Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you studied about website footprinting. In this blogpost, you will learn about a tool called eyewitness which helps you to decide which website to focus on.
In ethical hacking, before trying to footprint a website, it would be good if we have a general idea about what websites to target first. For example, a company you are going to pen test may have multiple websites and sub domains. Before we jump into password cracking or exploitation or directory busting or perform any other attack, it would be good if we are first able to decide what website and URLs to target first. The role of eyewitness tool comes there. Eyewitness takes the screenshots of the URLs or websites you provide. Apart from taking screenshot of the URL, it will also capture any header info and default passwords.
Let’s see how to use this tool. For this we will be using Kali Linux as this tool is available by default in Kali repositories. As target, we will be using Metasploitable 2 installed in our virtual hacking Lab. It can be installed as shown below.
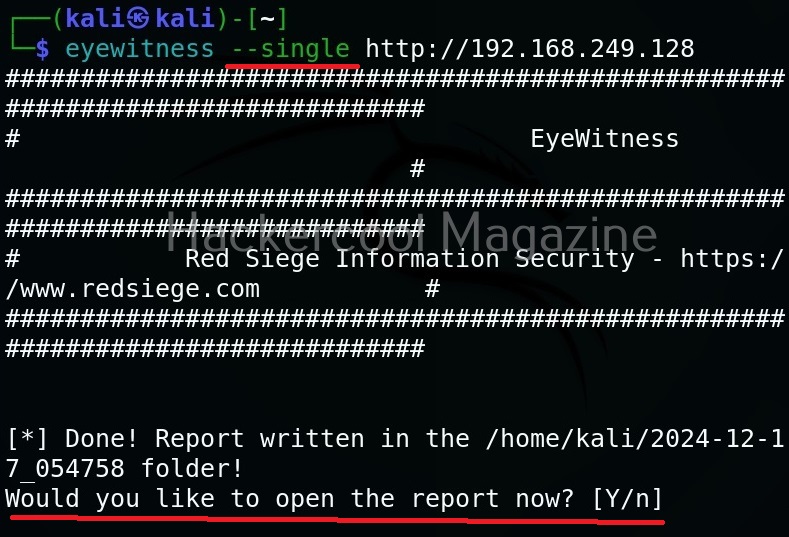
Target a single URL (–single)
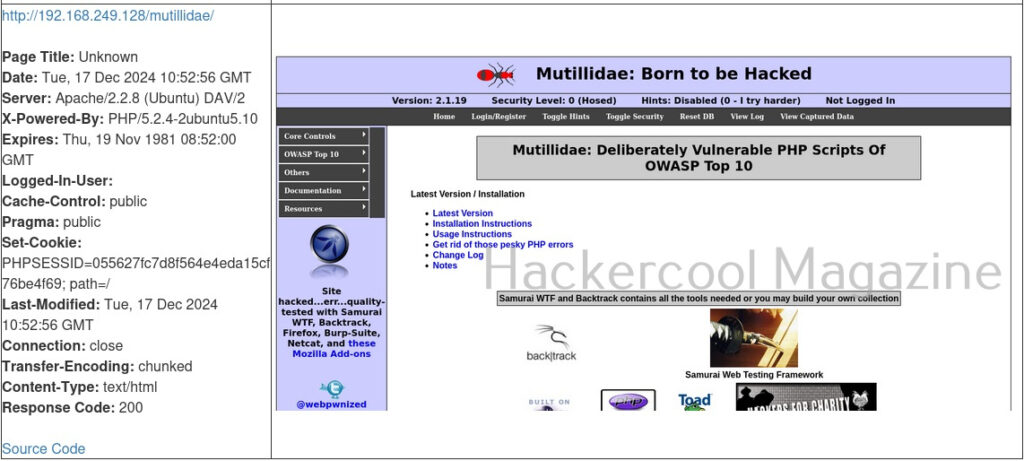
You can take screenshot of a single URL as shown below.
