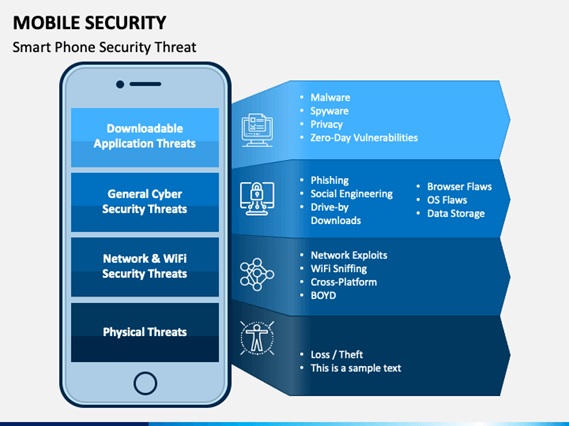
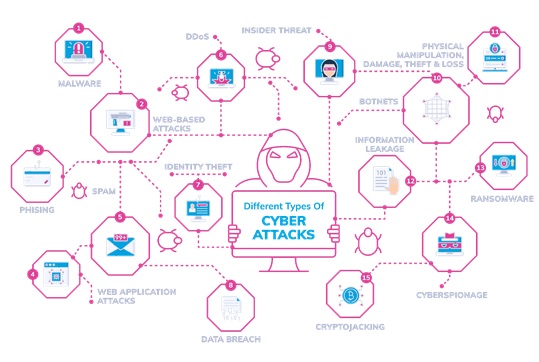
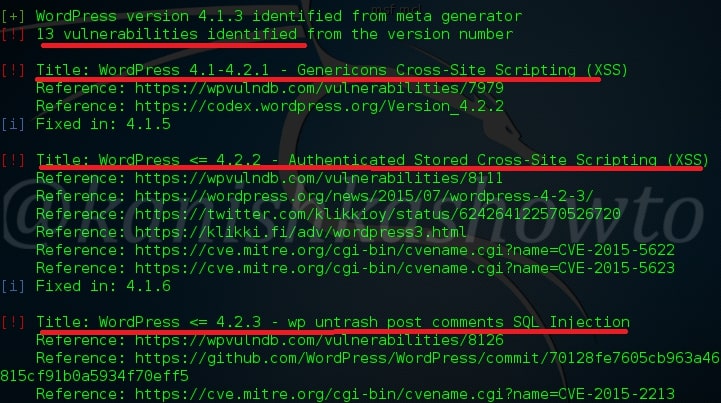
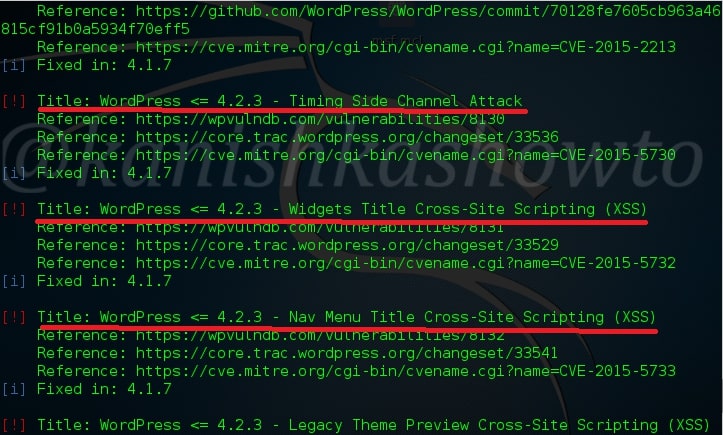
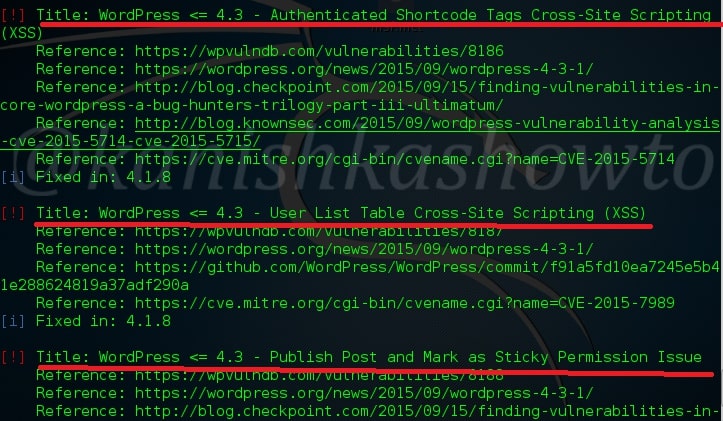
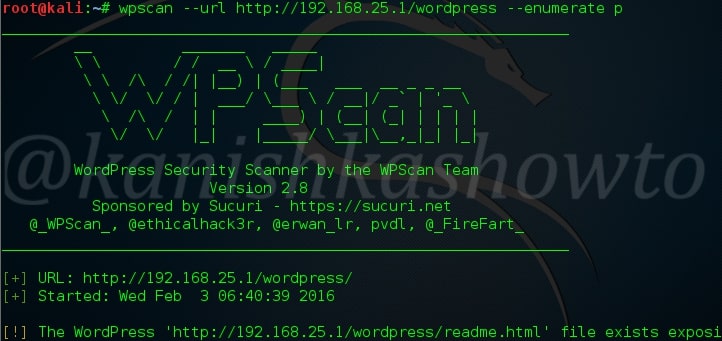
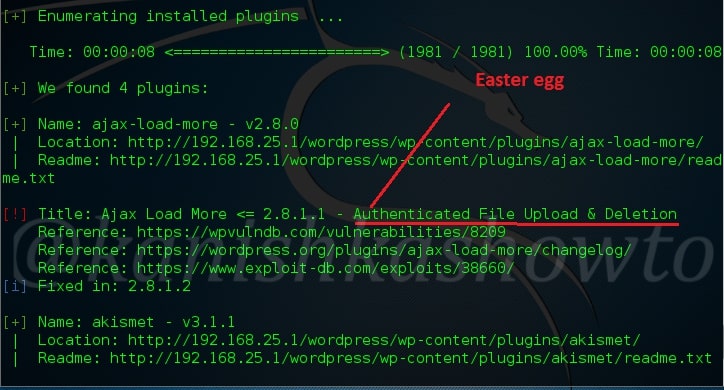
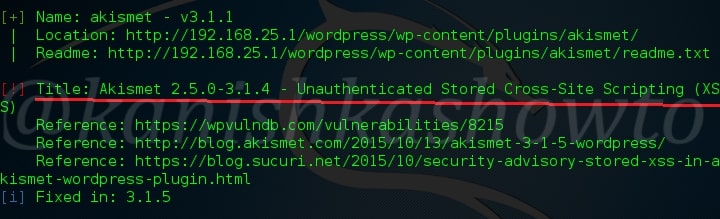
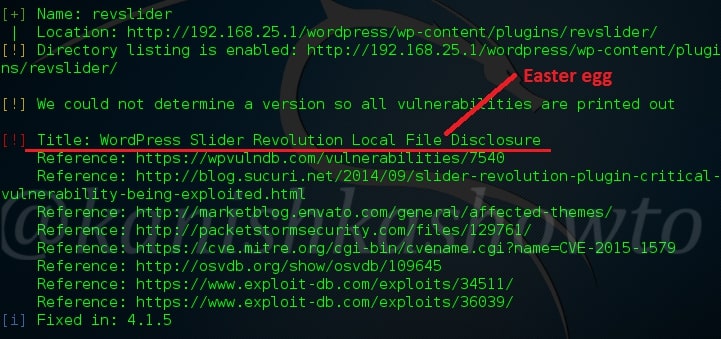
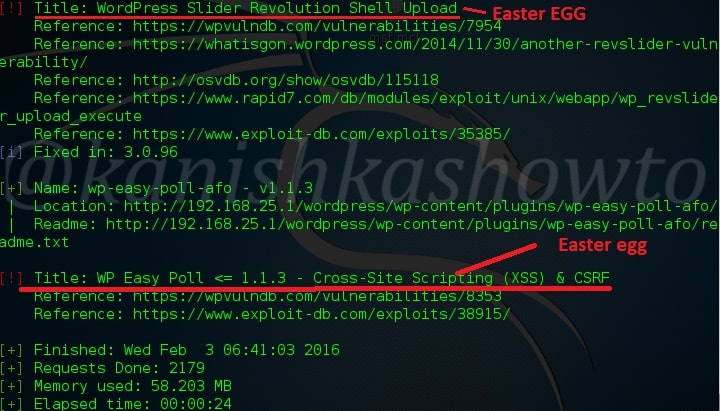
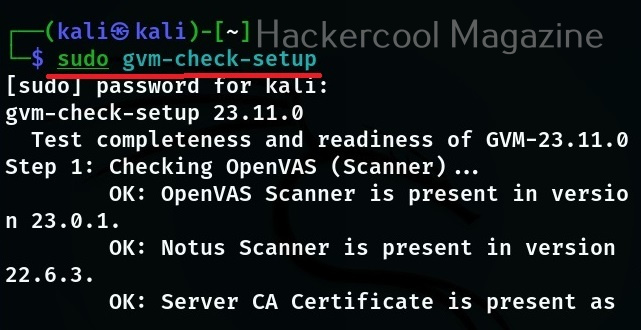
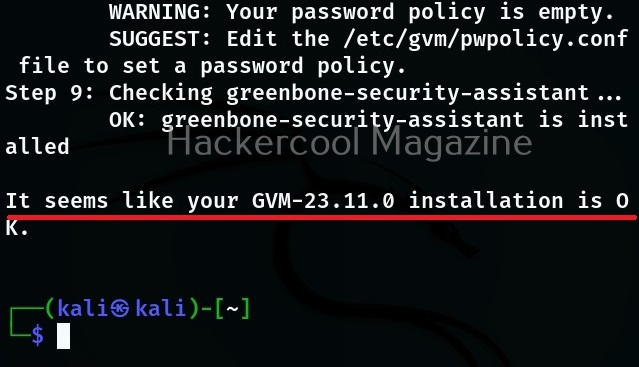
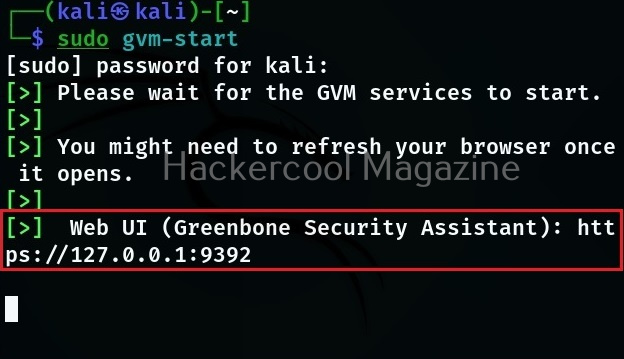
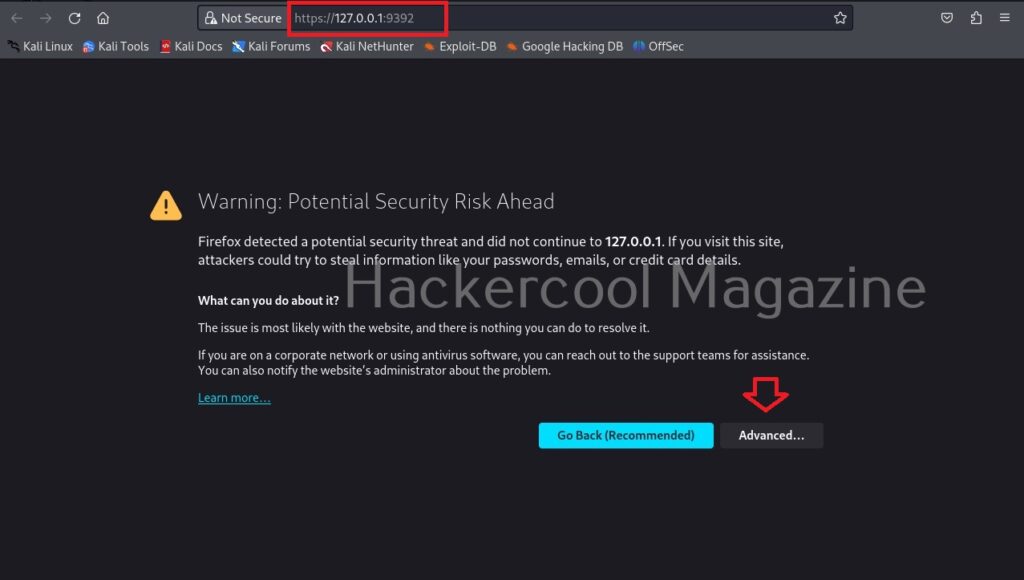
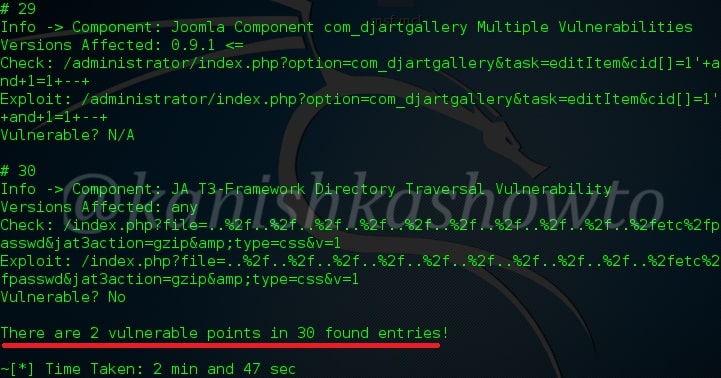
Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn everything about Mobile security. Mobile security refers to the measures taken to protect mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and other security threats. With the increasing use of mobile devices for activities such as online banking, shopping, and accessing sensitive information, it is more important than ever to take steps to protect your devices and personal information.
Mobile architecture and operating systems
