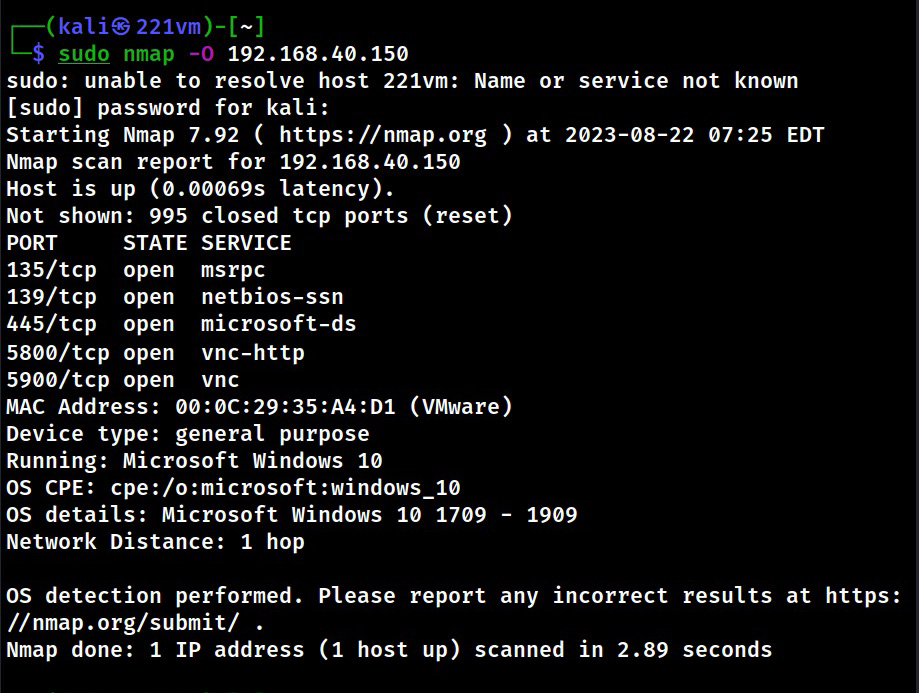
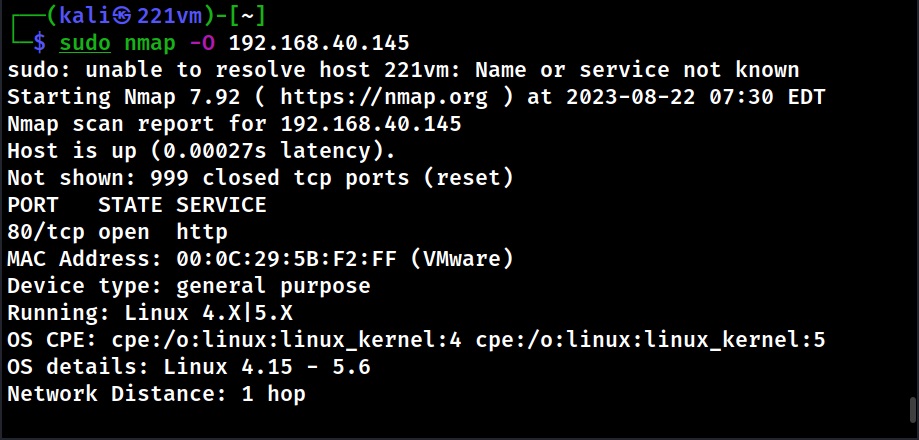
Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. This blogpost is an enumeration guide for beginners. The phase of enumeration actually comes after the port scanning stage in Ethical Hacking.
What is Enumeration?
In Enumeration, an attacker or a Pen Tester performs calculated queries to gather more detailed information about the target. Usually, enumeration is performed on the services running on the target (open ports) with the purpose of gaining access to the target system.
What information does enumeration reveal?
Enumeration can reveal valuable information like Network shares, usernames and passwords, version of the application running, users and groups, machine names, service settings and other network resources.
Which services can be enumerated?
