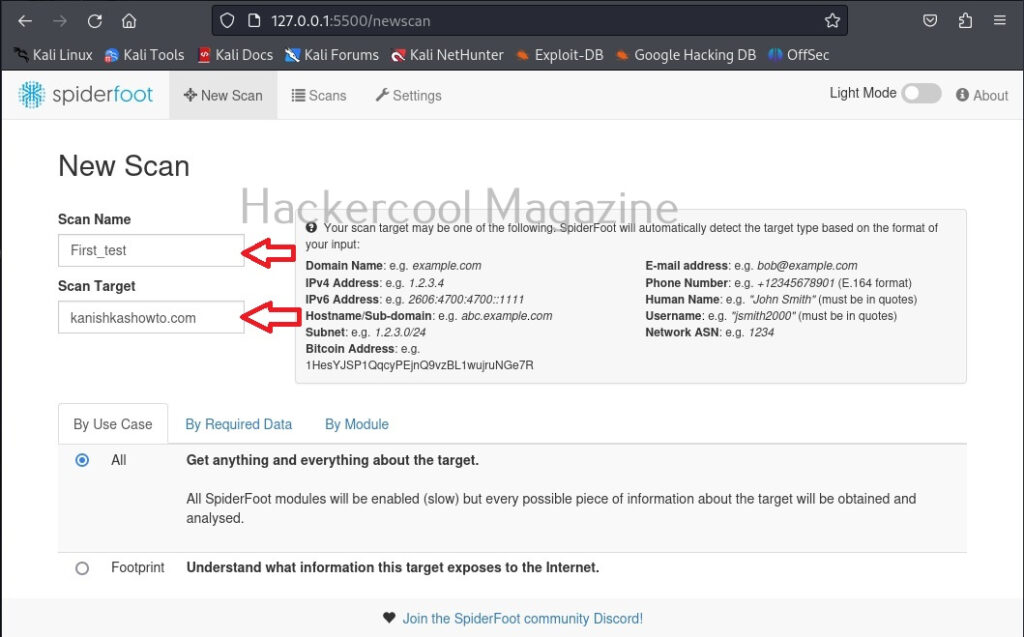
Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In one of our previous blogposts, you learnt about password cracking and different types of password cracking techniques. In this blogpost, you will learn about a password cracking tool called John password cracker. Originally, called John the Ripper, John password cracker is a cross-platform software and a very popular password cracker.
In one of our previous blogposts, you learnt in detail about encryption. Hashing is a method of encryption in which a plain string of text is converted into an encrypted hash. This is a one-way function and hashes cannot easily be converted back to plain string. This technique is often used for storing passwords.
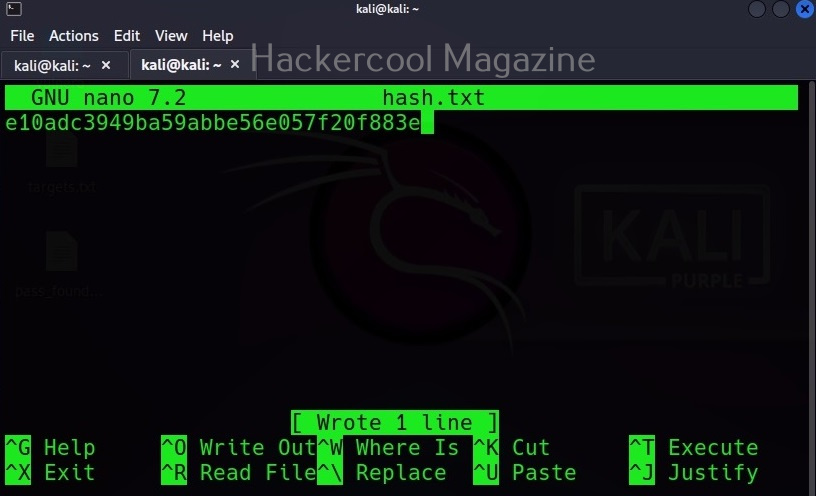
Being one of the most popular password hash cracking tools, John is installed by default in Kali Linux and I will be using the same for this tutorial. To demonstrate the power of John, first we need to create a hash. This can be done using online services like md5encrypt. I copy the generated MD5 hash to a text file named hash.txt as shown below.
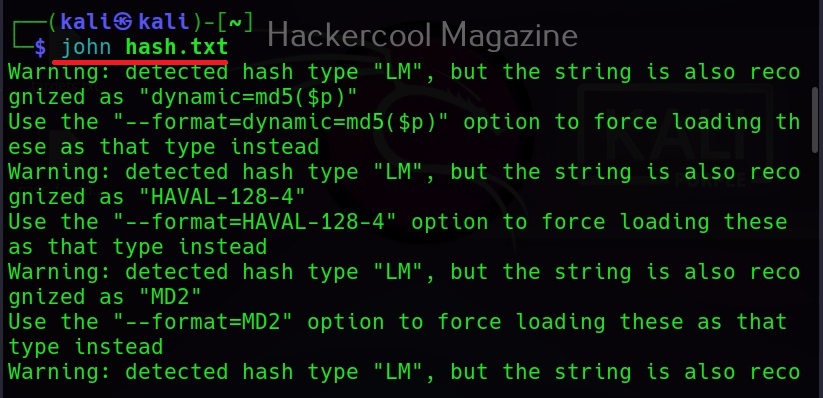
Then all we have to do is submit this file to John as shown below.