A mobile device’s architecture refers to its hardware and software components, including the operating system, firmware, and applications. Understanding the components that make up your device can help you identify potential security threats and take steps to protect your device.
There are several types of mobile operating systems, including iOS, Android, and Windows Phone. Each operating system has its own strengths and weaknesses when it comes to security, and it is important to be aware of the risks associated with using a particular device.
Rooting and jailbreaking are methods used to gain access to the root level of a device’s operating system, allowing users to install custom software and make changes to the device that are not possible with a standard setup. While these methods can offer greater flexibility and customization, they can also introduce security risks, such as allowingmalwareto bypass security measures and access sensitive information.
Android Architecture
Android is an open-source operating system for mobile devices developed by Google. The architecture of Android is composed of multiple layers that interact to provide the functionality of a mobile device. The layers of the Android architecture are:
- Linux kernel: The Linux kernel is the foundation of the Android operating system. It provides hardware abstraction, power management, and security features to the Android device.
- Native libraries: These are libraries that are written in C/C++ and are responsible for providing low-level functionality to the Android operating system. Some of the native libraries include SQLite, WebKit, and OpenSSL.
- Application framework: The application framework is a set of APIs that provide the functionality for the Android applications. It is responsible for managing the life cycle of applications, user interfaces, data storage, and many other functionalities.
Applications: The top layer of the Android architecture is the applications that are built using the APIs provided by the application framework. Applications are the software programs that are installed on the Android device and provide the functionality to the user.
iOS Architecture
iOS is a mobile operating system developed by Apple for its devices. The architecture of iOS is based on a layered approach, similar to Android. The layers of the iOS architecture are:
- Core OS: This is the lowest layer of the iOS architecture and is responsible for providing the core operating system services such as process management, file system access, and memory management.
- Core Services: The Core Services layer is responsible for providing essential services such as networking, database, and threading.
- Media Layer: This layer provides support for graphics, audio, and video processing.
- Cocoa Touch Layer: The Cocoa Touch layer is the top layer of the iOS architecture and is responsible for providing the user interface and application framework.
- Applications: Applications are the software programs that are installed on the iOS device and provide the functionality to the user.
Mobile hacking attacks
Bluetooth Attacks on Mobile
Bluetooth is a wireless technology used to transfer data between devices. Bluetooth attacks refer to the security threats that target Bluetooth-enabled devices. These attacks can compromise the privacy and security of the device and its data.
Types of Bluetooth Attacks
There are several types of Bluetooth attacks that can target mobile devices, some of them are:
- Bluejacking: This is a type of Bluetooth attack that involves sending unsolicited messages to another device. The messages can be anything from harmless messages to malicious code.
- Bluesnarfing: This is a type of Bluetooth attack that involves stealing data from a device. The attacker can access contacts, calendars, and other sensitive information stored on the device.