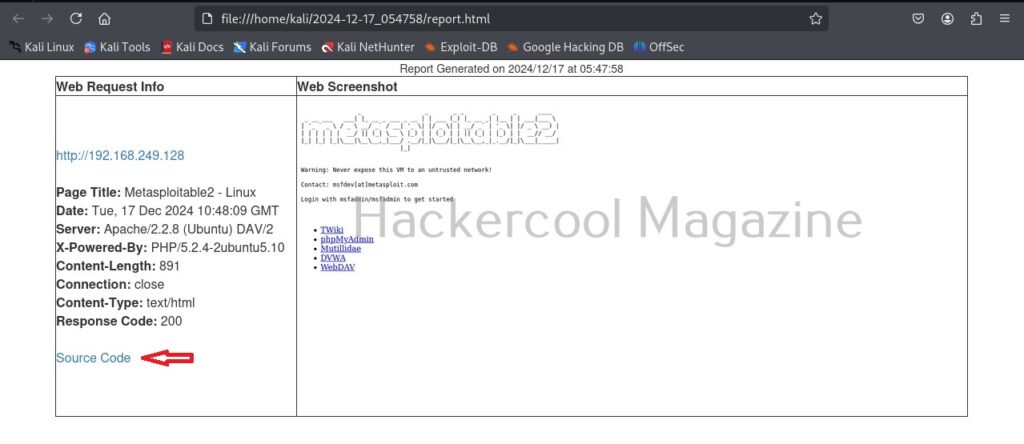
As soon as it writes a report for your target, it will ask you if you want to open the report. Click on “Yes”. It will open the report as shown below.
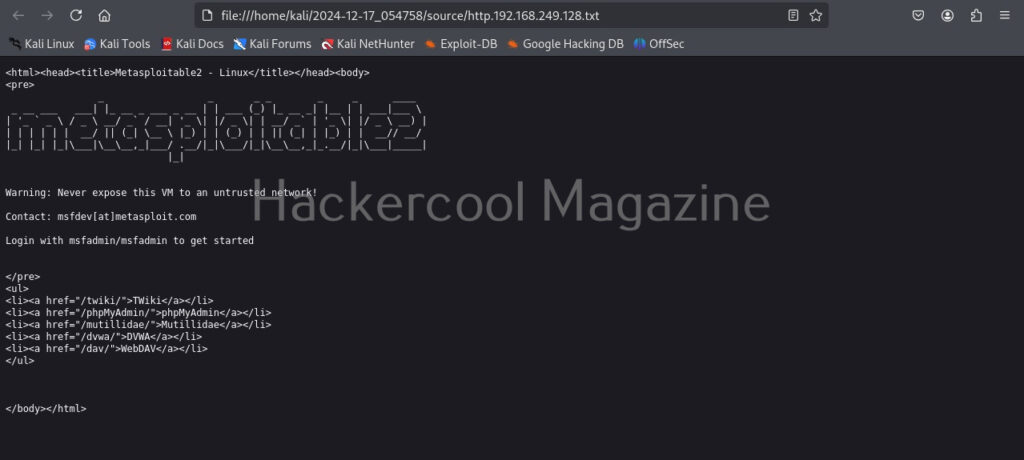
You can even view the code of the URL you scanned.
