Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogposts, you learnt what is sniffing and what is Man in the Middle (MITM) attacks etc. In this blogpost, you will learn about a tool named Ettercap. Ettercap is an open-source sniffer and a comprehensive suite for performing man in the middle attacks. With Ettercap we can perform both active and passive protocol analysis, data injection etc.
Let’s see how to use Ettercap for sniffing. For this tutorial, I will be using Kali Linux as my attacker system as ettercap is installed by default on it. As a target system, I am using Metasploitable 2 (see how to create a virtual hacking lab). Ettercap can be started in both command line and GUI. For this tutorial, let’s use the graphical version.
To start ettercap in graphical mode, start ettercap with the “-G” option as shown below.
sudo ettercap -G
The GUI version of Ettercap opens as shown below.
You can also open a network capture file (pcap file) using Ettercap. To start sniffing with ettercap, we have to click on the highlighted part as shown below after selecting the interface we want to sniff on.
As soon as you do this, Ettercap loads all its plugins and engines required for sniffing. By default, ettercap starts sniffing automatically. It can be stopped or started by clicking on the highlighted part as shown below.
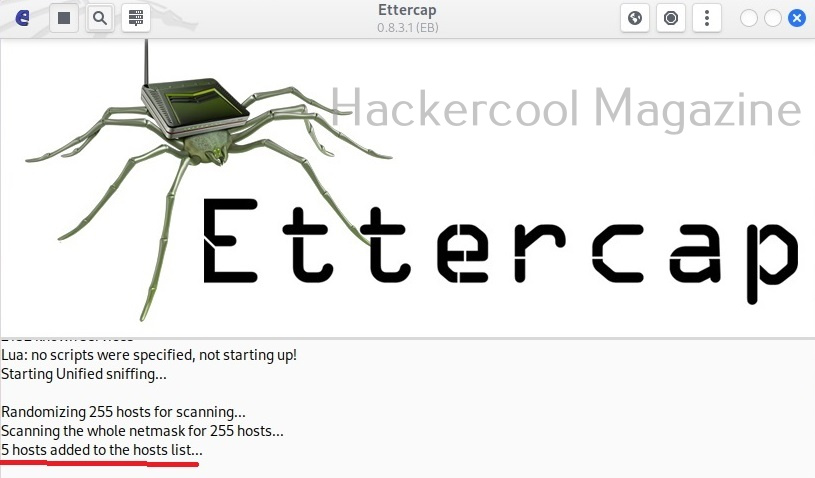
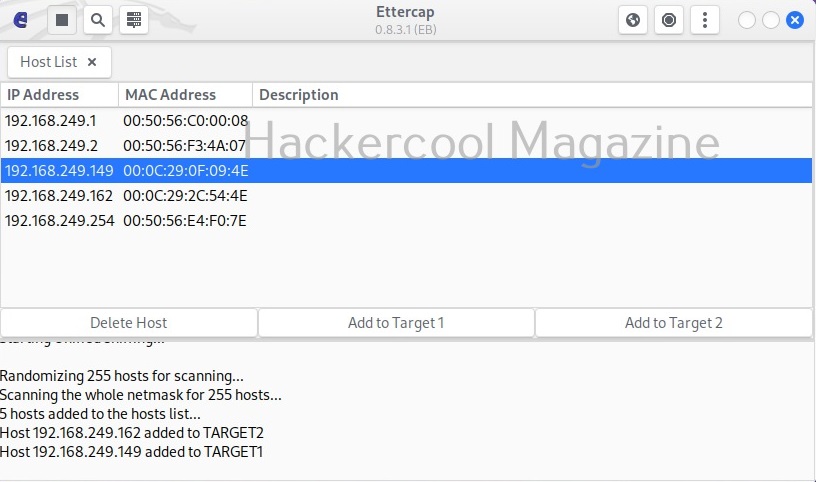
Before you perform any attack, you need to know about all the devices on the LAN. Clicking on the tab highlighted in the image below makes this tool scan for all the LIVE hosts on the network.
After the scan is finished, ettercap adds the detected hosts.
