Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn everything about fuzzing as an ethical hacker.
What is Fuzzing?
Fuzzing or fuzz testing is a term that comes from the domain of programming . It is a software testing technique in which invalid, unexpected or random data is provided to a computer program or a system to see how it responds.
It is usually checked if the program results in any crash, memory leaks or buffer overflows. Fuzz testing is usually performed to see if the software results in any vulnerability that can be exploited by hackers.
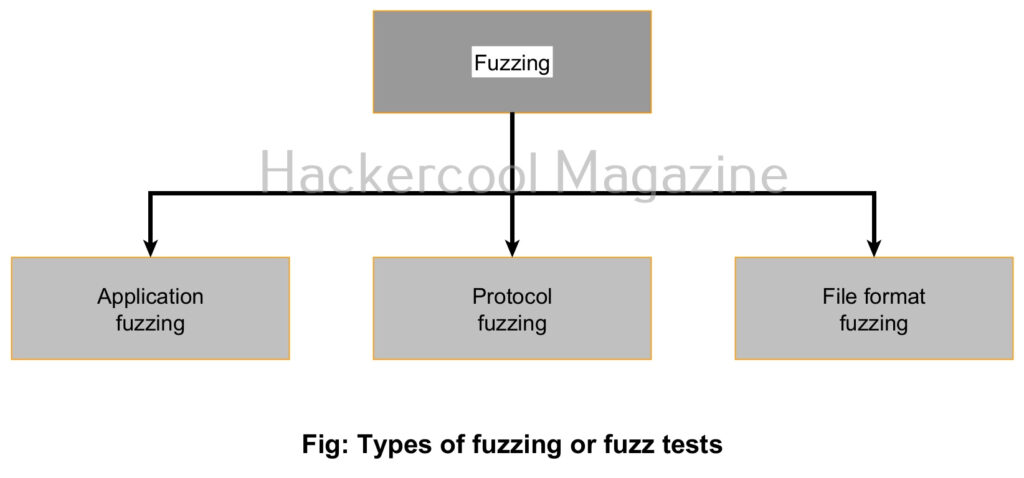
Types of Fuzzing
There are different types of fuzz tests. They are application fuzzing, protocol fuzzing and file format fuzz testing. Let’s learn about them in detail.
1. Application fuzzing:
In this type of fuzz test, options of a command line program or UI features such as buttons and input fields in forms are tested for any vulnerability by providing random inputs.
2. Protocol fuzzing:
Just like its name says, in this type of fuzz testing, protocols are tested to see how they react when random data is sent as input to them.
3. File format fuzzing:
In file format fuzz test, a different type of file format or a corrupted file is provided as input to the programs to see how they react. For example, let’s say a web application has file upload feature that takes docx files as input from users. This is the usual practice. But how does it react when a exe file or a exe file masquerading as docx file is uploaded to that application? This type of fuzz test intends to check this.
What is a Fuzzer?
A Fuzzer is a tool that tests software, operating systems or networks for security vulnerabilities. A Fuzzer is a program that automatically infects random data and detects vulnerability
Importance of fuzzing
Fuzz testing works on the concept that it is generally assumed that users will provide proper input to the web application or program or application. But what happens if random and unexpected input is provided to the same application. How does it behave? Does it pose a security threat that hackers can exploit? etc.