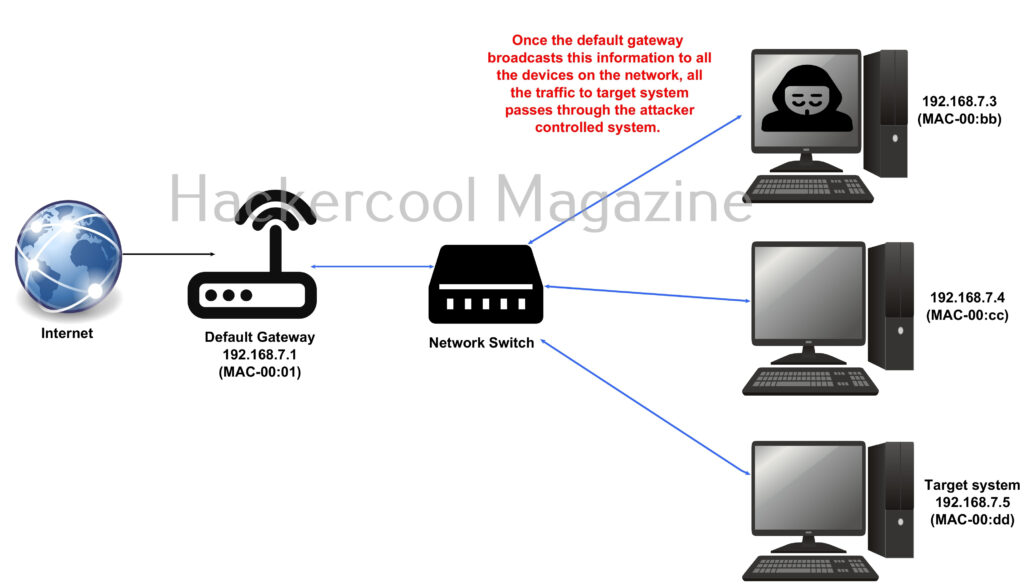
This allows hacker to perform packet sniffing, password sniffing and other MiTM attacks after successful ARP spoofing attack. ARP poisoning attack is performed after the hacker has finished gaining access on the target network. This attack is very difficult to detect as the common users will not find anything suspicious while the attack is going on.
Real-world examples of ARP spoofing
In 2008, a Chinese hacker performed ARP spoofing attack and redirected the website of none other than Metasploit to a Chinese forum where he kept on sale an exploit for a zero-day vulnerability. It is assumed he did this by targeting a router at the Internet Service Provider (ISP) level.
Follow Us