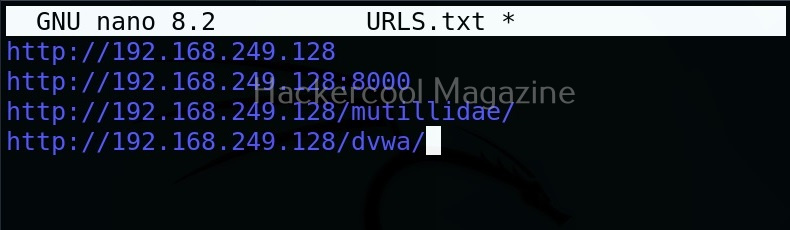
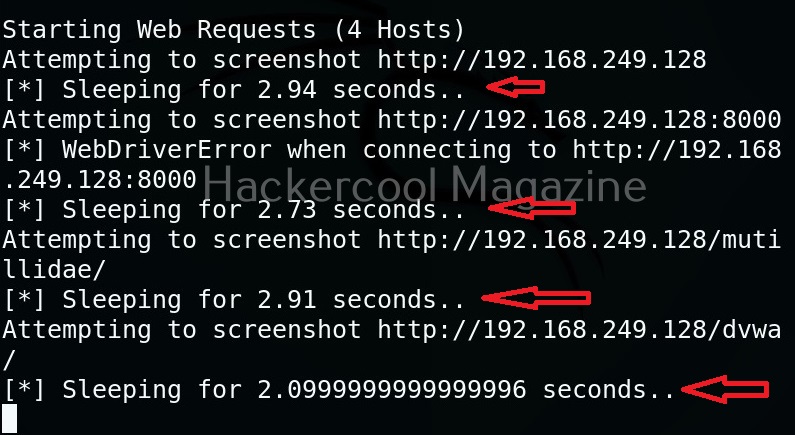
But the real power of eyewitness can be seen when we are targeting multiple URLs at once. For doing this, we will first create a file called URLS.txt and add some URLs we want to target as shown below.
Target multiple URLs (-f)
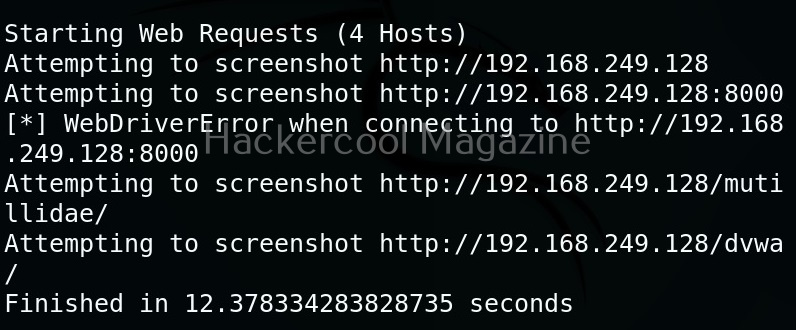
Multiple URLs can be targeted with this tool by specifying the above created file with (-f) option.
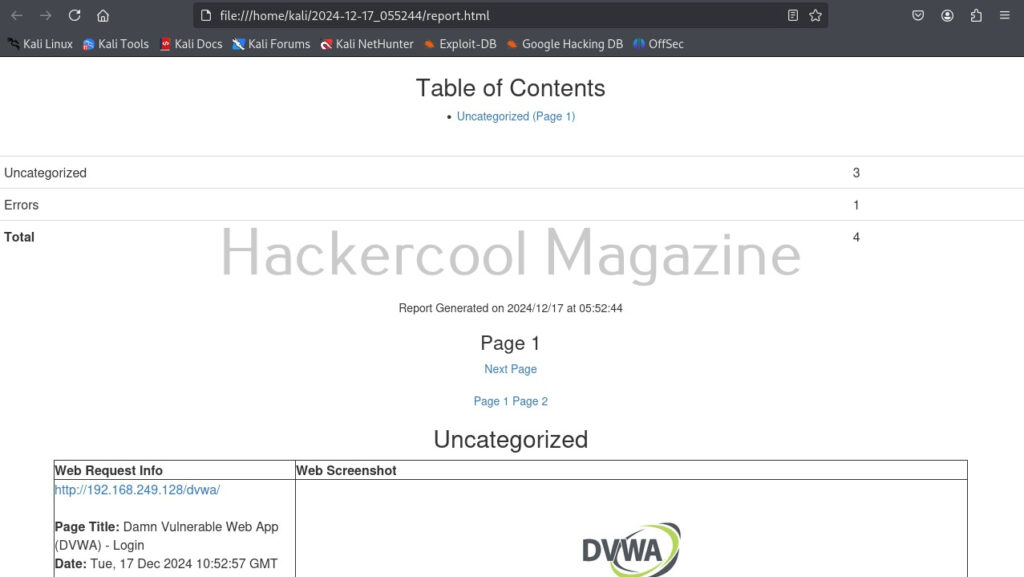
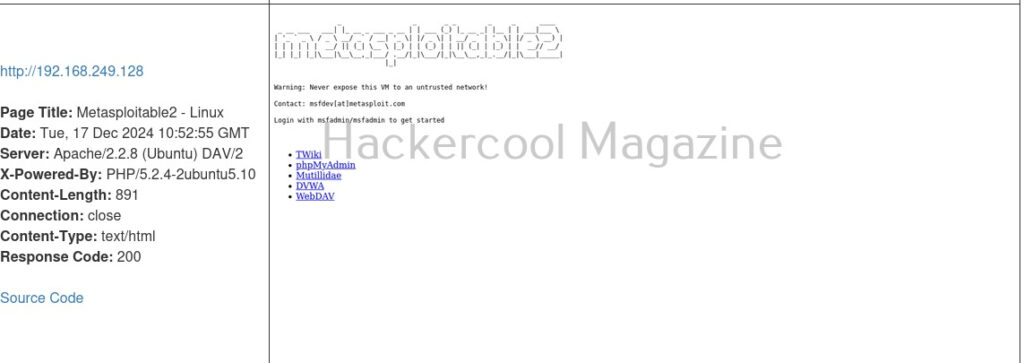
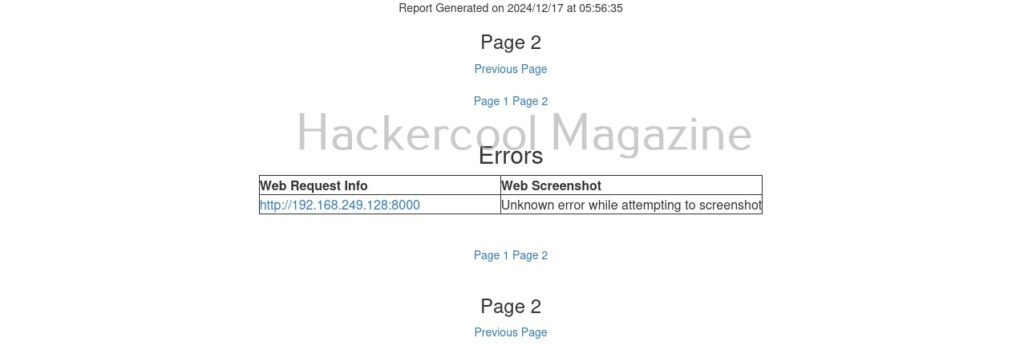
Here’s the report.
One of our URLs we targeted ended up in a error.
Skip DNS resolution(–no-dns)
In some cases, while using eyewitness tool, you may have to go through a VPN. In such cases, it is good to skip DNS resolution when connecting to the website. This option helps you to do it.
Resolve IP / host name for your target (–resolve)
Time to wait while requesting an URL (–timeout)
By default, eyewitness waits for 7 seconds before it goes to take a screenshot of a new webpage. However, this can be changed with this option. For example, let’s change the timeout time to 1 second.
Add jitter (–jitter)
Using this option, we can randomize the URLs specified and add a random delay.