- Bluebugging: This is a type of Bluetooth attack that involves taking control of a device. The attacker can access and control the device, including making phone calls and sending text messages.
- Bluespoofing: This is a type of Bluetooth attack that involves impersonating another device. The attacker can create a fake device and trick a user into pairing with it.
Malware attacks on Mobile
These are malicious software programs that are designed to steal sensitive information or compromise the functionality of your device. Common forms of malware include viruses, Trojans, and spyware. Malware can be spread through downloading infected apps or visiting infected websites, and it can hide in your device’s background, silently collecting information and transmitting it to attackers.
Some Famous Android Trojans
There are several Android trojans that have been discovered in recent years. Some of the most famous Android Trojans are:
- TimpDoor:This is a trojan that can steal sensitive information from infected devices. It can also install malicious applications and spread to other devices.TimpDoor Turns Mobile Devices Into Hidden Proxies
Devices running TimpDoor could serve as mobile backdoors for stealthy access to corporate and home networks because the malicious traffic and payload are encrypted. Worse, a network of compromised devices could also be used for more profitable purposes such as sending spam andphishingemails, performing ad click fraud, or launching distributeddenial-of-serviceattacks.
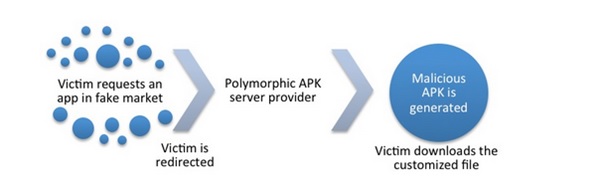
- FakeInstaller:This is a trojan that disguises itself as a legitimate app and tricks users into installing it. Once installed, the trojan can steal sensitive information from the device.
Android.FakeInstaller sends SMS messages to premium rate numbers, without the user’s consent, passing itself off as the installer for a legitimate application. There is a large number of variants for this malware, and it is distributed on hundreds of websites and fake markets. The spread of this malware increases every day.
- Slempo:This is a trojan that uses phishing techniques to steal sensitive information from the infected device. The trojan can also display fake advertisements and download additional malware onto the device.
JSocket:This is a trojan that opens a back door on the infected device, allowing the attacker to control the device remotely. It can also steal sensitive information and spread to other devices.
The malware is able to remotely control and access microphones and cameras, use a mobile device’s GPS systems to track victims and both modify and view text messages and phone call data.
The JSocket Trojan tends to spread through e-mail attachments masquerading as invoices, purchase orders and other financial documents which vary depending on the campaign.
To infect mobile devices, the Trojan is loaded into apps downloadable outside of the official Google Play store, as the malicious code requires an Android APK to function.
- Gemini:This is a trojan that can steal sensitive information, including bank account credentials and credit card numbers, from the infected device.
Some Famous iOS Trojans
Although iOS is considered to be more secure than Android, there have still been instances of trojans affecting iOS devices. Some of the most famous iOS Trojans are:
- KeyRaider:This is a trojan that affects jailbroken iOS devices. It can steal Apple account information and purchase data from the App Store.
It implemented the following malicious behaviors:
Stealing Apple account (user name and password) and device GUID, stealing certificates and private keys used by Apple Push Notification Service and preventing the infected device being unlocked by passcode or by iCloud service.
- XcodeGhost: This is a trojan that affects iOS applications. It can steal sensitive information from the infected device and spread to other devices through the infected application.
The apps that are infected by the XcodeGhostviruscan collect information about a device user, and then send encrypted messages off to a remote server through the HTTP protocol. Some of the information that is shared includes:
- Infected app’s name
- Current time
- The app’s bundle identifier
- Network type
- Device name and type
- Current system language and country
- Current device’s UUID
- Network type
Another risk that is associated with the XcodeGhost malware is that it allows an iOS device to receive commands from an attacker. Such attacks can make the app perform any of the following concerning actions:
Create a fake alert message that can trick a device user to give personal information, hijack the opening of various URLs based on their scheme. This opens the possibility of exploiting vulnerabilities in iOS and macOS, read and write data in the user’s clip This can be used to get passwords to various accounts
- Pegasus: This is a trojan that can infect an iOS device through a malicious text message or email. It can steal sensitive information and monitor the device’s activity.
