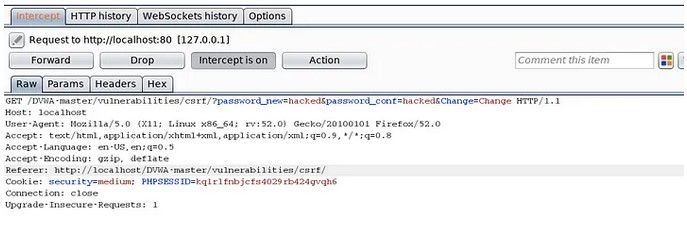
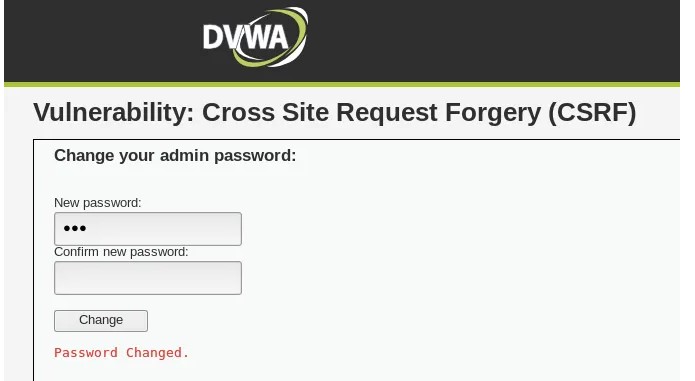
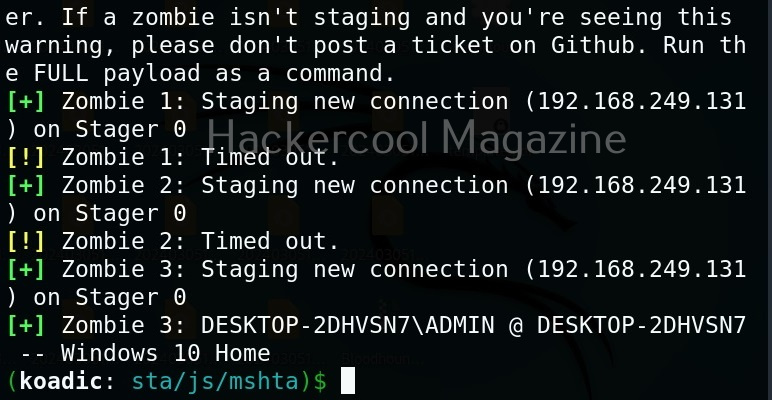
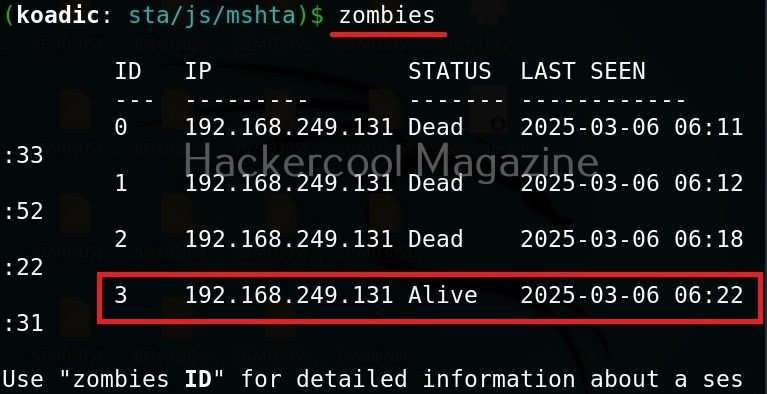
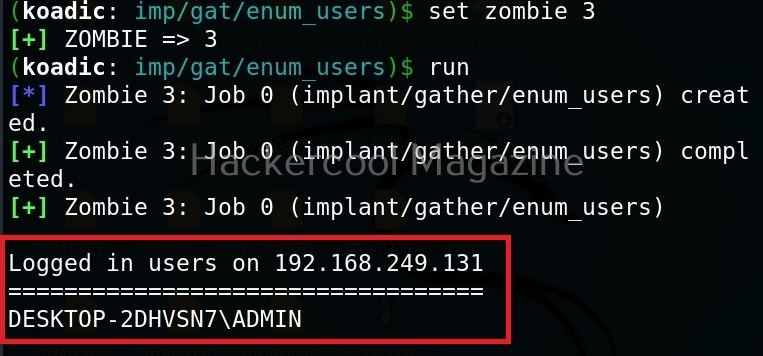
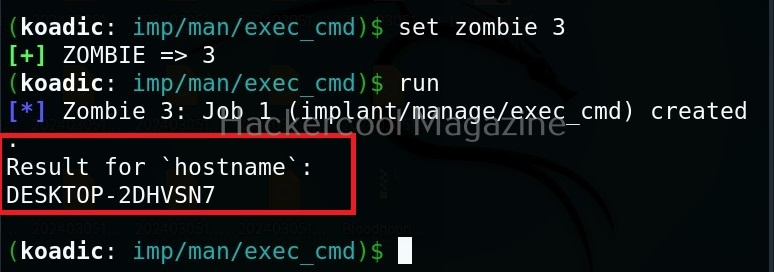
Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. In this article, you will learn about Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability. CSRF attacks can have serious consequences, including unauthorized money transfers, identity theft, and other forms of data theft or manipulation.