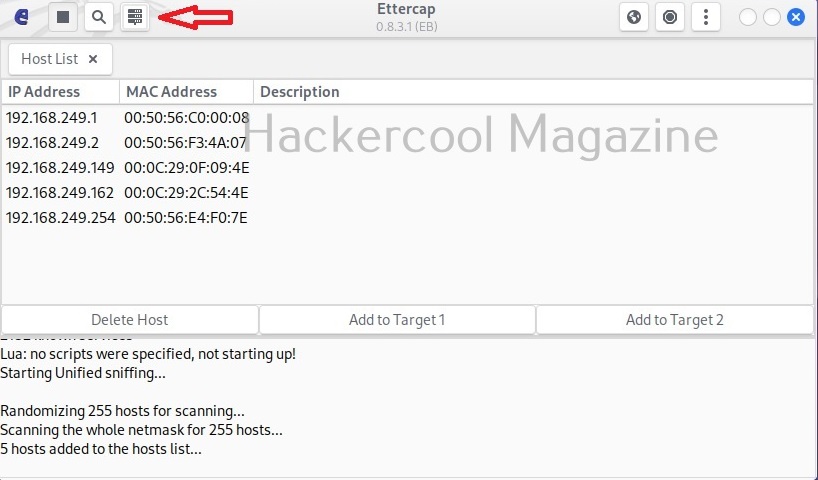
The added hosts can be viewed by clicking of the tab highlighted below.
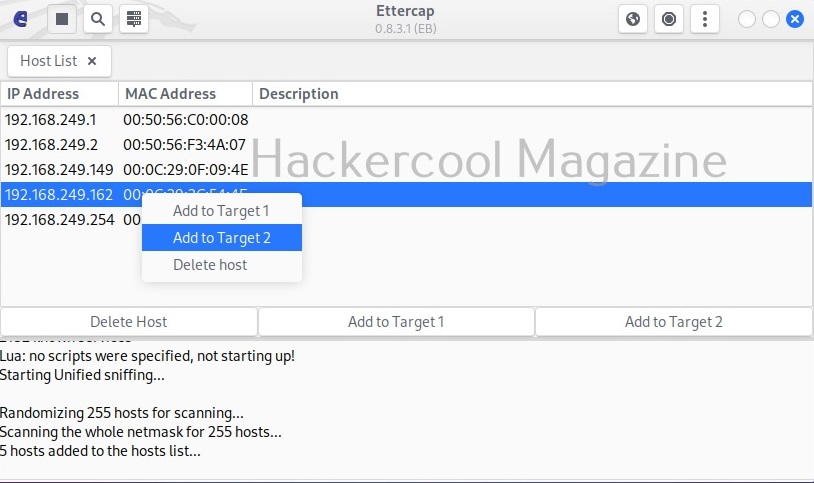
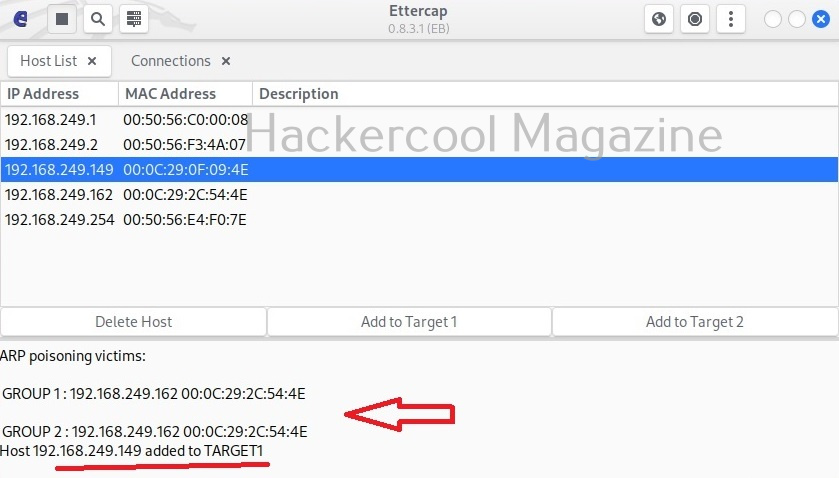
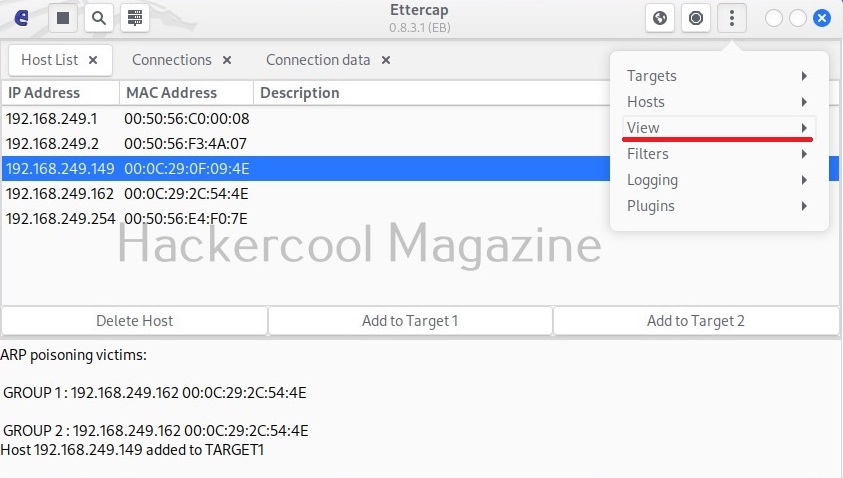
In our case five hosts have been added. I want to sniff the communication taking place between two machines. To do this, I right click on the IP of the client machine with IP 192.168.249.162 and add it as Target 2.