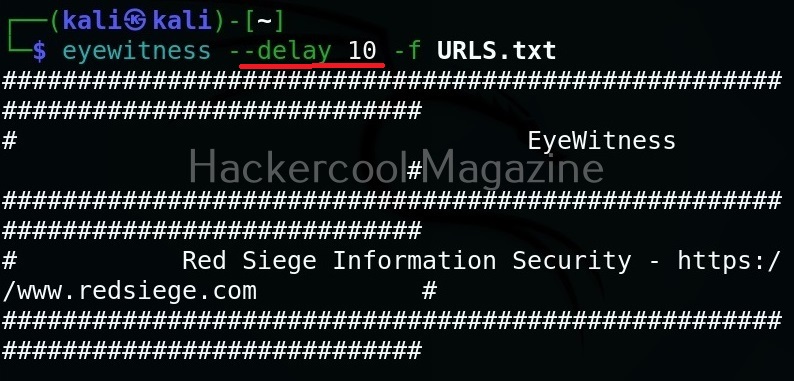
Add delay before taking a screenshot (–delay)
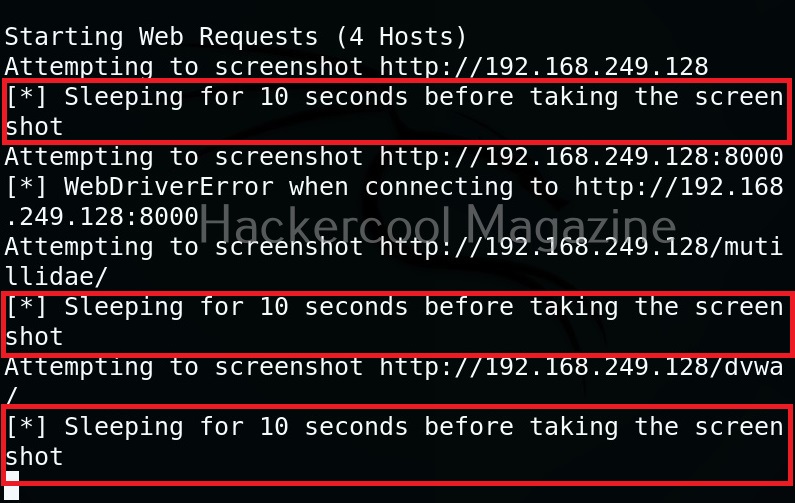
Using the option, we can add delay between opening of the navigator and taking a screenshot. This delay can be specified in seconds. For example, let’s add 10 seconds delay before taking screenshot.
Maximum retries (–max-retries)
This option specifies eyewitness tool how many retries it has to make if it fails to grab a screenshot on the first attempt.
Specify directory name for saving the report (-d)
This option is used to specify a directory name for saving the report.
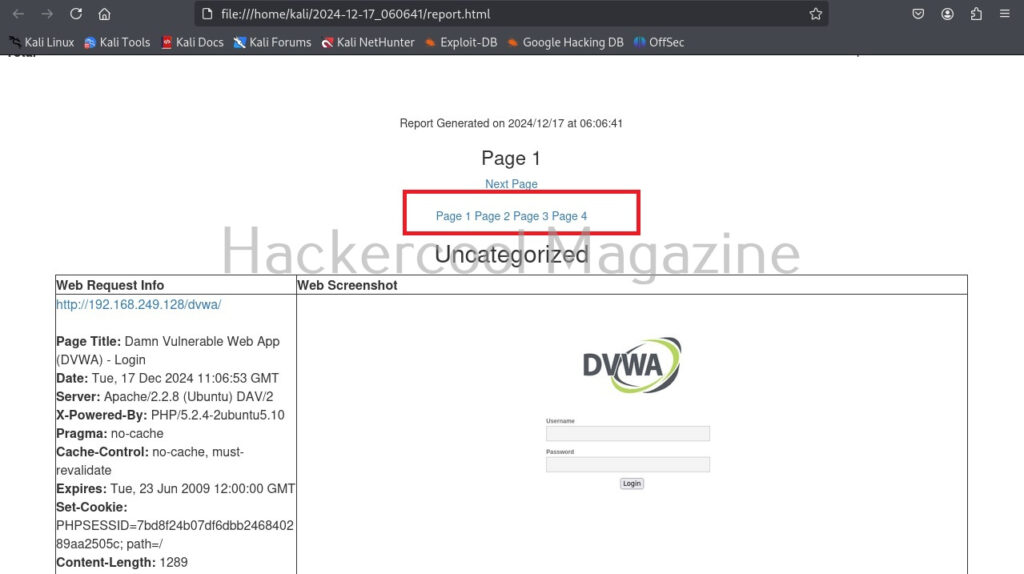
Number of results to show on one page (–results)
By default, eyewitness shows output for all the URLs given as input on a single page. This option can be used to specify how many results to show per page. For example, let’s set it to show 1 result per page.
As you can see, now, all the results are shown on separate pages.
You don’t want to be prompted for viewing the report (–no-prompt)
If you don’t want eyewitness to prompt you to open the report after finishing its work, you can use this option.