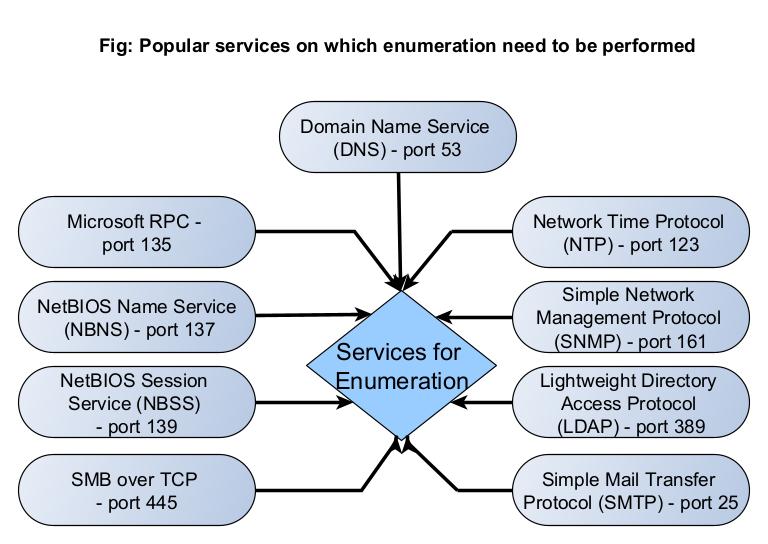
Although all services running on the target system can be enumerated upon, there are some specific services which are regularly enumerated to retrieve useful information. They are,
- DNS (Port 53)
- Microsoft RPC (Port 153)
- NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) (Port 137)
- NetBIOS Session Service (SMB over NetBIOS)
- SMB Over TCP (Port 445)
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) (Port 123)
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) (Port 161)