Similarly, I add the server machine with IP 192.168.249.149 as Target 1.
Needless to say, these two machines are the machines I want to perform sniffing on.
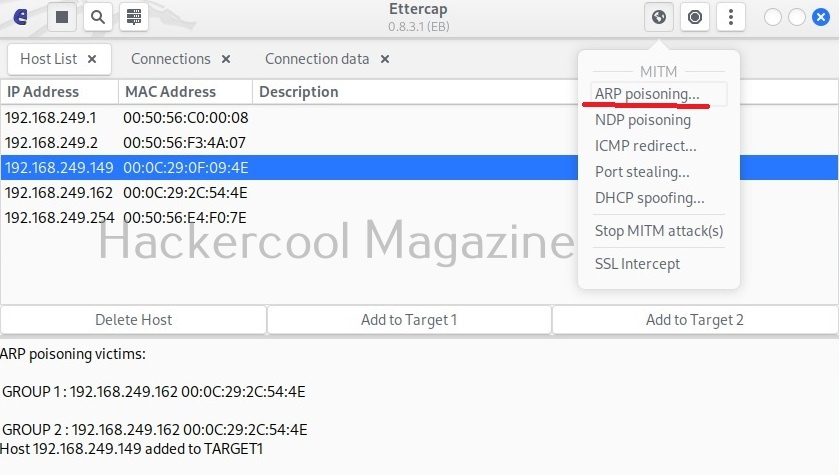
Then, I open the MiTM menu of this tool and select ARP poisoning as shown below.
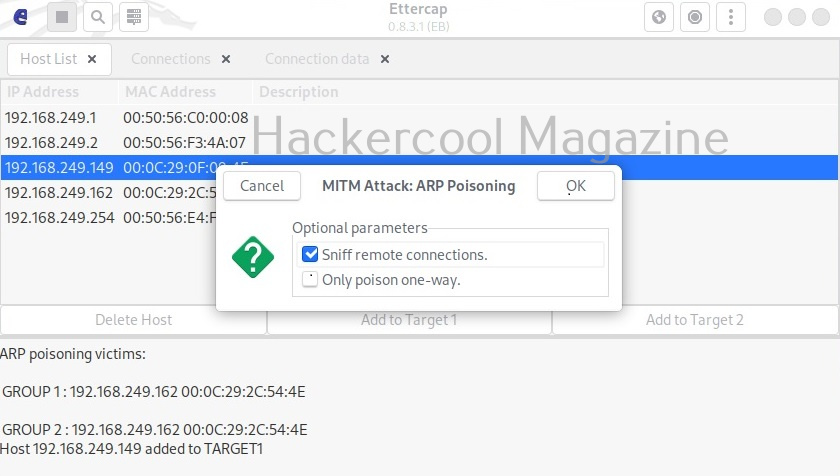
This opens a new window as shown below.
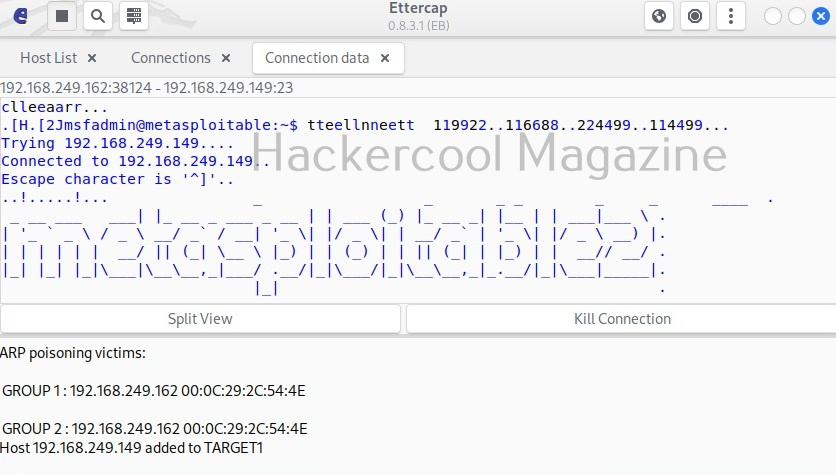
I select “sniff remote connections” option and click on “OK”. This starts the ARP poisoning attack and all the traffic intending to go for 192.168.249.162 (client machine) to192.168.249.149 (server machine) will be sniffed. From the client machine, I make a telnet connection to target system.
