Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn about cloud security. Before you learn about cloud security, you need to have a basic idea about what is cloud computing or cloud. Let me give you an example. Have you ever used Gmail or any other email service? What do you do to check your email? You open a browser or email client and go to the URL of the email service, enter your credentials and finally read your mails or start composing an email. Have you ever thought where all the mails are stored? Definitely not on your own system. They are stored elsewhere. Well, this is exactly how cloud computing works.
What is cloud computing?
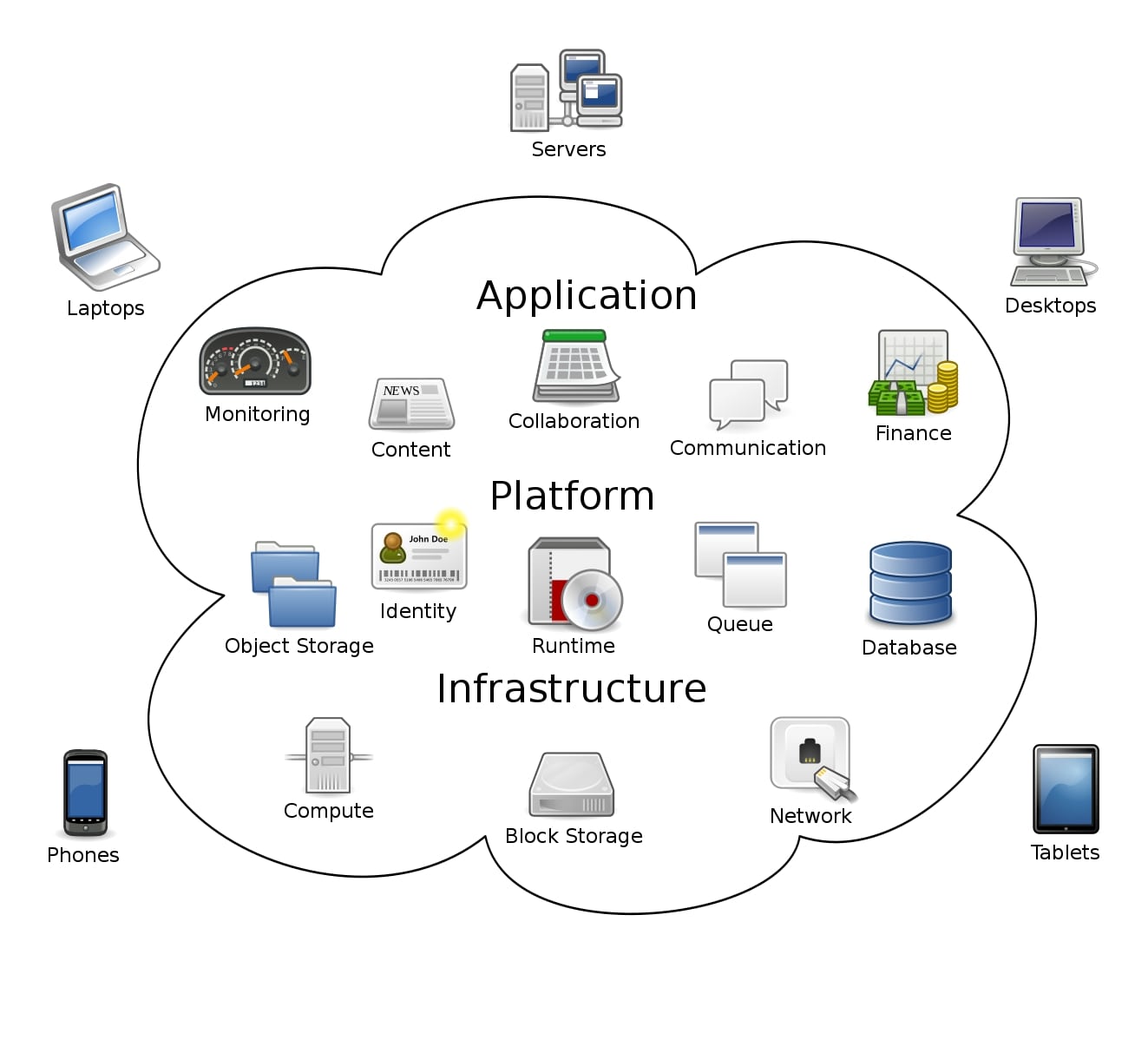
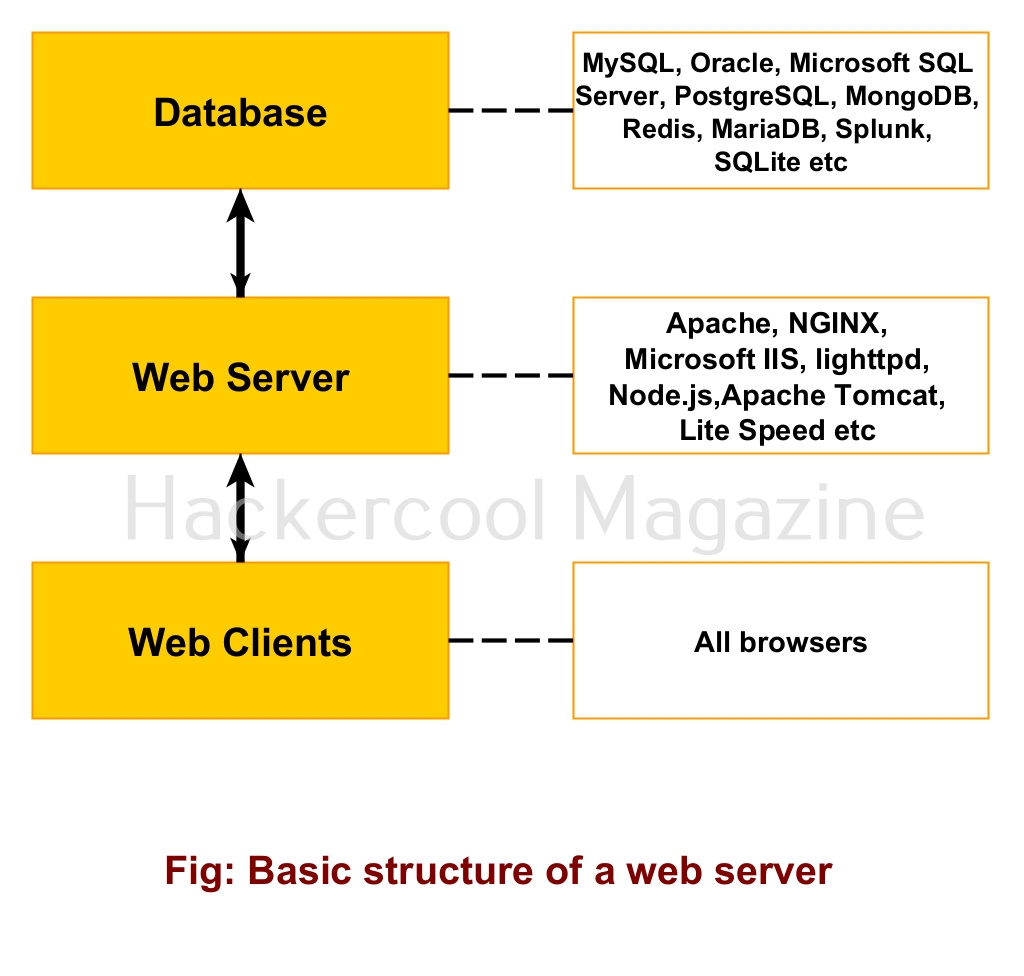
Cloud computing is providing of computer system resources like data storage, computing power, networking, servers and software etc over the internet on demand.
Types of Cloud computing
Services in cloud can be provided as per anyone’s need with customization. However, there are three models of cloud computing that are generally preferred.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
In this model of cloud service, customers rent the building blocks of computing like servers (physical or virtual), storage and networking. It is usually rented by those organizations which want to have complete control over their cloud. The needed software and applications are installed by the organization.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
What if organization or users don’t have the technical know how about installing everything on their rented hardware on cloud. The PaaS model comes to their rescue. This model comes with the installation of required tools and software along with basic computing resources provided in IaaS. For example, imagine you want to rent a WAMP server on cloud. Along with the basic computing resources, it comes with a Windows 10 machine with WAMP server installed on it. You still have to create the websites to be hosted on the WAMP server.
3. Software as a service (SaaS):
The most popular cloud model, it provides just all the resources and software you need. For example, let’s just say you rented a WordPress website on cloud for you. All you have to do is login into the WordPress website on your browser and upload blogposts. Rest all the cloud provider takes care for you.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security is the concept of providing security to the cloud-based systems from all the usual threats and dangers of cyber security. Cloud security is the responsibility of both the cloud service provider and the end user.
What are some cloud security threats?
Systems in cloud are vulnerable to all threats usual networks do like zero-day-vulnerabilities, DoS, phishing and malware etc.