What is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)?
Cross-Site Request Forgery is a type of web application security vulnerability that allows an attacker to execute unauthorized actions on behalf of a victim user.
How CSRF Attacks Work?
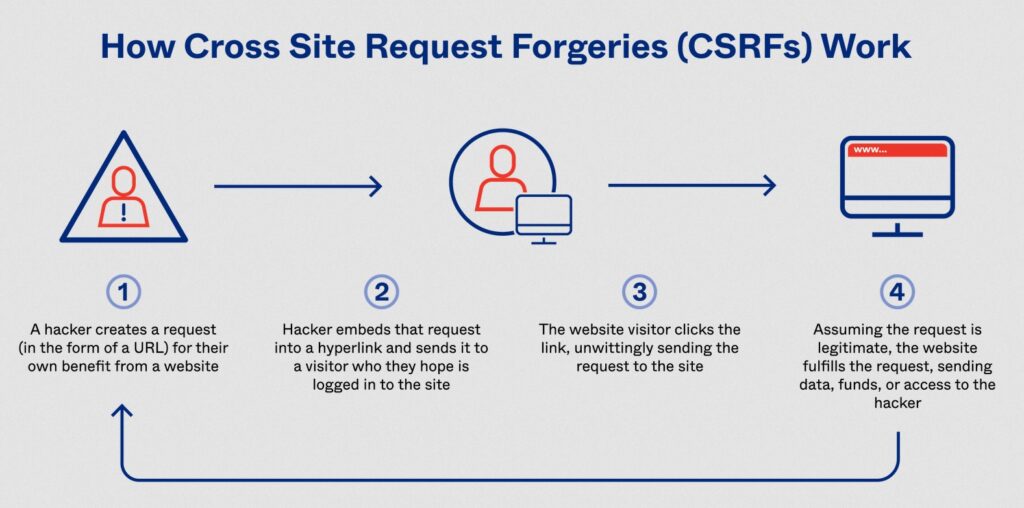
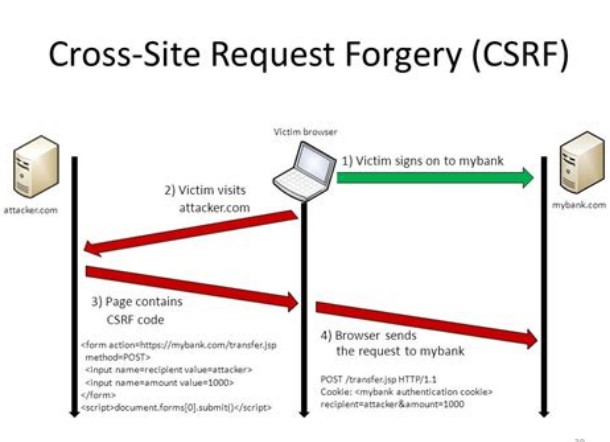
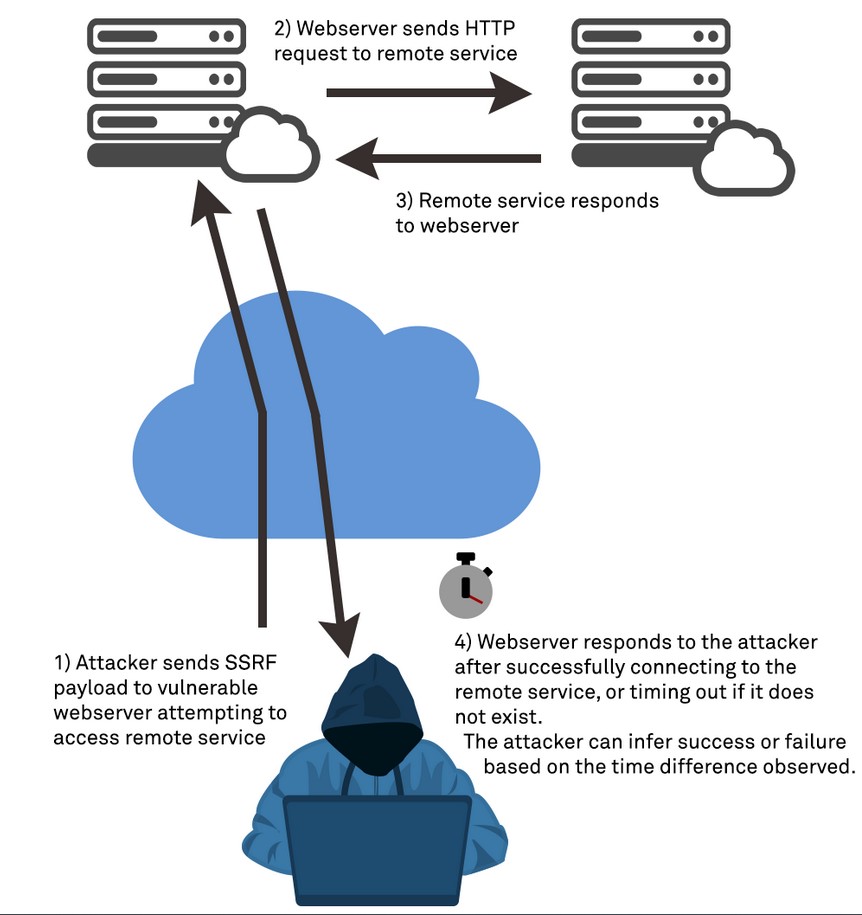
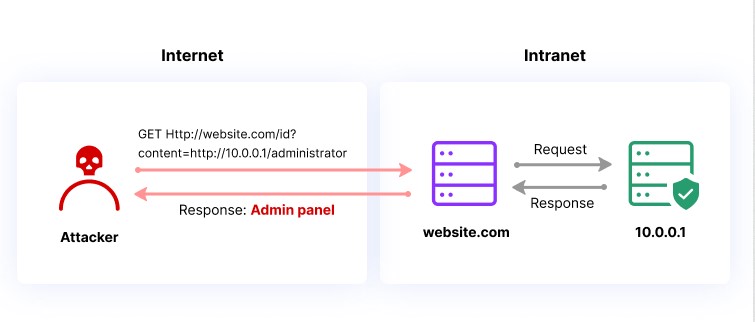
CSRF attacks work by exploiting the trust that a website or web application has in a user’s browser. When a user is logged into a website, the website creates a session for that user, which includes a unique session ID. This session ID is stored in a cookie on the user’s browser, and is sent to the website with every subsequent request made by the user.
An attacker who wants to execute a CSRF attack needs to trick the victim user into submitting a request to the target website that includes the victim’s session ID. This can be accomplished in a number of ways, including by embedding a malicious form or link on a third-party website, or by sending a malicious email or message to the victim user.
Once the victim user submits the request with their session ID, the website will process the request as if it came from the user directly. This can allow the attacker to execute actions on behalf of the victim user, such as changing their account information, making purchases, or transferring funds.
Examples of CSRF attacks include changing a user’s password or email address, making purchases or subscriptions without the user’s knowledge or consent, and performing unauthorized actions on social media accounts.
Real World Examples of CSRF Attacks
CSRF attacks are a serious threat to web applications and might have been responsible for numerous hacking attacks. In this section, we will discuss some real-world examples of this attacks.