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) (Port 389)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) (Port 25)
Let’s learn about each of these services in detail.
1. SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a TCP/IP protocol that is used to send email. It is mostly used by email clients but most of the organizations have their own Email Servers to send mail. Enumerating SMTP Service can reveal the list of valid users on the SMTP Servers. Learn how to perform SMTP enumeration.
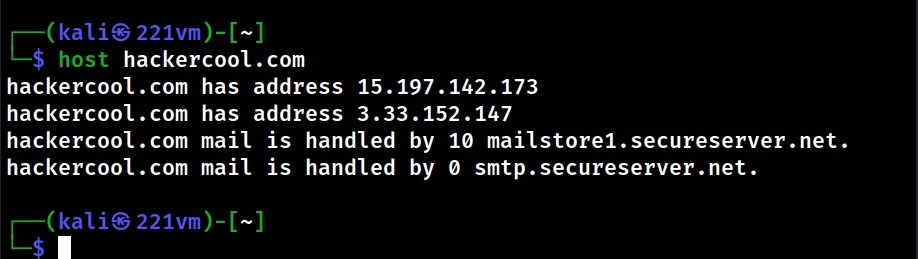
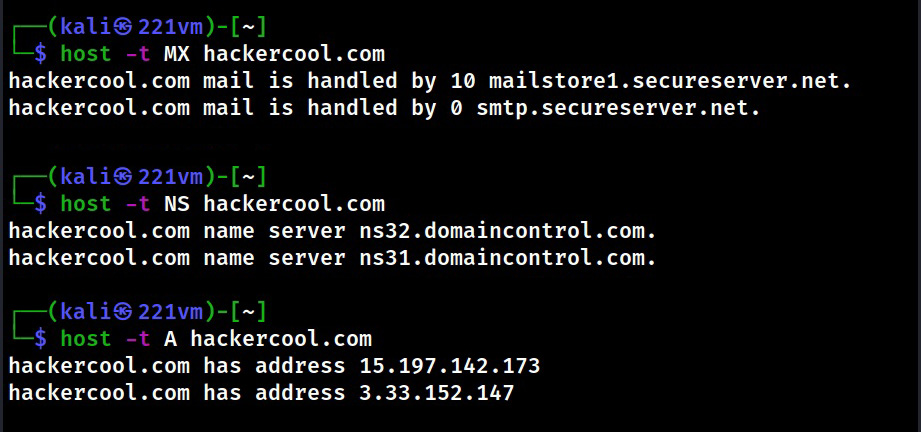
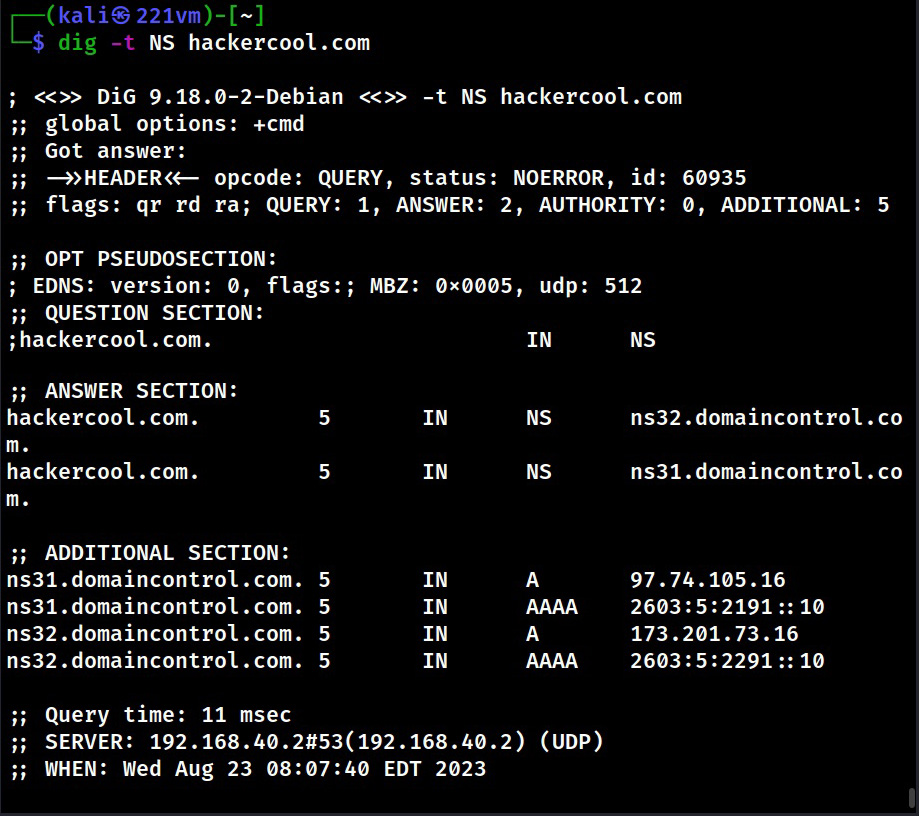
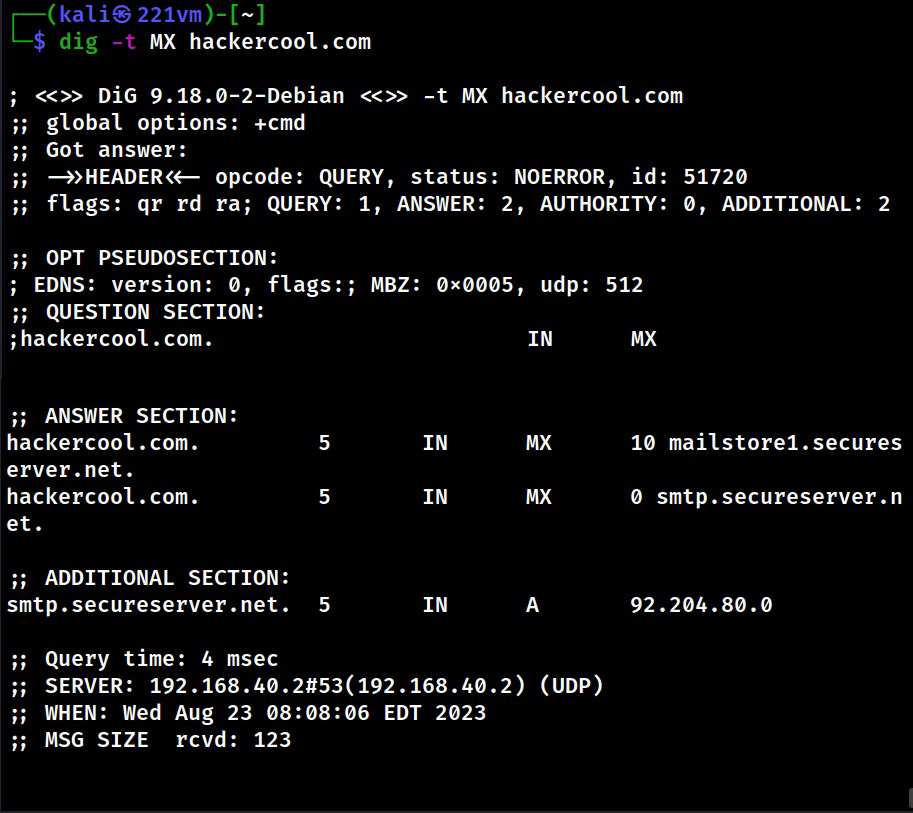
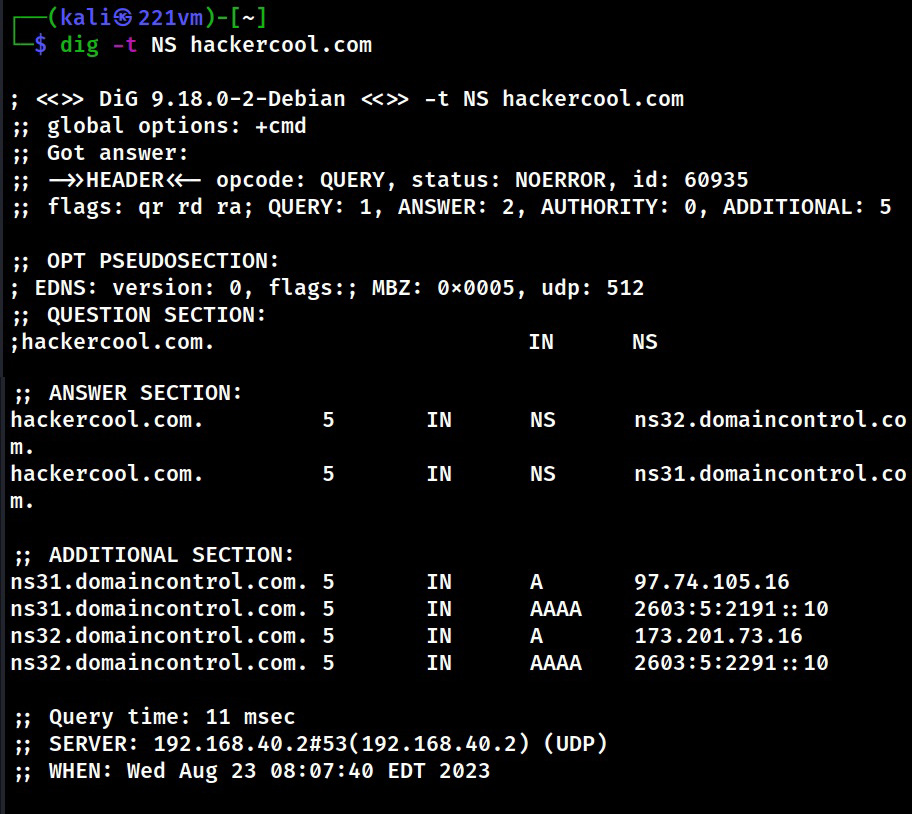
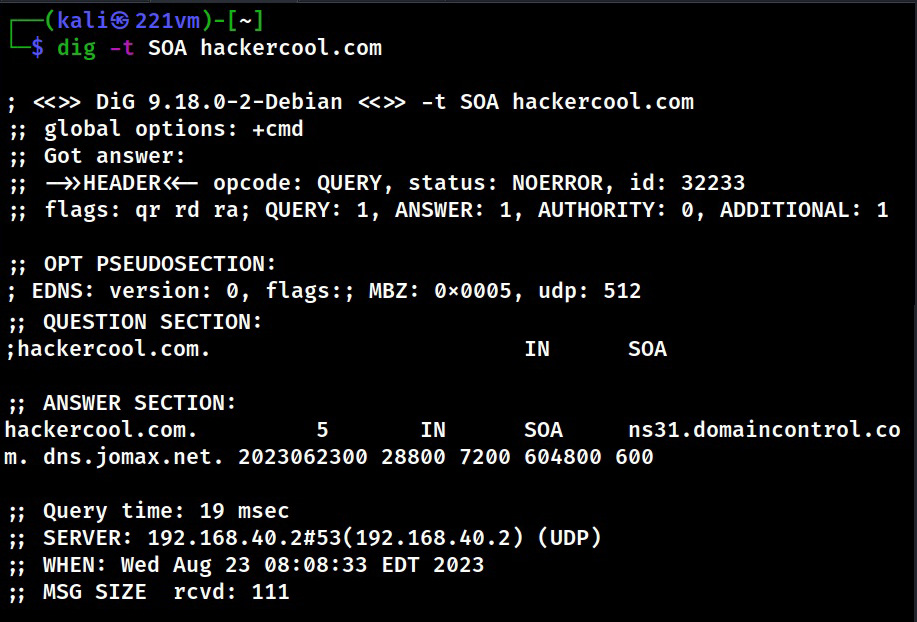
2. DNS
The function of Domain Name Service (DNS) is explained in our article DNS Footprinting. Enumerating DNS servers can reveal network information like host names, other DNS server names, machine names, IP addresses, potential targets and in some cases usernames too. Learn how to perform DNS enumeration.
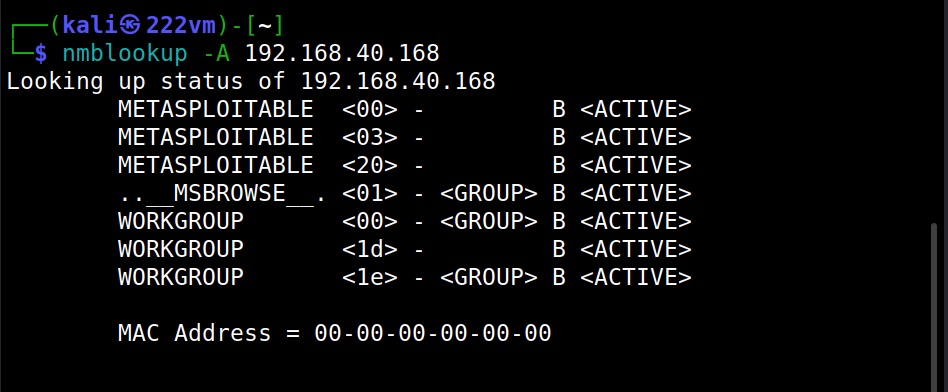