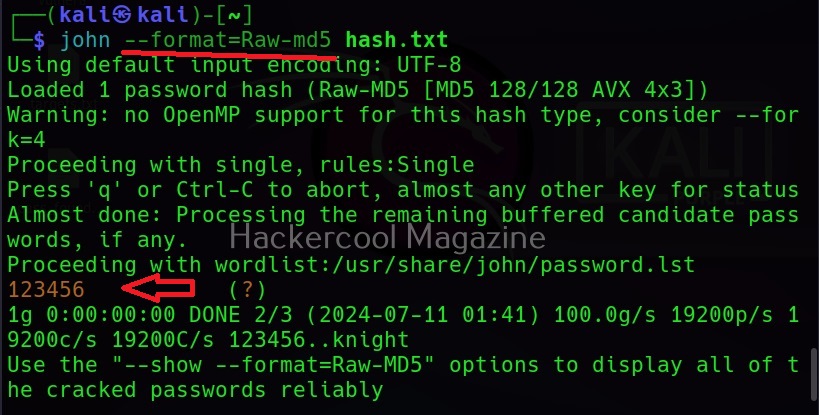
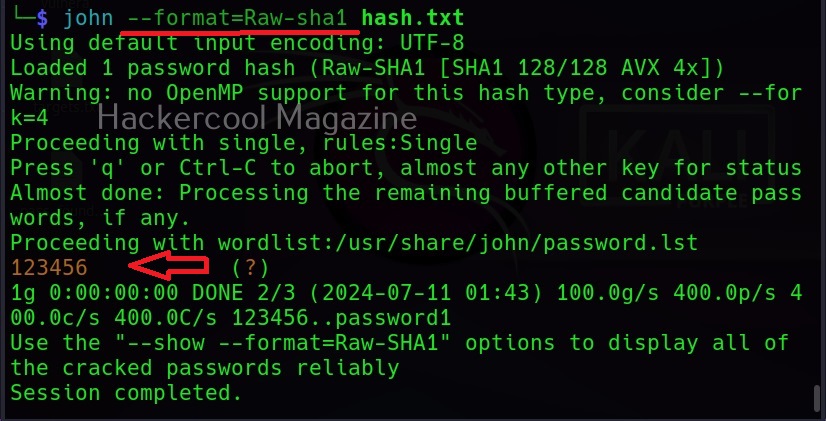
Then John begins to crack the hash in the file. In most of the real-world cases, this will consume lot of time. So, it is good to specify the format of the hash using the ‘–format’ option as shown below. The format of the hash can be identified using hash identification.
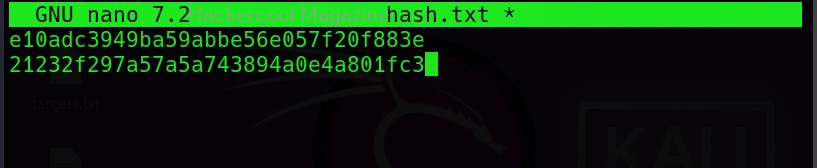
As you can see in the above image, John successfully cracked the password hash. Let’s add a SHA-1 hash now to the same file and try cracking it.
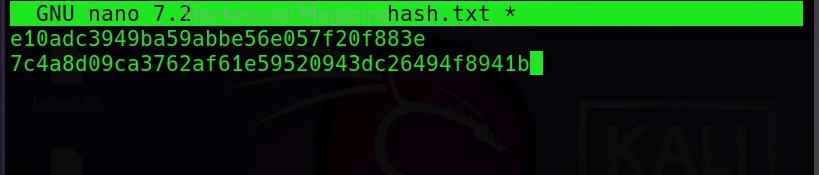
The list of all the hash formats John can crack are many. John can crack a number of password hashes at once. However, they should all be of same format. Let’s add another MD5 hash to the hash.txt file.
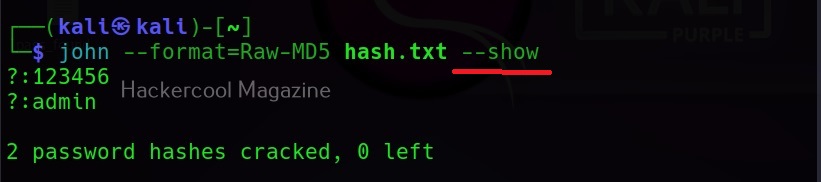
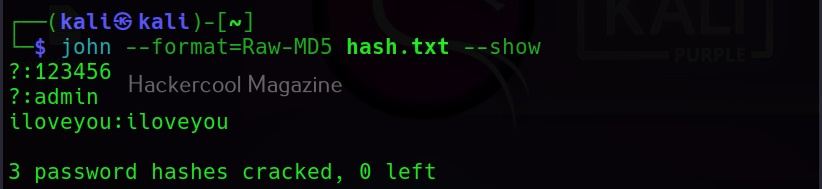
Once a hash is cracked by John, it can be viewed using the ‘–show’ option. For example, all the hashes in file “hash.txt” can be viewed as shown below.