As of 2016, Pegasus spyware was capable of reading text messages, tracking calls, collecting passwords, location tracking, accessing the target device’s microphone and camera, and harvesting information from apps.
The Pegasus spyware is a Trojan horse computer virus that can be sent “flying through the air” to infect cell phones. The NSO Group states that it provides “authorized governments with technology that helps them combat terror and crime.”
- AceDeceiver: This is a trojan that affects jailbroken iOS devices. It can steal sensitive information, such as Apple account credentials, and spread to other devices.
This malware is able to install itself without an enterprise certificate, unlike previous iOS malware that abused enterprise certificates in order to infect devices. This is also the first iOS malware that exploits design flaws in Apple’s DRM protection mechanism, FairPlay, which means that it can infect devices that aren’t jailbroken.
Protecting Yourself from Deceptive Threats
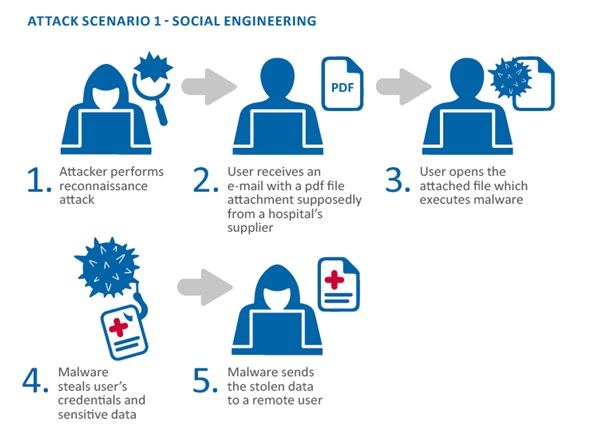
Social engineeringattacks are a common threat in the mobile space, and they involve tricking users into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware.
These attacks can take many forms, including phishing scams, vishing (voice phishing), and baiting (leaving a USB drive with malware in a public place).
To protect yourself from social engineering attacks, be cautious of unsolicited emails and phone calls, and never provide sensitive information or download attachments from unknown sources.
Securing Your Mobile Payments
With the increasing popularity of mobile payments, it is important to consider the security risks associated with using your mobile device for financial transactions. Make sure to only use trusted payment apps and avoid entering sensitive information on public Wi-Fi networks. Consider setting up two-factor authentication for an added layer of security, and be sure to regularly monitor your accounts for unauthorized transactions.
Protecting Your Data in theCloud
Cloud storage can be a convenient way to store and access data, but it is important to be aware of the security risks associated with storing sensitive information in the cloud. Consider usingencryptionand strong passwords, and be cautious of downloading apps from untrusted sources. Make sure to read the privacy policies of any cloud storage service you use, and be mindful of the types of information you store in the cloud.
Securing Your Physical Device
Physical security refers to protecting your device from theft or unauthorized access. Consider using a password or passcode to lock your device, and keep it in a secure location when not in use. If you lose your device, it is important to act quickly to erase the data on the device to prevent unauthorized access to your sensitive information.
In the Event of Loss or Theft
Remote wipingis a feature that allows you to erase the data on your device in the event of theft or loss. Make sure to enable this feature on your device, and familiarize yourself with how to use it in the event of an emergency. Consider setting up a tracking app to help locate your lost device, and report the loss or theft to your mobile carrier and local law enforcement as soon as possible.
These are malicious software programs that are designed to steal sensitive information or compromise the functionality of your device. Common forms of malware include viruses, Trojans, and spyware. Malware can be spread through downloading infected apps or visiting infected websites, and it can hide in your device’s background, silently collecting information and transmitting it to attackers.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks:This type of attack involves an attacker intercepting and altering the communication between two parties.
In the context of mobile security, this can happen when an attacker is able to intercept a Wi-Fi signal, allowing them to access and steal sensitive information transmitted over the network.
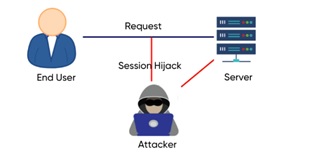
- Session Hijacking:This type of attack involves an attacker taking control of a user’s active session by stealing their session ID.