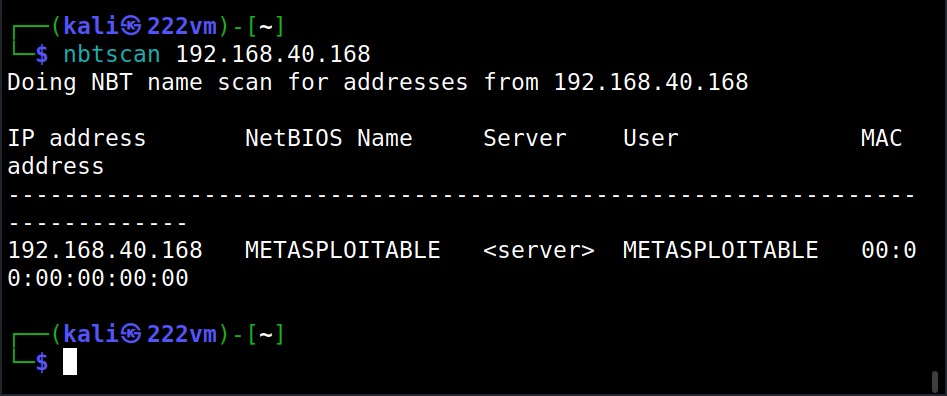
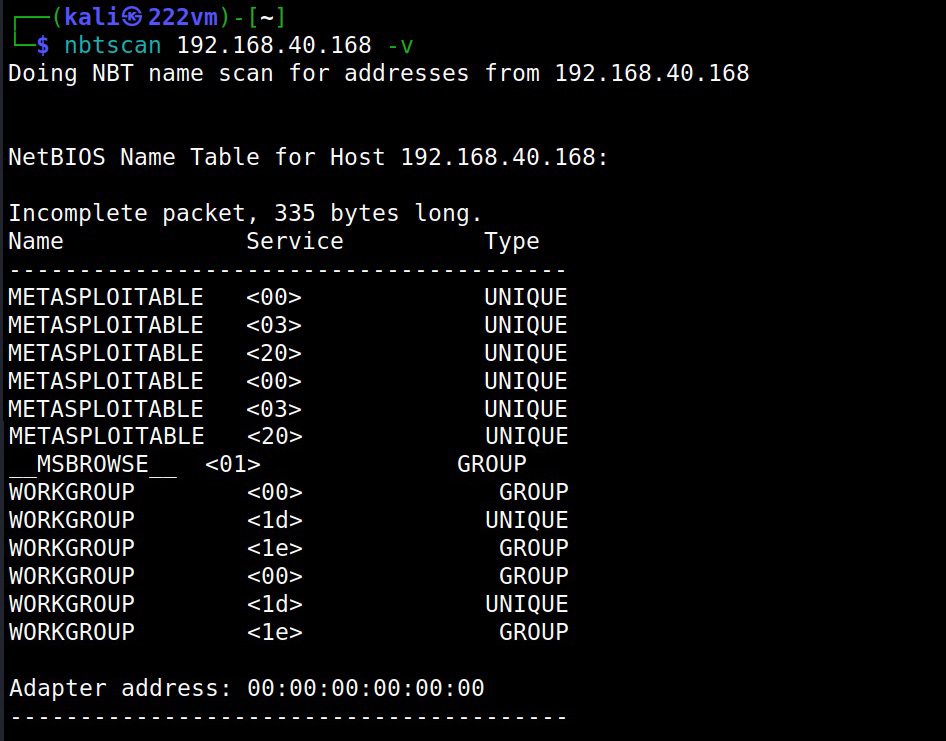
3. NetBIOS
NetBIOS service allows programs and computers on a local area network to communicate with each other. These include services like files, printers and device shares. Enumerating NetBIOS can reveal information like list of computers in a specific domain, lists of shares, policies and Passwords etc. Learn how to perform NetBIOS enumeration.
4. SMB
Just like NetBIOS, Server Message Block (SMB) is a protocol that allows applications and computers in a local network talk to each other. The only difference between them is that NetBIOS is an API whereas SMB is a protocol. Starting from Windows 2000, SMB which earlier ran on top of NetBIOS was made to operate on top of TCP and it got a dedicated port 445.
It also enables network services like file, printer and device sharing. Enumerating SMB service can reveal information like host names, lists shares, checking for null session, users, operating system details, password policies, info groups and printers connected etc. Learn how to perform SMB enumeration.
