Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn about various Data-Link Layer attacks (various hacking attacks that take place on the Data-Link layer).
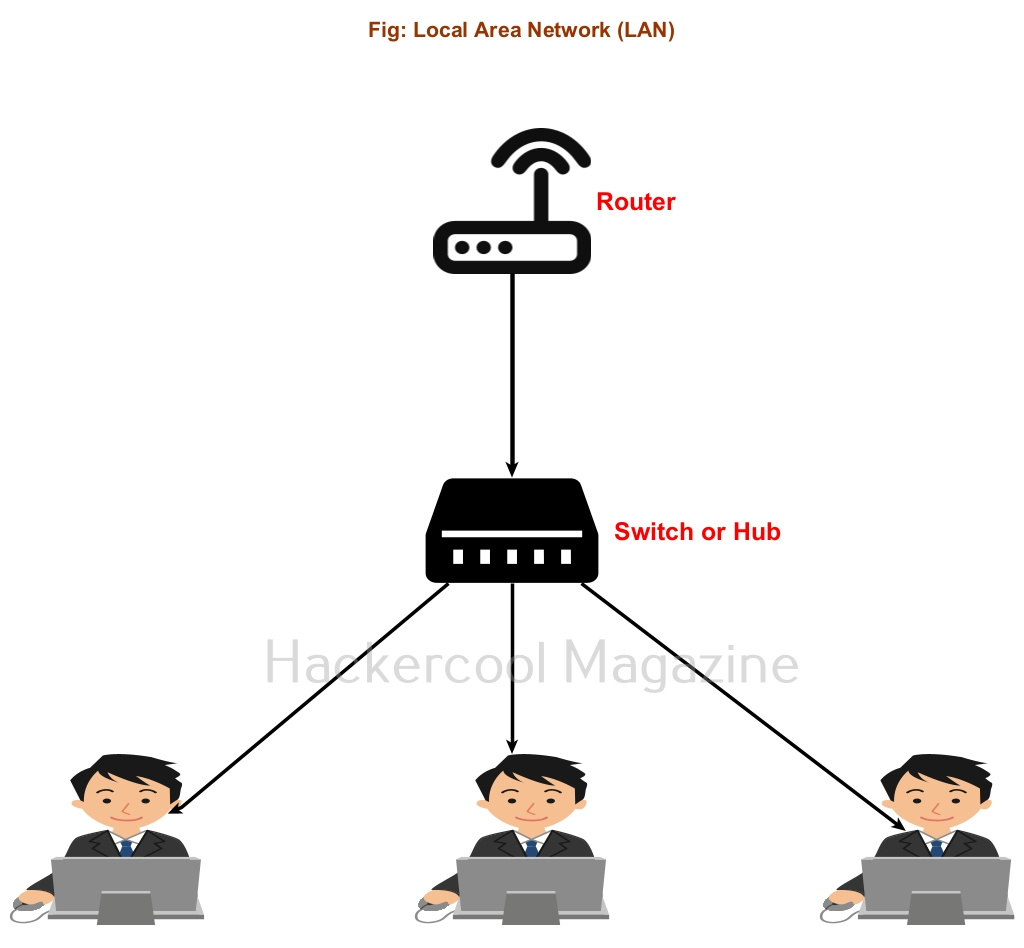
The Data-link layer is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model. This layer is the protocol layer that transports data between network nodes in a wide Area Network or nodes in the same Local Area Network (LAN). It is responsible for ensuring and confirming that the bits and bytes received are similar to the bits and bytes being transmitted. In this layer, data is transferred in frames and communication takes place using MAC addresses instead of IP addresses. The attacks in the Data-link Layer take place in a LAN.
What is a Network Hub?
A network hub is a hardware device that connects multiple devices to a network and allows them to communicate with each other and share resources.
Just imagine, you have a router with 5 LAN ports. Using LAN cables, you can connect 5 devices to this router. Now, what if you want to connect 10 devices to the same network. This is where the use of network hub comes. You can connect a network Hub to one of the ports of a router. Let’s say this network hub has 10 LAN ports. So you can connect 10 computer devices to the same network. Similarly you can connect Network Hub to all ports of the routers to extend the network.
The only disadvantage with Hub is that it sends traffic intended to be between two machines to all the devices of the network. Other than consuming bandwidth, it also poses security threats like sniffing.