1. Twitter Bug Bounty Program:
In 2018, a security researcher discovered a CSRF vulnerability in the Twitter Ads platform. The vulnerability allowed an attacker to create and launch an advertising campaign on behalf of the victim without their knowledge. The researcher reported the vulnerability to Twitter, who promptly patched the issue and awarded the researcher a $3,000 bounty.
2. Starbucks Gift Card Theft:
In 2015, security researchers discovered a vulnerability in the Starbucks gift card registration process that allowed attackers to steal gift card balances. The vulnerability was caused by a lack of CSRF protection, which allowed attackers to change the email address associated with a gift card and then transfer the balance to their own account. The researchers notified Starbucks of the vulnerability, and the company promptly patched the issue.
3. Google Drive CSRF Attack:
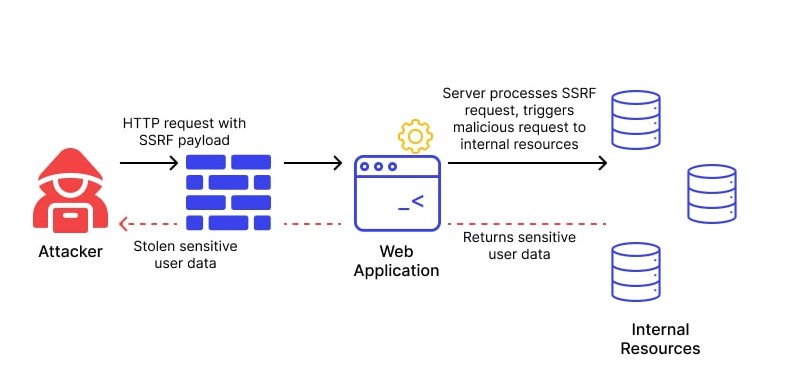
In 2016, security researchers discovered a CSRF vulnerability in Google Drive that allowed attackers to steal sensitive user data, including email addresses and contact lists. The vulnerability was caused by a lack of anti-CSRF tokens, which allowed attackers to execute unauthorized actions on behalf of the user. Google was notified of the vulnerability and quickly patched the issue.
These are just a few examples of the devastating consequences of command injection attacks.
Mitigation and Prevention
There are several techniques that can be used to prevent CSRF attacks, including token-based prevention, SameSite cookies, and double-submit cookies.
Token-based prevention involves generating a unique token for each user session, and requiring that this token be included in every form submission or request made by the user. When a user submits a form or request, the website checks to make sure that the token included in the submission matches the token associated with the user’s session. If the tokens do not match, the request is rejected.
SameSite cookies are another technique that can be used to prevent CSRF attacks. SameSite cookies restrict the scope of cookies to the domain that set them, preventing them from being sent in cross-site requests. This can prevent attackers from using the victim user’s session ID to execute unauthorized actions.
Double-submit cookies involve setting a cookie that includes a random value, and requiring that this value be included in both the request header and the request body. When a request is submitted, the website checks to make sure that the value in the header matches the value in the body. If the values do not match, the request is rejected.
While all of these techniques can be effective in preventing CSRF attacks, token-based prevention is generally considered to be the most secure and reliable method.
To protect against CSRF attacks, developers can implement various measures, including:
1. Anti-CSRF Tokens:
One effective method of mitigating CSRF attacks is by using anti-CSRF tokens. These tokens are unique to each user session and are included in all requests that modify data or state. The server can then verify that the token is valid before processing the request, thereby ensuring that the request is legitimate.
2. SameSite Cookies:
Developers can also use SameSite cookies to mitigate CSRF attacks. SameSite cookies prevent cookies from being sent in cross-site requests, making it more difficult for attackers to launch CSRF attacks.
3. CSRF Protection Frameworks:
Many web application frameworks, such as Django, Ruby on Rails, and ASP.NET, provide built-in CSRF protection features. These features can include automatic generation of anti-CSRF tokens and enforcing the use of SameSite cookies.
4. Input Validation:
As with all web application security, input validation is essential to protect against CSRF attacks. Developers should validate all user input on the server side to ensure that it is safe and does not contain any malicious code.
5. Multi-Factor Authentication:
Implementing multi-factor authentication can also help protect against CSRF attacks. By requiring users to provide an additional form of authentication, such as a one-time password, attackers will have a more difficult time launching CSRF attacks.
That’s all about Command Injection. We will be back with a new vulnerability vey soon. Until then, Good Bye.