This can occur when an attacker is able to intercept a user’s login credentials, allowing them to access the user’s session and sensitive information.
- Rootkit Attacks:Rootkits are malicious software programs that are designed to hide their presence and bypass security measures. They can be particularly dangerous on mobile devices, as they can grant attackers full access to your device, allowing them to steal sensitive information and control the device.
- Ransomware Attacks: This type of attack involves an attacker encrypting a user’s files and demanding a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. On mobile devices, ransomware can be spread through infected apps or visiting infected websites, and it can lock down the device and make it difficult for the user to access their sensitive information.
- SMS Spoofing:This type of attack involves an attacker sending text messages from a fake or spoofed number, tricking the recipient into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. SMS spoofing can be used for phishing attacks or to spread malware.
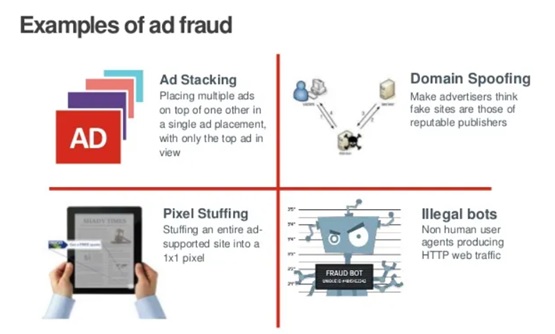
- Ad Fraud:This type of attack involves attackers using bots or malware to artificially inflate the number of clicks or impressions on an ad, resulting in increased revenue for the attacker.
Ad fraud can impact both the advertisers and users, as it can result in increased costs and decreased security.
- BlueBorne Attack:This type of attack involves an attacker exploiting vulnerabilities in the Bluetooth communication protocol to gain access to a device. This can allow an attacker to steal sensitive information, install malware, or take control of the device.
- Rogue App Attack:This type of attack involves an attacker offering a fake or malicious app, disguised as a legitimate app, in app stores or through third-party sources. When a user downloads the rogue app, it can steal sensitive information, install malware, or take control of the device.
- Cloud Jacking Attack:This type of attack involves an attacker accessing and stealing sensitive information stored in the cloud, such as contacts, photos, or financial information. Cloud Hackers can gain access to the cloud through unsecured Wi-Fi networks or by exploiting vulnerabilities in the cloud storage service.
Protecting Your Mobile Device
To protect your mobile device from hacking and malware attacks, it is important to follow some basic security measures. Here are a few tips:
- Keep software up to date:Regular software updates include security patches that fix vulnerabilities in your device. Make sure to regularly check for and install updates for both the operating system and installed applications.
- Use strong passwords:A strong password consists of a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols and should be unique to your device. Avoid using easily guessable passwords such as “1234” or “password”.
- Be cautious of public Wi-Fi:Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured and can provide hackers with an easy way to steal sensitive information. Avoid using public Wi-Fi for financial transactions or entering sensitive information.
- Install security software:Consider installingantivirussoftware and a mobile security app to protect your device from malware and hacking attacks.
- Avoid downloading from untrusted sources:Only download apps from trusted app stores, such as the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. Avoid downloading apps from untrusted websites, as they may contain malware.
- Be aware of phishing scams:Be cautious of emails, text messages, or links that ask for sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial information. Always double-check the sender and look for signs of a phishing scam before providing any information.
- Use encryption:Encrypting your device’s data helps to protect it from theft and unauthorised access.
By following these simple tips, you can help to protect your mobile device from security threats. Remember, being proactive about mobile security can help keep your personal information and data safe.
Conclusion
It is clear that there are many different types of mobile hacking attacks that pose a threat to your device and sensitive information. By being aware of these threats and taking steps to protect your device, you can help ensure that your personal information and sensitive data remain safe and secure. Keep your device and software updated, use strong passwords and encryption, and be cautious when downloading apps or visiting websites to minimize your risk of a successful attack.
Mobile security is a growing concern; as mobile devices are becoming increasingly integral to our daily lives. By understanding the different types of threats and taking steps to protect your device, you can help ensure that your personal information and sensitive data remain safe and secure. Stay informed and stay protected by keeping your device and software updated, using strong passwords and encryption, and being cautious when downloading apps or visiting websites. Watch out this blogpost for more updates on mobile security