For example, let’s say someone from machine “B” in a network is logged into telnet server on machine “A”. You have seen in our packet sniffing blogpost that in telnet protocol, data is transferred in plain text format. So in a Hub based network, the network traffic intended to be between “A” and “B” will even go to another machine in the network “C”. If a hacker is on machine “C” he can view the telnet credentials by sniffing.
What is a Network Switch?
The above reasons are why, network Hubs have been replaced by Network Switches. A Switch, similar to a Network Hub in a hardware device that connects all the device of a network. The only difference in switch sends the traffic to the intended device instead of all the devices in the network
What is a MAC address?
Just now, you have read that communication between devices in a LAN takes place using MAC addresses. But what is a MAC address? Every computing device on Internet (Desktop, Laptop and Mobiles etc) has a Network Interface Card (NIC). This Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware circuit in the computing devices that enables the devices to be able to connect to a network.
Each NIC is given a unique hardware address that is also popularly known as a Media Access Control (MAC) address. A MAC addresses is a 48-bit number consisting of six groups of two hexadecimal digits. To learn how MAC addresses are assigned to devices and how to find MAC address of your device, you can read this blogpost.
Types of Data-Link layer attacks
Since now you have understood how Data-Link layer works and what is a MAC address, let’s learn about various Data-link layer attacks.
- MAC spoofing
- MAC flooding
- ARP spoofing or poisoning
- DNS spoofing
- DHCP starvation
Let’s learn about each attack in detail.
1. MAC spoofing:
Although every computing device has its unique MAC address, it can be spoofed. Normally, when a MAC address of a device (say A) is spoofed to that of another device (say B) all the traffic that is intended to move toward device B goes to device A and the attacker can view all the traffic belonging to device B.
2. MAC flooding:
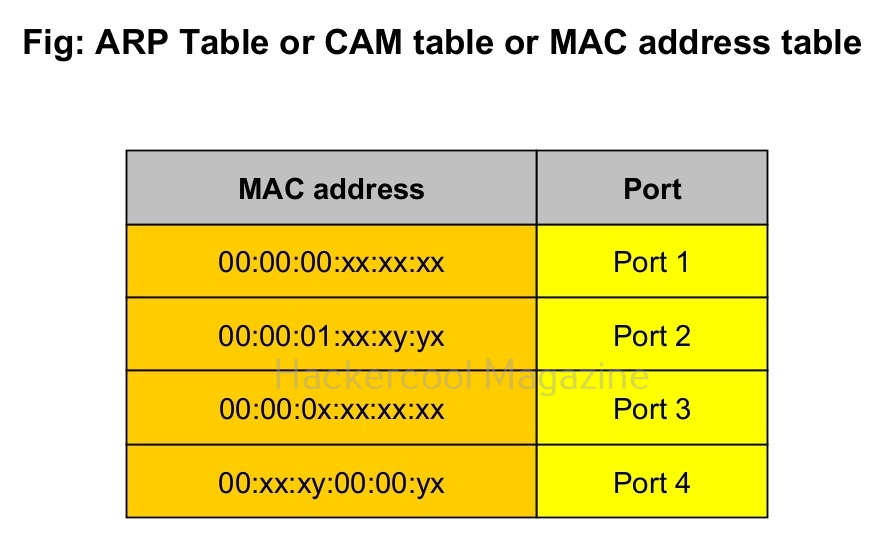
You have just now learnt about what is a Hub and what is a Switch and the differences between a Hub and Switch. You also learnt about CAM table or ARP table. In a MAC flooding attack, the CAM table is bombarded with a number of fake MAC addresses disabling the Switch’s ability to detect which MAC address belongs to which port.
To overcome this problem, a network Switch uses its broadcast address to transmit frames to the intended destination. In typical sense, the network switch here behaves like a Hub and you know about the dangers of using a Hub. A hacker already in the network can monitor the network traffic he wants via packet sniffing.
3. ARP spoofing and poisoning:
In this type of attack, the attacker sends fake ARP packets to the network from the attacker-controlled system (System A). Here, the attacker-controlled system acts as the gateway. This leads to all other devices querying the attacker-controlled system resulting in the attackers using packet sniffing again to sniff on traffic.
4. DNS spoofing:
This attack requires ARP spoofing to work. In this type of attack, attacker responds to DNS queries of the target system instead of the legitimate DNS server.