Single mode
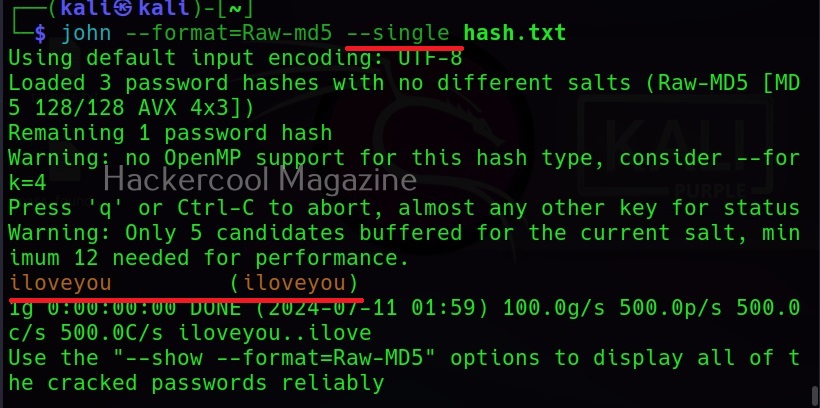
As already mentioned at the beginning of this article, John can use different techniques to crack password hashes. One of them is single mode. People in some cases use the username as a password (or a variation of username as password). Single mode is mostly useful in these cases. When single mode is specified, it tries all the variations of the username to crack the hash. Let’s try it out. I add a password hash along with the username to the file hash.txt.
Then, specifying single mode does this.
Wordlist mode or Dictionary mode
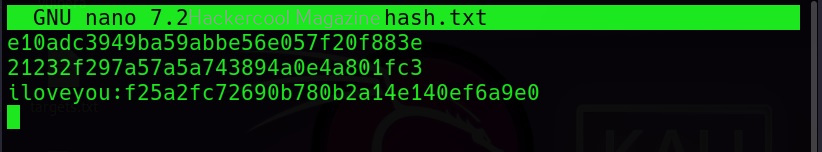
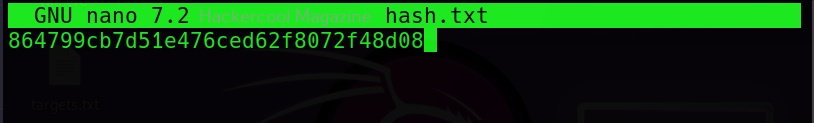
John can also use dictionary mode to crack the hash. I add a new hash to the file hash.txt.
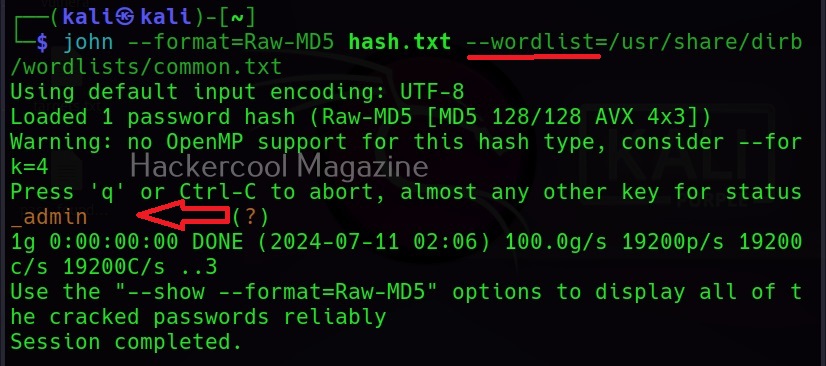
Then all we need to do is specify a wordlist as shown below.
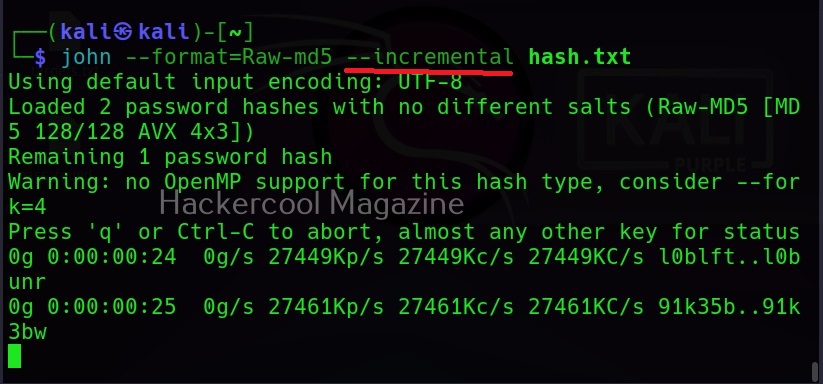
Incremental mode
If all those options fail, John still has incremental mode in which the combination of all the techniques are used. But this may take lot of time and resources.
But password cracking is all about patience. Learn how to crack hashes with hashcat.