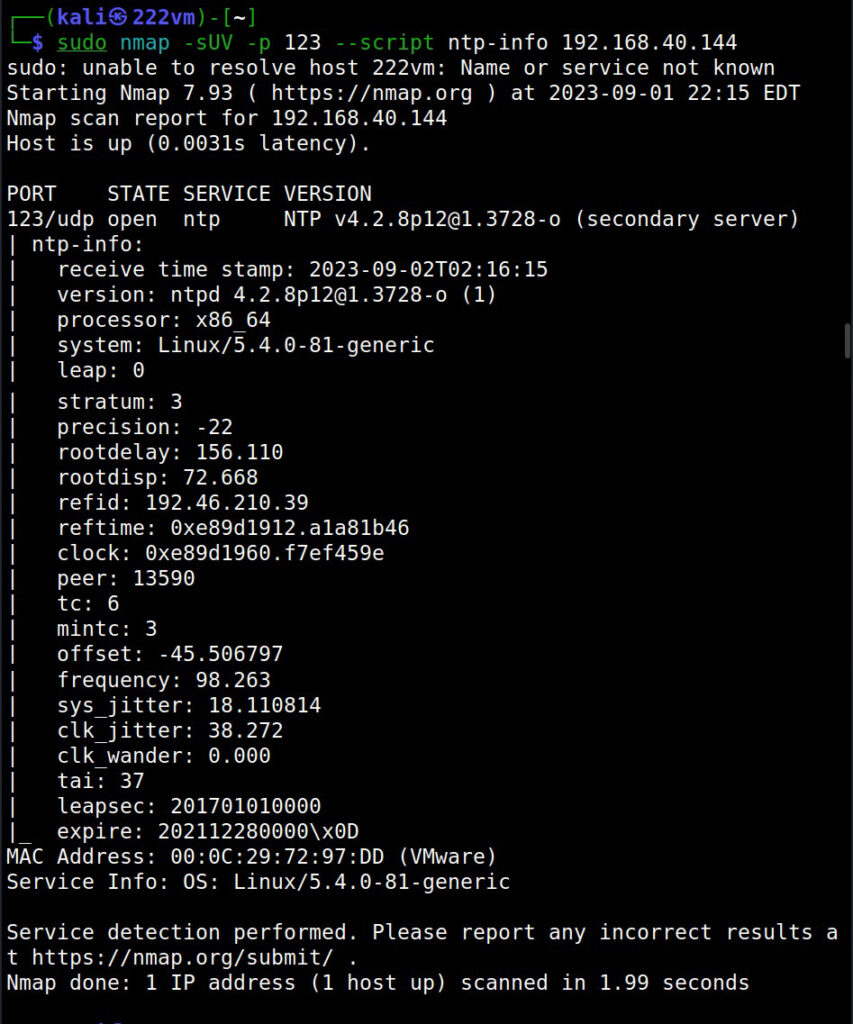
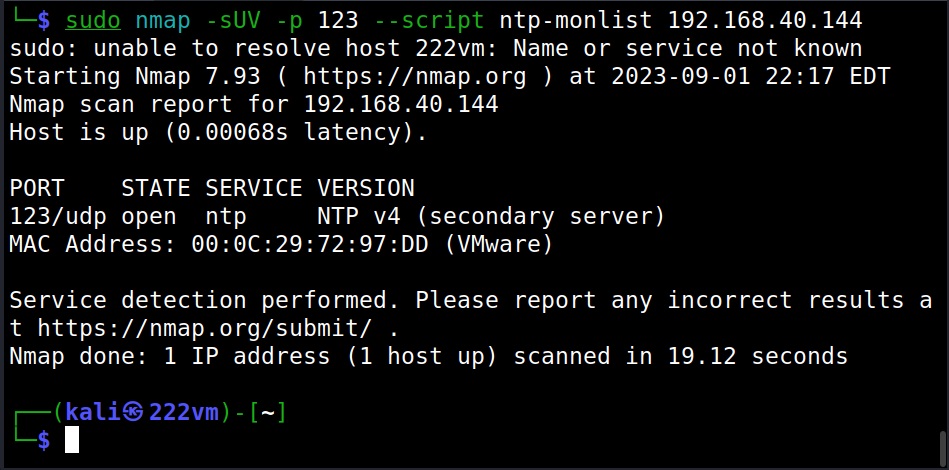
5. NTP
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol designed to synchronize clocks of all computers on the same network. Enumerating NTP can reveal information about hosts connected to the NTP server and IP addresses of the machines in the network etc. Learn how to perform NTP enumeration.
6. SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a protocol that is used to monitor and manage computer systems in the same network. Enumerating SNMP can reveal information about network resources like hosts, routes, shares, ARP tables, routing tables, etc. Learn how to perform SNMP enumeration.
7. LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an internet protocol that is used to access information from directories like Active Directory. Enumerating LDAP can reveal information such as valid usernames, addresses and other details. Learn how to perform LDAP enumeration.