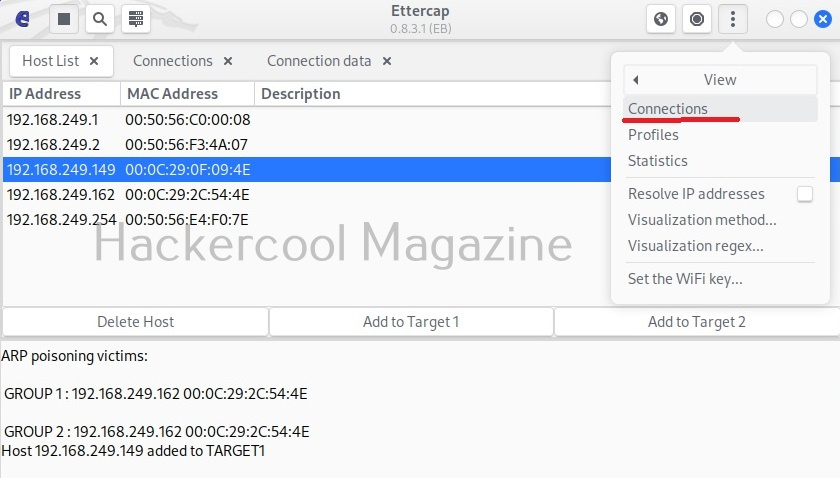
Then on ettercap, I open the menu and go to view > connections.
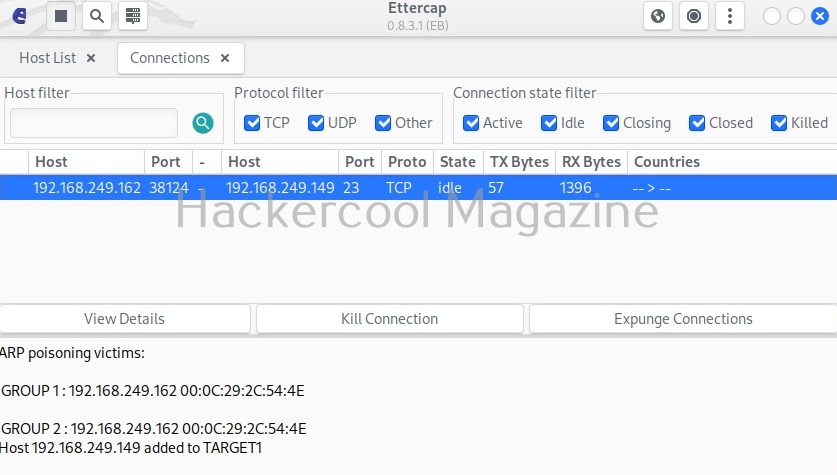
This will show all the connections being made between client and the server.
In the above image, we can see one connection from IP 192.168.244.162 to port 23 of 192.168.249.149. Clicking on it will reveal the connection data exchanged between the two machines.
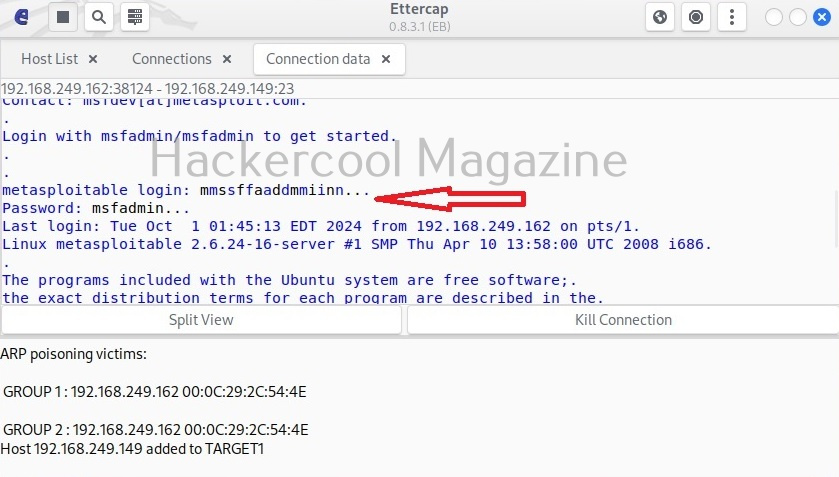
By default, the data from the client and server machines are shown in different tabs. You can see the credentials being exchanged between client and server. You can even join both the views for clarity.
Here, you can see the clear text credentials used to login into the telnet server.
Follow Us